Content for TS 23.682 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4.2
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.5.14…
4.6…
5…
5.3…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.2…
5.6.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15
5.16
5.17…
5.18
5.19…
A…
C…
5 Functional Description and Information Flow
5.1 Control and user plane
5.2 Device triggering procedures
5.2.1 Device triggering procedure over Tsp
5.2.2 Trigger Delivery using T4
5.2.3 Device triggering recall/replace procedures
...
...
5 Functional Description and Information Flow p. 43
5.1 Control and user plane p. 43
5.1.1 Control Plane p. 43
5.1.1.1 HSS - MTC-IWF p. 43
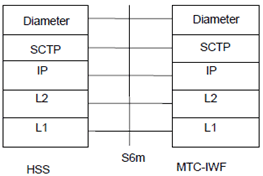
Legend:
- Diameter: This protocol supports transferring of subscription and UE related information for identifier mapping and serving node information retrieval between MTC-IWF and HSS (S6m). Diameter is defined in RFC 3588.
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP): This protocol transfers signalling messages. SCTP is defined in RFC 4960.
5.2 Device triggering procedures p. 44
5.2.1 Device triggering procedure over Tsp p. 44
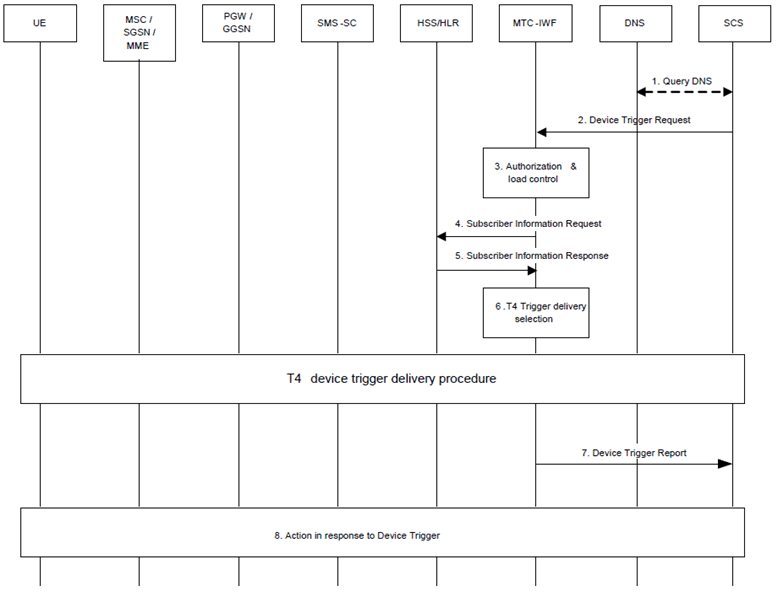
Step 1.
The SCS determines the need to trigger the device. If the SCS has no contact details for an MTC-IWF, it may determine the IP address(es)/port(s) of the MTC-IWF by performing a DNS query using the External Identifier or using a locally configured MTC-IWF identifier.
Step 2.
The SCS sends the Device Trigger Request (External Identifier or MSISDN, SCS Identifier, trigger reference number, validity period, priority, Application Port ID and trigger payload) message to the MTC-IWF. The SCS includes a trigger payload that contains the information destined for the MTC application, along with the information to route it to the MTC application. The Application Port ID is set to address a triggering function within the UE.
Step 3.
The MTC-IWF checks that the SCS is authorised to send trigger requests and that the SCS has not exceeded its quota or rate of trigger submission over Tsp. If this check fails the MTC-IWF sends a Device Trigger Confirm message with a cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition and the flow stops at this step. Otherwise, the flow continues with step 4.
Step 4.
The MTC-IWF sends a Subscriber Information Request (External Identifier or MSISDN and SCS Identifier) message to the HSS/HLR to determine if SCS is authorized to trigger the UE, to resolve the External Identifier or MSISDN to IMSI and retrieve the related HSS stored "Routing information" including the identities of the UE's serving CN node(s).
