Content for TS 23.682 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4.2
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.5.14…
4.6…
5…
5.3…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.2…
5.6.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15
5.16
5.17…
5.18
5.19…
A…
C…
5.8 Procedure for Informing about Potential Network Issues
5.8.1 General
5.8.2 Request procedure for one-time or continuous reporting of network status
5.8.3 Report procedure for continuous reporting of network status
5.8.4 Removal procedure for continuous reporting of network status
...
...
5.8 Procedure for Informing about Potential Network Issues |R13| p. 91
5.8.1 General p. 91
This clause contains the detailed description and the procedures for the service capability exposure feature Informing about Potential Network Issues.
An SCS/AS may request for being notified about the network status. The following methods are supported:
- The SCS/AS requests to be informed, one-time, about the network status by providing a geographical area. This procedure is referred to as one-time network status request;
- The SCS/AS requests to be informed, continuously, about the network status by providing a geographical area. This procedure is referred to as continuous network status request.
- Congestion level or an indication of the "no congestion" state;
- ECGI, or eNodeB-ID, or SAI for which the congestion level is being provided.
5.8.2 Request procedure for one-time or continuous reporting of network status p. 92
This procedure is used by an SCS/AS to retrieve Network Status Information (NSI) from the network. This procedure can be used to request a one-time or continuous reporting of network status. Figure 5.8.2-1 illustrates the procedure.
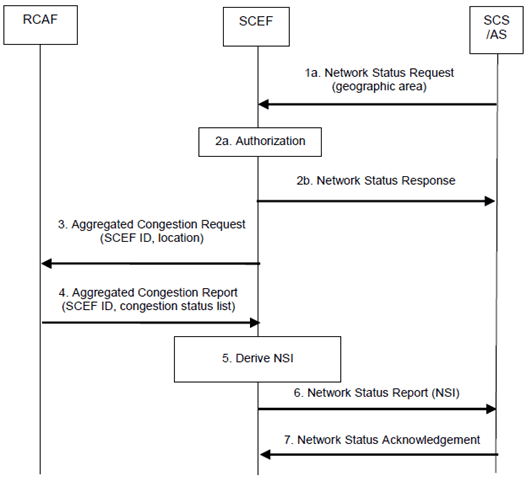
Figure 5.8.2-1: Request procedure for one-time or continuous reporting of network status
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
When the SCS/AS needs to retrieve NSI, the SCS/AS sends a Network Status Request (Geographical area, SCS/AS Identifier, Duration, Threshold) message to the SCEF. Duration indicates the time for which a continuous reporting is requested. The absence of Duration indicates a one-time reporting. Threshold indicates a range at which the SCS/AS wishes to be informed of the network status. Multiple Threshold values may be included. The SCEF assigns a TLTRI that identifies the Network Status Request.
Step 2a.
The SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request for notifications about potential network issues. The SCEF stores SCS/AS Address, TLTRI, Duration, if present, and Threshold, if present. The SCEF assigns an SCEF Reference ID.
Step 2b.
The SCEF sends a Network Status Response (TLTRI, cause). The cause value indicates that the network has accepted the request in step 1. Based on operator policies, if either the SCS/AS is not authorized to perform this request (e.g. if the SLA does not allow for it) or the SCS/AS has exceeded its quota or rate of submitting requests, the cause value indicates the error and the flow stops at this step.
Step 3.
The SCEF assigns an SCEF Reference ID and identifies, based on local configuration (as described in clause 5.8.1), the RCAF(s) responsible for the provided Geographical Area. For every identified RCAF, the SCEF derives a Location Area from the Geographical Area provided by the SCS/AS. The Location Area is according to operator configuration either a 3GPP location area (e.g. list of TA/RAs, list of cell(s), list of eNodeBs, etc.) or a sub-area of the Geographical Area provided by the SCS/AS. The SCEF sends an Aggregated Congestion Request (SCEF Reference ID, Location Area, Duration, Threshold) message to the identified RCAF(s). Duration indicates the time for which a continuous reporting is requested. The absence of Duration indicates a one-time reporting. The SCEF, based on operator policies, may chose a different Threshold value than the one indicated by the SCS/AS in step 1.
Step 4.
The RCAF examines the Aggregated Congestion Request message. If the SCEF provided a Duration, the RCAF stores the SCEF instructions and starts to monitor the set of cells or eNodeBs belonging to the Location Area for a change in the congestion status that is crossing a Threshold (if provided by the SCEF). The RCAF sends an Aggregated Congestion Report to the SCEF including the SCEF Reference ID and, depending on the operator configuration and current RCAF knowledge, the congestion status for every cell or eNodeB belonging to the Location Area requested by the SCEF.
Step 5.
