Content for TS 23.292 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
5…
7…
7.2…
7.3…
7.3.2.2…
7.3.2.2.4…
7.4…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.2.3…
7.4.2.2.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.6.1.2.2.6…
7.6.1.2.3…
7.6.1.2.3.5…
7.6.1.2.3.6…
7.6.2…
7.6.2.7
7.6.2.8…
7.6.2.11…
7.6.3…
7.7…
7.7.2…
7.9…
7.9.2…
7.9.2.4
7.9.2.5
8…
A…
G…
H…
H.5…
H.5.3…
H.5.3 Outbound-roaming support p. 138
H.5.3.1 Call flows for outbound-roamers p. 138
H.5.3.1.1 Attach/Registration Procedure for outbound roamer p. 138
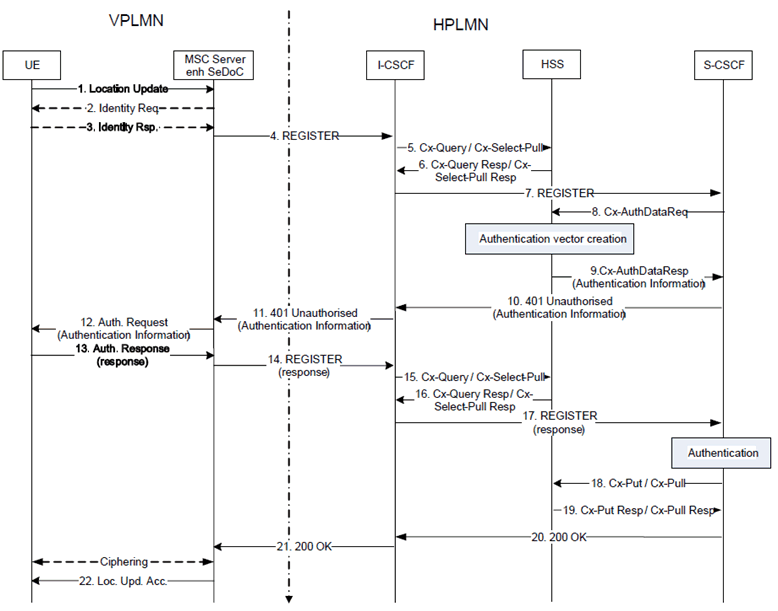
Figure H.5.3.1.1-1: Authentication/Registration for outbound roamer in a SeDoC enhanced network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.-22.
The flow description is the same as in annex XXX of this specification.
H.5.3.1.2 Originating session for own users roaming (outbound roamer) p. 138
For session origination for own users please refer to clause 7.3.2.1.2 of this specification.
H.5.3.1.3 Terminating session for own users roaming (outbound roamer) p. 138
For session termination for own users please refer to clause 7.4.2.1.2 of this specification.
H.5.3.1.4 Call flow for outbound-roamers to a not enhanced network p. 138
The ICS-IWF acts as a HLR towards the not enhanced MSC in the VPLMN, the procedures between MSC and ICS-IWF follow the normal VLR - HLR procedures.
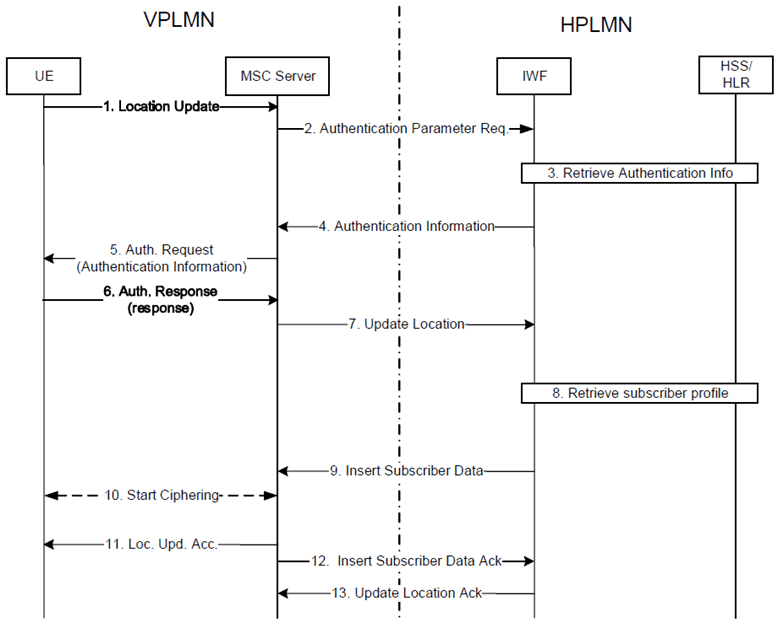
Figure H.5.3.2-1: Authentication/Registration for outbound roamer in a not enhanced network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE sends a Location Update Request message to the MSC-Server in the VPLMN and includes its IMSI and the LAI. In case of a combined attach, or CSFB etc., then the Location Update Request may be sent from the MME or the SGSN of the VPLMN.
Step 2.
The MSC detects based on the IMSI that the UE does not belong to the own network and is an inbound roamer. If the request is coming from the MME/SGSN, then the CS authentication may be skipped. The MSC contacts the ICS IWF, acting as a HLR of the HPLMN, indicating that CS authentication is required with a Authentication Parameter Request.
Step 3.
The ICS IWF retrieves the CS authentication data from the HSS.
Step 4.
The ICS IWF (acting as HLR to the MSC-Server) provides the Authentication Info parameters to the MSC-Server. The MSC-Server stores the parameters and triggers the CS authentication procedure.
Step 5.
The MSC-Server sends a Authentication Request with the RAND value to the UE.
Step 6.
The UE computes the SRES and provides it back to the MSC-Server in the Authentication Response.
Step 7.
The MSC-Server sends an Update Location Request with the IMSI and MSRN to the ICS-IWF, acting as the HLR of the HPLMN.
Step 8.
The ICS IWF retrieves the subscription profile and service settings from the HSS and maps them into a CS profile with CS settings.
Step 9.
The ICS IWF replies with the Insert Subscriber Data message according to normal VLR-HLR procedures.
Step 10.
The MSC Server starts ciphering according to normal procedures.
Step 11.
The MSC-Server provides a Location Update Accept message to the UE (or MME,SGSN if originated request comes from here) according to the normal procedures.
Step 12.
The MSC-Server exchanges the Subscriber Data Insert Acknowledgement and Location Update Acknowledgement according to normal VLR-HLR procedures.