Step 5.
The HSS/HLR sends the Subscriber Information Response (IMSI and/or MSISDN and related "Routing information" including the serving node(s) identities, cause) message. HSS/HLR policy (possibly dependent on the VPLMN ID) may influence which serving node identities are returned. If the cause value indicates the SCS is not allowed to send a trigger message to this UE, or there is no valid subscription information, or "Absent subscriber" is received from HSS and the validity period of this trigger message is set to zero, the MTC-IWF sends a Device Trigger Confirm message with a cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition and the flow stops at this step. Otherwise this flow continues with step 6a.
Step 6.
The MTC-IWF attempts T4 trigger delivery procedure according to clause 5.2.2. MTC-IWF may deliver device trigger as DL user data to the UE via SCEF using mobile terminated NIDD procedure as defined in clause 5.13.3. Otherwise, this flow continues with step 7.
Step 7.
The MTC-IWF sends the Device Trigger Report (External Identifier or MSISDN and trigger reference number) message to the SCS with a cause value indicating the trigger delivery outcome (e.g. succeeded, unknown or failed and the reason for the failure). The MTC-IWF generates the necessary CDR information including the External Identifier or MSISDN and SCS Identifier.
Step 8.
In response to the received device trigger, the UE takes specific actions that take into consideration the content of the trigger payload. This response typically involves initiation of immediate or later communication with the SCS or an AS.
5.2.2 Trigger Delivery using T4 p. 45
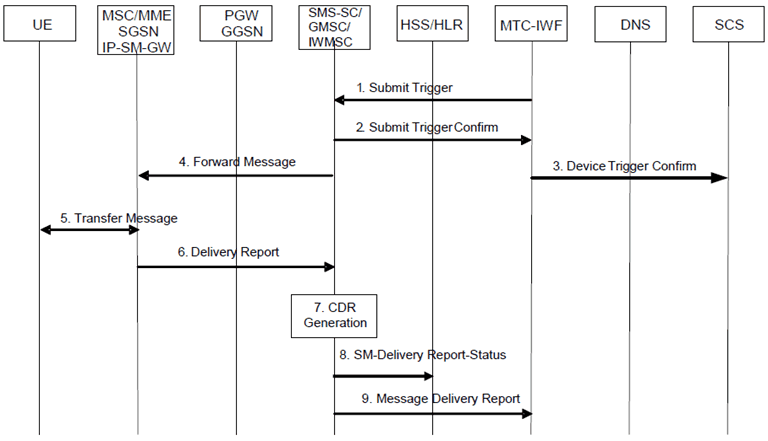
Step 1.
The MTC-IWF selects a suitable SMS-SC based on configured information. The MTC-IWF sends a Submit Trigger (External Identifier or MSISDN, IMSI, SCS Identifier, trigger reference number, validity period, priority, serving node ID(s) if available from HSS, SMS Application port ID, trigger payload, Trigger Indication) message to the SMS-SC. The SMS-SC should avoid an initial HSS/HLR interrogation (SRI for SM) when it has already received necessary parameters in the Submit Trigger message from the MTC-IWF. The MTC-IWF forwards the Application Port ID received from SCS as the SMS Application port ID which is used to address the triggering function within the UE. The Trigger Indication is a standardised identifier to allow the UE and the network to distinguish an MT message carrying device triggering information from any other type of messages. The SMS-SC does any necessary segmentation for larger messages.
If the MTC-IWF indicates that "Absent subscriber" was received from HSS, the SMS-SC should not submit the message, but store it directly and send Routing Information for SM to request the HSS to add the SMS-SC address to the Message Waiting List.
Step 2.
The SMS-SC sends a Submit Trigger Confirm message to the MTC-IWF to confirm that the submission of the SMS has been accepted by the SMS-SC.
Step 3.
The MTC-IWF sends a Device Trigger Confirm message to the SCS to confirm that the Device Trigger Request has been accepted for delivery to the UE.
