Content for TS 23.203 Word version: 19.1.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.1.4…
6.1.7…
6.1.10…
6.1.17…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3
6.4…
6.8…
7…
7.3…
7.4…
7.7…
7.7.3…
7.8…
A…
A.4…
D…
P…
P.4.2.4…
P.7…
P.7.5…
P.8
Q…
S…
S.7…
S.8.8
T…
P Fixed Broadband Access Interworking with EPC
P.1 Definitions
P.2 Abbreviations
P.3 High Level Requirements
P.4 Architecture model and reference points
P.4.1 Reference points
P.4.2 Reference architecture
P.4.2.0 General
P.4.2.1 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming
P.4.2.2 Reference architecture - Home Routed
P.4.2.3 Reference architecture - Visited Access
...
...
P (Normative) Fixed Broadband Access Interworking with EPC |R11| p. 212
This Annex specifies the enhancement to PCC framework for supporting dynamic QoS interworking with Policy Framework defined by Broadband Forum.
P.1 Definitions p. 212
UE local IP address is defined as:
either the public IPv4 address and/or IPv6 address/IPv6 network prefix assigned to the UE by the BBF domain in the no-NAT case, or the public IPv4 address assigned by the BBF domain to the NATed RG that is used for this UE.
H(e)NB local IP address is defined as:
either the public IPv4 address and/or IPv6 address/IPv6 network prefix assigned to the H(e)NB by the BBF domain in the no-NAT case, or the public IPv4 address assigned by the BBF domain to the NATed RG that is used for this H(e)NB.
Non-seamless WLAN offload (NSWO):
is a capability of routing specific IP flows over the WLAN access without traversing the EPC as defined in clause 4.1.5 of TS 23.402.
EPC-routed:
User plane traffic that is routed via a PDN GW in EPC as part of a PDN Connection. EPC-routed applies to non-roaming, roaming with traffic home-routed and roaming with traffic local break-out cases.
P.2 Abbreviations p. 212
The following abbreviations are relevant for this Annex only:
BBF
Broadband Forum
BPCF
Broadband Policy Control Function
NSWO
Non-Seamless WLAN offload
NSWO-APN
Non-Seamless WLAN offload APN
P.3 High Level Requirements p. 212
The same requirements as defined in clause 4 applies with the following exceptions:
- no UE initiated resource reservation procedures are supported for EPC-based Fixed Broadband Access.
- The support of traffic steering control for the traffic in the (S)Gi-LAN is only applicable to the EPC-routed traffic of Home-routed scenario.
- perform resource reservation (e.g. admission control request to the Fixed Broadband Network) based on the bandwidth requirements and the QoS attributes of a service request for EPC-routed traffic in the Fixed Broadband network;
- provide information to identify a 3GPP UE in the Fixed Broadband Network.
- perform resource reservation (e.g. admission control request to the Fixed Broadband Network) based on the bandwidth requirements and the QoS attributes of a service request for non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic in the Fixed Broadband network. In this case the non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic shall be managed by PCRF as an IP-CAN session identified by one IPv4 and/or an IPv6 prefix together with UE identity information and Non-seamless WLAN offload APN. The IP-CAN session for NSWO exists as long as UE Local IP addresses/prefix is announced to the IP network and authorized by EPC. The NSWO-APN is an APN allowing the BPCF to indicate to PCRF that for subscribers of a certain HPLMN the IP-CAN session is related to NSWO traffic.
P.4 Architecture model and reference points p. 213
P.4.1 Reference points p. 213
P.4.1.1 S9a Reference point p. 213
The S9a reference point resides between:
- the PCRF in the PLMN and the BPCF in the Fixed Broadband Access Network (BPCF);
- the PCRF in the VPLMN (V-PCRF) and the BPCF in the Fixed Broadband Access Network (BPCF).
P.4.1.2 S15 Reference Point p. 213
The S15 reference point between the HNB GW and the PCRF and between the HNB GW and the V-PCRF. It enables the transfer of dynamic QoS control policies from the (V-)PCRF to the BPCF for the purpose of allocation of QoS resources in the Fixed Broadband Access Network for HNB CS calls.
P.4.1.3 Gxx reference point p. 213
When this reference point corresponds to the Gxb*, it transports access information for WLAN UEs such as the UE local IP address and the UDP port number. It is used scenarios in which the ePDG provides the access information via Gxb* to trigger the PCRF to initiate the S9a session i.e. S2b-PMIP and untrusted S2c.
For the case of H(e)NB with S5/S8 PMIP, this reference point corresponds to Gxc and the requirements in clause 5.2.7 applies. In addition for the purpose of fixed broadband access interworking, Gxc transports the H(e)NB Local IP address and the UDP source port, if available, in the fixed broadband access network where the H(e)NB connects to.
P.4.1.4 S9 reference point p. 213
In addition to the specification of the S9 reference point defined in clause 5.2.6, this reference point is used to trigger the V-PCRF to initiate the Gateway Control Session establishment over S9a. The S9 interface is enhanced to carry from the H-PCRF to the V-PCRF the UE local IP address, the UDP port number, if available, the H(e)NB local IP address and UDP port, if available and the ePDG IP address (for S2b and untrusted S2c access) or the PDN GW IP address (for trusted S2c access), if available.
P.4.1.5 Gx reference point p. 214
In addition to the specification of the Gx reference point defined in clause 5.2.2, this reference point is enhanced as described in the following. The IP-CAN establishment/modification request message, send from PCEF to PCRF, should include:
- the UE local IP address and the UDP port number, if available, when WLAN access and GTP is used.
- the UE local IP address and the UDP port number, if available, when trusted S2c is used.