The SCEF verifies whether the Network Status Request identified via the SCEF Reference ID is valid and active and stores the report. After receiving reports from all the involved RCAF(s) to which step 3 was executed, the SCEF derives the NSI for the requested Geographical Area by combining all reports with the same SCEF Reference ID in an operator configurable way (governed by SLAs, network topology, usage, etc.).
Step 6.
The SCEF sends a Network Status Report (TLTRI, NSI) message to the SCS/AS.
Step 7.
The SCS/AS sends a Network Status Acknowledgement to the SCEF.
5.8.3 Report procedure for continuous reporting of network status p. 93
This procedure is used by the SCEF to report a change of Network Status Information (NSI) to the SCS/AS which requested a continuous reporting of network status. Figure 5.8.3-1 illustrates the procedure.
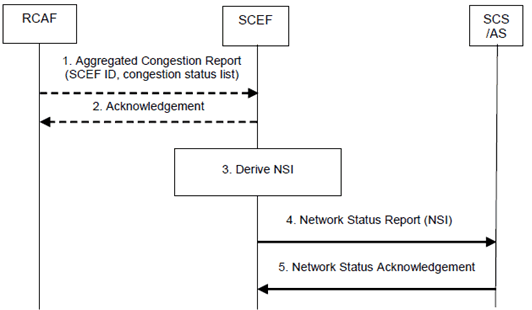
Figure 5.8.3-1: Report procedure for continuous reporting of network status
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The RCAF detects a change in the congestion status that is crossing a Threshold (if provided by the SCEF) for the set of cells or eNodeBs belonging to the Location Area requested by the SCEF. An Aggregated Congestion Report message is sent to this SCEF including the SCEF Reference ID and, depending on the operator configuration, the congestion status for every cell or eNodeB belonging to the Location Area requested by the SCEF.
Step 2.
The SCEF acknowledges the report to the RCAF.
Step 3.
Whenever a new Aggregated Congestion Report message arrives, the SCEF stores the report and derives a new NSI for the requested geographical area by combining this report with all other reports having the same SCEF Reference ID in an operator configurable way (governed by SLAs, network topology, usage etc.).
Step 4.
Triggered by a NSI change (derived in step 3) that is crossing a Threshold (if provided by the SCS/AS), the SCEF sends a Network Status Report (TLTRI, NSI) message to the SCS/AS.
Step 5.
The SCS/AS sends a Network Status Acknowledgement to the SCEF.
5.8.4 Removal procedure for continuous reporting of network status p. 94
This procedure is used for termination of the continuous reporting of network status. It can be triggered by the SCS/AS at any time before the Duration is over or if no Duration was provided. The SCEF will trigger this procedure when the Duration is over. Figure 5.8.4-1 illustrates the procedure.
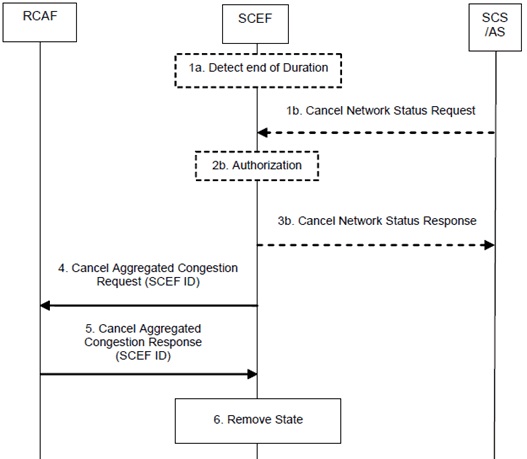
Figure 5.8.4-1: Removal procedure for continuous reporting of network status
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1a.
The SCEF detects that the requested Duration for an ongoing continuous reporting of network status to an SCS/AS is over and identifies the corresponding SCEF Reference ID.
Step 1b.
When the SCS/AS needs to terminate an ongoing continuous reporting of network status, the SCS/AS sends a Cancel Network Status Request (SCS/AS Identifier, TLTRI) message to the SCEF.
Step 2b.
If the SCS/AS requested to terminate an ongoing continuous reporting of network status in step 1b, the SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request and identifies the corresponding SCEF Reference ID.
Step 3b.
If the SCS/AS requested to terminate an ongoing continuous reporting of network status in step 1b, the SCEF sends a Cancel Network Status Response (Cause) message to the SCS/AS.
Step 4.
The SCEF identifies the RCAF(s) involved in the continuous reporting represented by the SCEF Reference ID. The SCEF sends a Cancel Aggregated Congestion Request (SCEF Reference ID) message to the identified RCAF(s).
Step 5.
The RCAF removes the related SCEF instructions and stops monitoring the set of cells or eNodeBs belonging to the Location Area for a change in the congestion status. Afterwards, a Cancel Aggregated Congestion Response is sent to the SCEF including the SCEF Reference ID.
Step 6.
The SCEF removes all state information related to this continuous reporting represented by the SCEF Reference ID.