Step 4, 5, 6.
The short message is delivered to the UE (see MT-SMS procedures specified in TS 23.040). This may involve delivery attempts in MSC or MME, SGSN or over IMS via IP-SM-GW (see MT-SMS without MSISDN procedures specified in TS 23.204).
The SMS-delivered trigger payload is processed and handled by the triggering function in the UE. Any information contained within the trigger payload is forwarded to the related or addressed UE-application.
Step 7.
The SMS-SC generates the necessary CDR information and includes the SCS Identifier. The SMS Application port ID which is included in the SM User Data Header and the Trigger Indication are included in the CDRs in order to enable differentiated charging. The SMS-SC stores the trigger payload, without routing information. If the message delivery fails and is attempted to be delivered again, HSS interrogation will be performed.
Step 8.
If the message delivery fails and the validity period of this trigger message is not set to zero, the SMS-SC shall send a SM Message Delivery Status Report to request the HSS to add the SMS-SC address to the Message Waiting list. When the message delivery is later re-attempted, a new HSS interrogation will be performed by the SMS-GMSC using IMSI or MSISDN. HSS interrogations using IMSI shall not be forwarded or relayed to SMS-Router or IP-SM-GWs. HSS may include up to three serving node identities (MSC or MME, SGSN, IP-SM-GW) in the response to SMS-GMSC.
Step 9.
If the message delivery fails and depending on the failure cause either directly or when validity period of the trigger message expires, or when the message delivery succeeds, the SMS-SC shall send a Message Delivery Report (cause code, trigger reference number, SCS Identifier) to the MTC-IWF.
5.2.3 Device triggering recall/replace procedures |R12| p. 46
5.2.3.1 Device trigger recall/replace procedure over Tsp p. 46
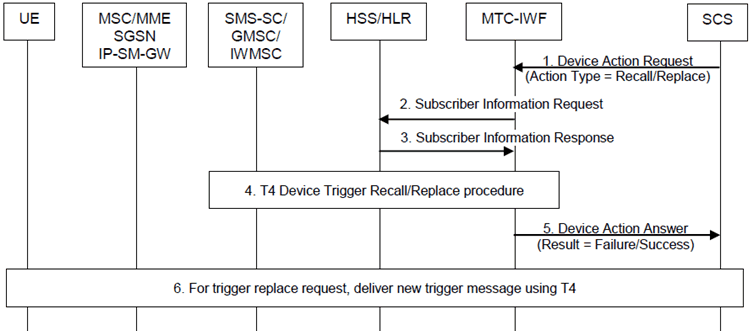
Step 1.
The SCS determines it needs to recall/replace a trigger message that it has previously submitted. The SCS sends Device Action Request (External Identifier or MSISDN, SCS Identifier, old trigger reference number, new trigger reference number, validity period, priority, Application Port ID and trigger payload) message with action type set to "Trigger Recall Request" or "Trigger Replace Request". The SCS needs to include new trigger reference number, validity period, priority, Application Port ID and trigger payload for trigger replace request only. The old trigger reference number indicates the trigger reference number which was assigned to the previously submitted trigger message that the SCS wants to cancel. The new trigger reference number is assigned by the SCS to the newly submitted trigger message.
If the SCS is not authorized to perform device triggering or the SCS has exceeded its quota or rate of trigger submission over Tsp, the MTC-IWF rejects the Device Action Request message with action type set to "Trigger Recall Request" or "Trigger Replace Request" by sending a Device Action Answer message with a cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition, and the flow stops at this step.
Step 2.
The MTC-IWF sends a Subscriber Information Request (External Identifier or MSISDN and SCS Identifier) message to the HSS/HLR to determine if SCS is authorized to perform device triggering to the UE. This message is also to resolve the External Identifier or MSISDN to IMSI and retrieve the related HSS stored "Routing information" including the identities of the UE's serving CN node(s) which are needed for trigger replace request only.
Step 3.
