Content for TS 23.292 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
5…
7…
7.2…
7.3…
7.3.2.2…
7.3.2.2.4…
7.4…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.2.3…
7.4.2.2.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.6.1.2.2.6…
7.6.1.2.3…
7.6.1.2.3.5…
7.6.1.2.3.6…
7.6.2…
7.6.2.7
7.6.2.8…
7.6.2.11…
7.6.3…
7.7…
7.7.2…
7.9…
7.9.2…
7.9.2.4
7.9.2.5
8…
A…
G…
H…
H.5…
H.5.3…
H.5 Interworking with networks not supporting IMS and/or ICS
H.5.1 Overview
H.5.2 Inbound-roaming support
H.5 Interworking with networks not supporting IMS and/or ICS p. 133
H.5.1 Overview p. 133
In this scenario, one network is fully supporting IMS and SeDoC but the interworking network does not support IMS or ICS.
For inbound roamers, the basic enhancement is to provide VLR services towards the HLR in the HPLMN in an interworking function for inbound roamers, which has the role of a centralized VLR.
The architecture is similar to the normal ICS architecture with the difference that the ICS Interworking Function is shared by all SeDoC -MSCs to support inbound roamers without IMS roaming agreement. The inbound roamers will have a temporary IMS subscription for the VPLMN, all services are executed in the VPLMN.
For outbound roaming UEs, it is the opposite way, i.e. the interworking function provides HLR services to the VLR in the VPLMN and in addition provides interworking of the IMS/CS profile and the service settings. The interworking function provides also signalling interworking towards the MSC in the VPLMN.
H.5.2 Inbound-roaming support p. 133
H.5.2.1 Roaming Architecture with legacy home network p. 133
For the migration phase the SeDoC enabled network operator is required to provide legacy support for inbound roamers. The architecture proposed in this solution is for the SeDoC enabled visited network to emulate a VLR and allocate to the inbound CS roaming subscriber a temporary IMS identity so that they can also be served by the IMS domain.
CAMEL can be supported by collocating the IP Multimedia Service Switching Function (IM SSF) with the AS. The IM SSF retrieves the CAMEL Subscription Information (CSI) from the ICS IWF at the time of the Attach of the UE. The IM SSF would perform the normal CAMEL requests to the gsmSCF in the HPLMN as specified in TS 23.278.
The detailed architecture diagram is depicted in Figure H.5.2.1-1.
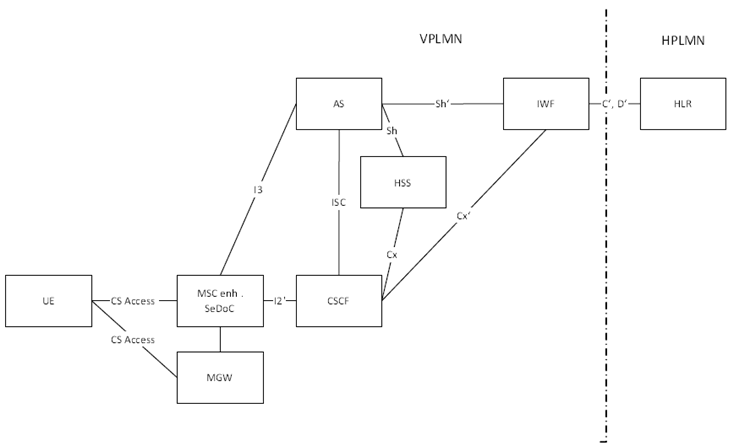
H.5.2.2 IMS Centralized Services Interworking Function (ICS-IWF) Features p. 134
The ICS-IWF is necessary to support roaming scenarios. The interworking function terminates:
- the Cx' interface towards the I-CSCF to provide the role of HSS for procedures related to Serving CSCF assignment.