- the H(e)NB local IP address and the UDP port number, if available, when UE accesses from H(e)NB and GTP S5/S8 is used.
P.4.2 Reference architecture p. 214
P.4.2.0 General p. 214
The reference architecture described in clause 5.1 is:
-
extended to include S9a reference point to support fixed broadband access interworking to EPC for the following scenarios:
- S9a reference point between PCRF and BPCF in the non-roaming case for traffic that is routed via EPC and for traffic that is non-seamless WLAN offloaded in the fixed broadband access network; and
- S9a reference point between the V-PCRF and BPCF for roaming cases with visited access and home routed for traffic that is routed via EPC; and for traffic that is non-seamless WLAN offloaded in the fixed broadband access network;
- extended to include the S15 reference point as defined in clause P.4.1.2;
- PCEF resides in the PDN GW;
- for WLAN access: BBERF resides in the ePDG. The BBERF only applies for cases 2b (i.e. S2b-PMIP, S2c-untrusted);
- for H(e)NB access with S5/S8 PMIP: BBERF resides in the Serving GW.
P.4.2.1 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming p. 215
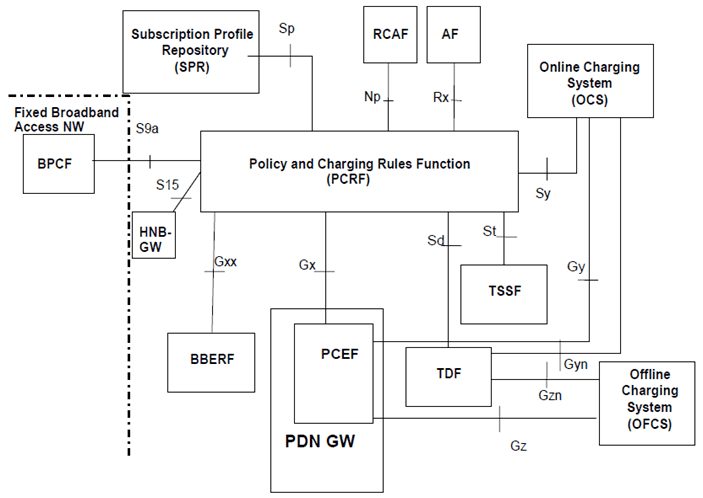
Figure P.4.2.1-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.4.2.2 Reference architecture - Home Routed p. 216
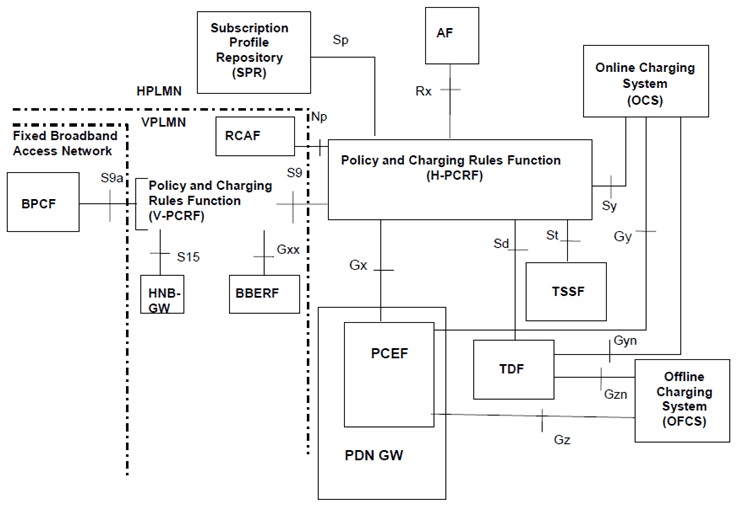
Figure P.4.2.2-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (home routed)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.4.2.3 Reference architecture - Visited Access p. 217
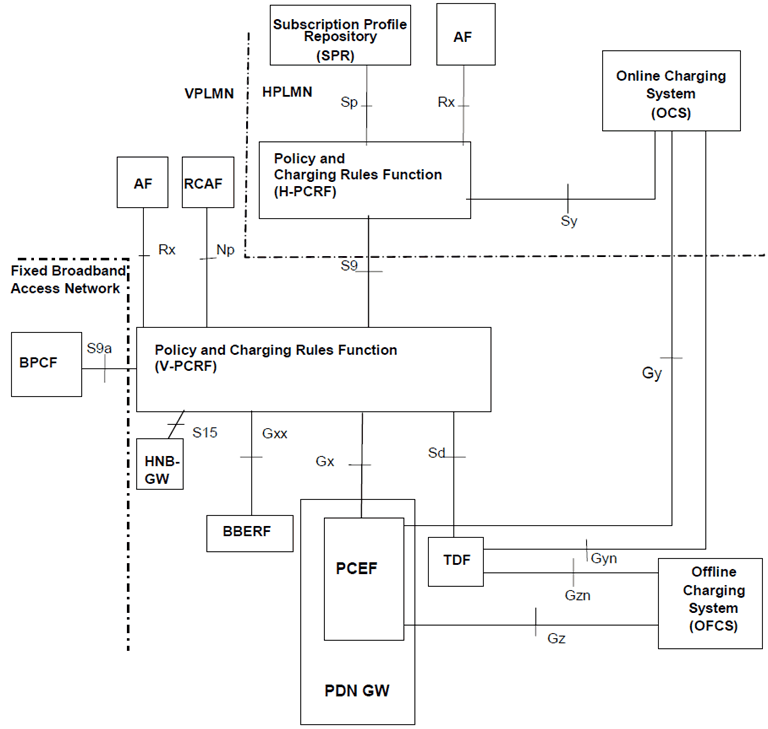
Figure P.4.2.3-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (visited access)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)