The HSS/HLR sends the Subscriber Information Response (IMSI and/or MSISDN and related "Routing information" including the serving node(s) identities, cause) message. The IMSI and/or MSISDN and related "Routing information" including the serving node(s) identities in the Subscriber Information Response message is only needed for trigger replace request and not used by MTC-IWF for trigger recall request. HSS/HLR policy (possibly dependent on the VPLMN ID) may influence which serving node identities are returned. If the cause value indicates the SCS is not allowed to perform device triggering to this UE, or there is no valid subscription information, the MTC-IWF sends a Device Action Answer message with a cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition and the flow stops at this step. Otherwise this flow continues with step 4.
Step 4.
If trigger message which should be recalled or replaced was submitted to a SMS-SC as defined in clause 5.2.2, T4 device trigger replace procedure according to clause 5.2.3.2 or T4 device trigger recall procedure according to clause 5.2.3.3 is performed.
Step 5.
The MTC-IWF indicates trigger recall/replace success or failure in Device Action Answer message to the SCS. The MTC-IWF generates the necessary CDR information including the External Identifier or MSISDN and SCS Identifier.
If recall/replace of a trigger is successful, this is reflected in the "Device Trigger Report" of the original trigger message (per step 7 in clause 5.2.1) with delivery outcome "Recalled"/"Replaced".
Step 6.
For trigger replace request, the new trigger message will be delivered to the UE immediately or when the UE is available following steps 4 - 9 as defined in clause 5.2.2.
5.2.3.2 Replace procedure for trigger delivery using T4 p. 48
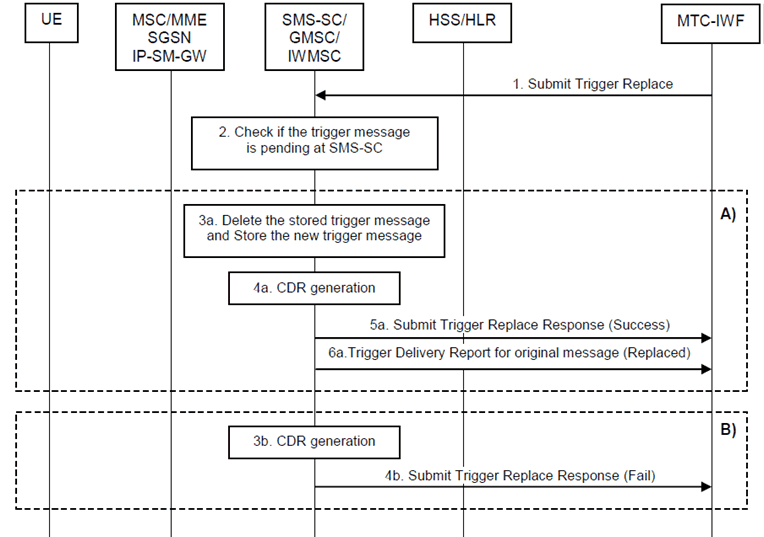
Step 1.
Based on the Action type in Device Action Request message, the MTC-IWF sends a Submit Trigger Replace (External Identifier or MSISDN, IMSI, SCS Identifier, old trigger reference number, new trigger reference number, validity period, priority, serving node ID(s) if available from HSS, SMS Application port ID, trigger payload, Trigger Indication) message to the SMS-SC. The MTC-IWF selects the SMS-SC to which the old trigger message was submitted, e.g. based on configured information.
Step 2.
The SMS-SC determines whether the trigger message identified by the External Identifier or MSISDN, SCS Identifier, and old trigger reference number in the received Submit Trigger Replace message, is pending at SMS-SC.
A)
B)
If the trigger message is pending at SMS-SC, steps 3a - 6a are performed.
3a)
The SMS-SC deletes the stored trigger message and stores the new trigger message to deliver it when the UE is available.
4a)
The SMS-SC generates the necessary CDR information and includes the SCS Identifier. The SMS Application port ID which is included in the SM User Data Header and the Trigger Indication are included in the CDRs in order to enable differentiated charging.