- the Cx' interface towards the S-CSCF for procedures related to routing information retrieval from ICS-IWF to CSCF and procedures related to authorisation (e.g. checking of roaming agreement) and procedures related to authentication: transfer of security parameters of the subscriber between ICS-IWF and CSCF
- the C interface towards HLR for inbound roamer during migration phase to provide the role as VLR towards HLR to retrieve authentication and subscription data during authentication/registration procedure and to retrieve routing information for the terminating case
- the Sh' interface for the role as HSS towards AS in VPLMN for local IMS registration,
- role as VLR towards HPLMN HLR, i.e. in course of registration the ICS-IWF retrieves the user profile from HPLMN and creates a temporary user profile. The temporary user profile may be updated due to MAP ISD or deleted due to MAP Cancel or IMS de-registration or IMS registration time out.
- role as HSS towards the S-CSCF in VPLMN for local IMS registration.
- role as AS towards HSS in VPLMN for 3rd party IMS registration to enable terminating session routing to the VPLMN.
- maps supplementary services management commands for inbound roamers to the respective CS MAP command to the HLR
- role as HLR towards VLR for outbound roamers in a legacy network.
H.5.2.3 Call Flows for Inbound roamer p. 135
H.5.2.3.1 Authentication/Registration for Inbound roamers p. 135
The main difference to the procedure for own users is that for inbound roamers the registration flow goes through an ICS IWF that acts as a HSS towards the I-CSCF and S-CSCF in the VPLMN and as a VLR towards the HPLMN HLR.
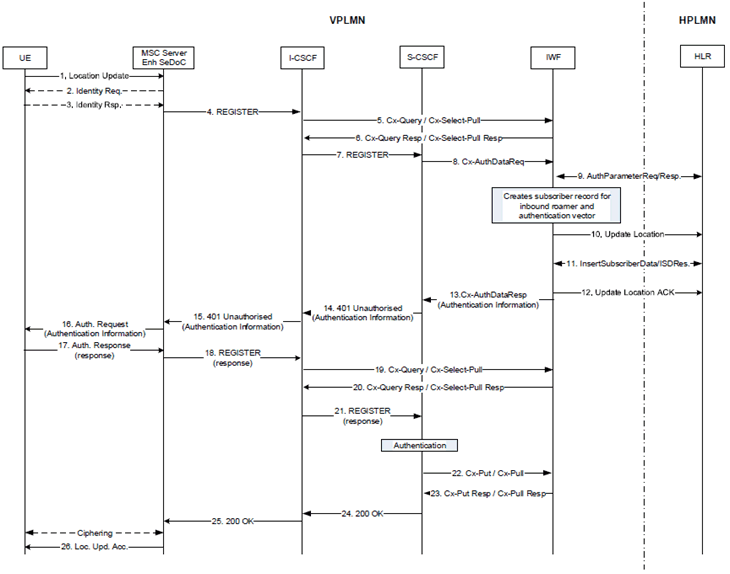
Figure H.5.2.3.1-1: Authentication/Registration procedure for inbound roamer
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1. -7.
Same as steps as in Annex G of this specification with the difference that in step 5, the I-CSCF detects the inbound roaming UE based on a comparison of the MNC/MCC in the IMPI/IMPU. The I-CSCF queries the IWF which may look up a database whether the MNC/MCC operator network (HPLMN of the inbound roaming UE) has an IMS roaming agreement or not. If there is no IMS roaming agreement or any other related Service Level Agreements (SLA) in place with this network, then the IWF selects an S-CSCF which is able to handle the CS authentication procedure and provides the S-CSCF address to the I-CSCF. I-CSCF marks the SIP REGISTER with an inbound roaming indication towards the S-CSCF.
Step 8.
The S-CSCF identifies the REGISTER as being from the MSC Server enhanced for SeDoC for an inbound roamer. The S-CSCF requests the authentication info from the ICS IWF which acts as a HSS towards the S-CSCF.
Step 9.-13.
The ICS-IWF acting as VLR retrieves the Authentication Info parameters (authentication quintets required for UMTS AKA) from the HLR. The ICS IWF retrieves the service profile via the D interface, i.e. it behaves like a VLR towards the HPLMN HLR by performing an Update Location Procedure and Insert Subscriber Data Procedure. The ICS IWF creates a temporary record (subscription profile). For invoking other AS(s), the ICS IWF generates the corresponding iFC(s).
Step 14-26.
Same as steps 10.-22 Annex G of this specification.
H.5.2.4 Originating session for Inbound roamer p. 136
The Origination session for inbound roamers is very similar to the Origination using I2 reference point as described in clause 7.3.2.1.2 of this specification with the difference that the S-CSCF and AS is located in the VPLMN.
H.5.2.5 Terminating session for Inbound roamer p. 136
UEs which have been successfully registered in IMS by the MSC Server have a registration binding at the S-CSCF containing the MSC Server as the contact address.
The SCC AS shall be inserted in the IMS session path using the terminating iFC. The SCC AS performs T-ADS for selection of an access and returns information to assist with S-CSCF selection of a registered contact address. When the T-ADS function selects the MSC Server enhanced for SeDoC, the SCC AS directs the IMS terminating session towards the contact address of the MSC Server.
On receipt of the session initiation message, the MSC Server enhanced for ICS shall perform the necessary interworking between the I2 reference point and CS signalling (e.g. as described in TS 24.008). The MSC Server shall also control a CS-MGW using the Mc reference point to perform the necessary interworking between RTP bearers on the Mb reference point and CS access bearers and adds the User Location Information (e.g. CGI or SAI) and/or UE Time Zone Information to the response to the session initiation.
The SCC AS selects to breakout an incoming session to the CS domain in case UE is registered in IMS as being attached to the CS network at an MSC Server enhanced for SeDoC. In this case, terminating iFC forwards the call to the SCC AS.
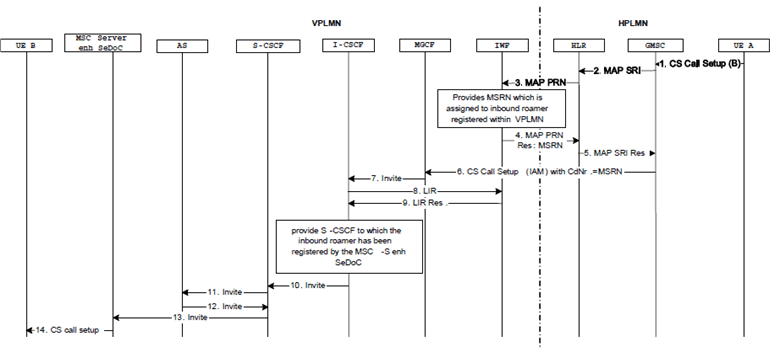
Figure H.5.2.5-1: Terminating session via CS Access for inbound roamer
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE A originates a call in the CS domain to party-B according to standard origination procedures.
Step 2.
The GMSC sends a Send Routing Information (SRI) request to the HLR.
Step 3.-4.
The HLR fetches a MSRN from the ICS-IWF acting as VLR by a Provide Roaming Number (PRN) request/response sequence.
Step 5.
The HLR forward the MSRN in the SRI Res. message.
Step 6.
The GMSC sets up the call towards the MGCF of the VPLMN with the received MSRN.
Step 7.
The MGCF initiates an INVITE towards the I-CSCF in the visited IMS of the UE B.
Step 8.-9.
The I-CSCF retrieves the address assigned to the SeDoC user from the ICS-IWF. For the LIR the I-CSCF uses the called party from the INVITE which is the MSRN. The IWF has assigned this MSRN according to the called user (MSISDN) (step 3,4) and has stored the relation MSISDN/MSRN.
Step 10.
The I-CSCF routes the INVITE to the S-CSCF.
Step 11.
The S-CSCF performs standard service control execution procedures. Filter criteria direct the S-CSCF to send the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 12.
The SCC AS performs terminating access domain selection. The SCC AS chooses the CS access network and the MSC Server contact address, amongst the registered contact addresses for the UE B, for the setup of the media. The SCC AS establishes a new session by sending an INVITE to the UE B via the S-CSCF.
Step 13.
The S-CSCF forwards the INVITE to the MSC Server based on the contact address stored during registration, using standard IMS procedures.
Step 14.
The MSC Server sends a Setup message to the UE B.