5a)
The SMS-SC sends a Submit Trigger Replace Response message to the MTC-IWF to inform that the previously submitted trigger message has been successfully replaced by the new one in the SMS-SC.
6a)
The SMS-SC sends a Trigger Delivery Report for the original trigger message indicating that this message has been replaced.
If the trigger message is not pending at SMS-SC, steps 3b - 4b are performed. In this case, the SMS-SC treats the new trigger message as a trigger message that it has to deliver to the UE.
3b)
The SMS-SC generates the necessary CDR information and includes the SCS Identifier. The SMS Application port ID which is included in the SM User Data Header and the Trigger Indication are included in the CDRs in order to enable differentiated charging.
4b)
The SMS-SC sends a Submit Trigger Replace Response message to the MTC-IWF to inform that the replace request failed and the SMS-SC shall deliver the new trigger message.
5.2.3.3 Recall procedure for trigger delivery using T4 p. 49
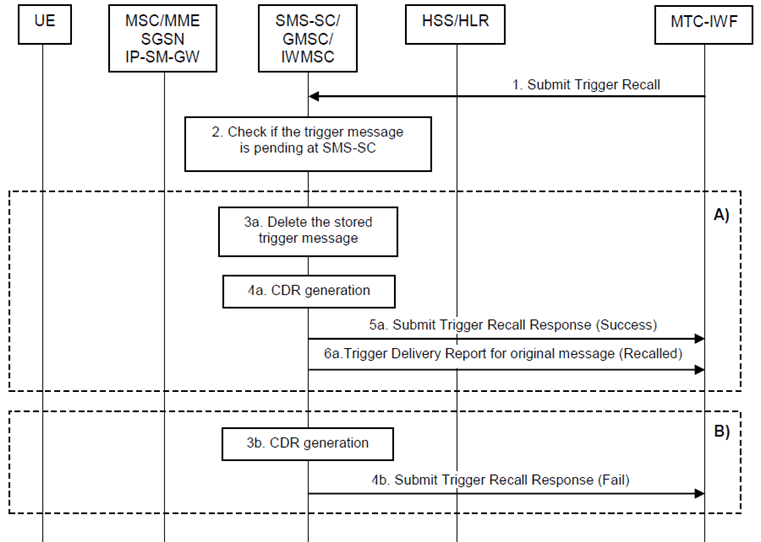
Step 1.
Based on the Action type in Device Action Request message, the MTC-IWF sends a Submit Trigger Recall (External Identifier or MSISDN, SCS Identifier, old trigger reference number) message to the SMS-SC. The MTC-IWF selects the SMS-SC to which the old trigger message was submitted, e.g. based on configured information.
Step 2.
The SMS-SC determines whether the trigger message identified by External Identifier or MSISDN, SCS Identifier, and old trigger reference number in the received Submit Trigger Recall message, is pending at SMS-SC.
A)
B)
If the trigger message is pending at SMS-SC, steps 3a - 6a are performed.
3a)
The SMS-SC deletes the stored trigger message.
4a)
The SMS-SC generates the necessary CDR information and includes the SCS Identifier. The SMS Application port ID which is included in the SM User Data Header and the Trigger Indication are included in the CDRs in order to enable differentiated charging.
5a)
The SMS-SC sends a Submit Trigger Recall Response message to the MTC-IWF to inform that the previously submitted trigger message has been successfully deleted in the SMS-SC.
6a)
The SMS-SC sends a Trigger Delivery Report for the original trigger message indicating that this message has been recalled.
If the trigger message is not pending at SMS-SC, steps 3b - 4b are performed.
3b)
The SMS-SC generates the necessary CDR information and includes the SCS Identifier. The SMS Application port ID which is included in the SM User Data Header and the Trigger Indication are included in the CDRs in order to enable differentiated charging.
4b)
The SMS-SC sends a Submit Trigger Recall Response message to the MTC-IWF with a cause value indicating that the recall request failed.