Content for TS 23.002 Word version: 18.0.0
A Description for GLR-related entities and interfaces
A.1 Normative references
A.2 Definitions related to Gateway Location Register (GLR)
A.3 The entities of the mobile system
A.4 Configuration of a Public Land Mobile Network
A.5 PLMN interfaces
$ Change history
A Description for GLR-related entities and interfaces p. 110
This annex describes the GLR-related entities and the interfaces. This annex is an informative annex. The 'informative' means just that the GLR is an optional functional entity to optimize signalling traffic between PLMNs. Therefore, this annex is normative to a PLMN which introduce the GLR.
The GLR is only applicable for GERAN and UTRAN access. The GLR is not applicable to the EPC.
A.1 Normative references p. 110
A.2 Definitions related to Gateway Location Register (GLR) p. 110
A.2.1 Gateway Location Register (GLR) p. 110
This entity handles location management of roaming subscriber in visited network without involving HLR. The location register function in the GLR stores subscription information and routeing information for both CS services and PS services. This entity can be only located in a visited PLMN.
A.2.2 Intermediate Mobile-services Switching Centre (IM-MSC) p. 110
This entity is used as serving MSC towards home network and relay some messages between home network and serving MSC. This entity can be only located in a visited PLMN.
A.2.3 Intermediate GPRS Serving Node (IM-GSN) p. 110
This entity is used as serving GSN towards home network and relay some PDU notification messages between serving GSN and Gateway GSN. This entity can be only located in a visited PLMN.
A.3 The entities of the mobile system p. 110
A.3.1 Gateway Location Register (GLR) p. 110
GLR is pseudo-HLR located in visited network. The roamer's information is stored in it and handles location management of it within the network. Presence of GLR is invisible from home network therefore interface between HLR and GLR is same as one of HLR and VLR. Also, the interface between the VLR and GLR is the same as the one between the VLR and the HLR.
The GLR is a logical node and acts as a VLR for MAP signalling (e.g. PRN) from the HPLMN point of view. The GLR acts as a HLR for MAP signalling (e.g. Register SS) from the VPLMN point of view.
The GLR also acts as an SGSN for MAP signalling only (e.g. ISD) from the HPLMN point of view. This is because MAP operations such as ISD must be terminated at the GLR for the purpose of subscriber data caching.
The GLR shall terminate all TC dialogues and start new dialogues towards the HLR or the VLR. The GLR shall generate SCCP address of the HLR (i.e. E.214 MGT) from IMSI.
A.3.2 Intermediate Mobile-services Switching Centre (IM-MSC) p. 111
The Intermediate MSC (IM-MSC) is the logical node, which represent MSCs in the visited network. Some service features use the MSC Number stored in the HLR directly to deliver message from a certain node in home network (e.g. SMS-GMSC) to serving MSC in visited network. In such case, the message is firstly distributed to representative MSC (i.e. IM-MSC) and it relays it to actual serving MSC interrogating routing information to GLR.
- The Intermediate MSC (IM-MSC) is a logical node and represents the VMSC in the GLR equipped VPLMN.
- The IM-MSC acts as the VMSC for the HPLMN in the same way that the GLR acts as a VLR for HPLMN. The IM-MSC terminates MAP signalling from the HPLMN towards the VMSC and forwards the signal to the actual VMSC.
- The IM-MSC has an address interrogation function with which it is able to obtain the actual VMSC Number from the GLR.
- The IM-MSC is implemented in the same physical node as the one in which the GLR is implemented.
- The GLR alters the VMSC Number to the IM-MSC Number within an Update Location message.
- The IM-MSC Number is the E.164 Number assigned to the IM-MSC [53].
- The interrogation function of the IM-MSC is similar to that in the SMS-GMSC.
A.3.3 Intermediate GPRS Serving Node (IM-GSN) p. 111
The Intermediate GSN (IM-GSN) is a logical node and represents the SGSN for some GTP signalling termination in a GLR equipped VPLMN.
The IM-GSN acts as an SGSN for only some GTP signalling messages (i.e. PDU_Notification request/response, PDU_Notification_reject request/response) from the HPLMN point of view. The IM-GSN terminates these GTP signalling messages from the HPLMN towards SGSN and forwards the signal to the actual SGSN. The IM-GSN has an address interrogation function with which it is able to request the actual SGSN address from the GLR.
Apart from the case described above (i.e. PDU_Notification request/response, PDU_Notification_reject request/response), all other GTP signalling should be handled directly between the SGSN and the GGSN.
A.4 Configuration of a Public Land Mobile Network p. 111
A.4.1 Basic configuration with GLR introduction p. 111
In the basic configuration with GLR introduction presented in Figure A.1, all the functions related to GLR introduction are considered implemented in different equipment. Therefore, all the interfaces within PLMN are external. Interfaces GLa, GLb, GLc, GLd, GLf, GLg, GLh, and GLi need the support of the Mobile Application Part of the signalling system No. 7 to exchange the data necessary to provide the mobile service. No protocols for the GLe interface are standardized. GLj and GLk need the support of GPRS Tunnelling Protocol - Control to provide the packet domain services.
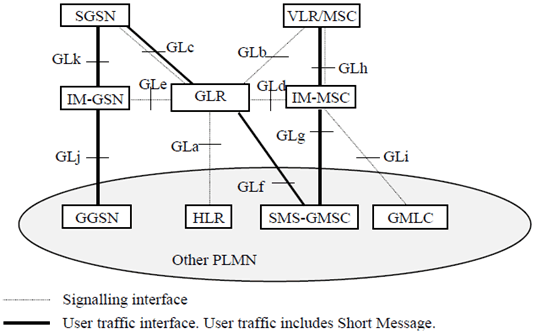
A.5 PLMN interfaces p. 112
A.5.1 Interface between the HLR and the GLR (GLa-interface) p. 112
In circuit switched domain, this interface is the same as that between the VLR and the HLR (see TS 29.002). The HLR regards the GLR as the VLR via this interface. On the other hand, in packet switched domain, this interface is the same as that between the SGSN and the HLR (see TS 29.002). The HLR regards the GLR as the SGSN via this interface
A.5.2 Interface between the VLR and the GLR (GLb-interface) p. 112
This interface is the same as those between the VLR and the HLR (see TS 29.002). The VLR regards the GLR as the HLR via this interface.
A.5.3 Interface between the SGSN and the GLR (GLc-interface) p. 112
This interface is the same as those between the SGSN and the HLR (see TS 29.002). The SGSN regards the GLR as the HLR via this interface.
A.5.4 Interface between the GLR and the IM_MSC (GLd interface) p. 112
In the network with the GLR, when the IM_MSC receives a message, it interrogates the GLR for the routing information of the MSC. However, this interface is internal because GLR and IM-MSC are implemented in the same physical node and the protocol on this interface is not specified.
A.5.5 Interface between the GLR and the IM_GSN (GLe interface) p. 112
In the network with the GLR when the IM_GSN receiving a PDU notification from the GGSN, the IM_GSN relays the notification to the SGSN by interrogating via the interface the routing information to the GLR. The interrogation uses the same operation on the interface between the SGSN and the HLR (see TS 29.002).
A.5.6 Interface between the SMS-GMSC and the GLR (GLf interface) p. 113
This interface is used to forward mobile-terminated short messages in the network with the GLR in case of SMS transfer over GPRS. Signalling on this interface uses the Mobile Application Part (MAP) (see TS 29.002).
The SMS-GMSC regards the GLR as the SGSN via this interface.
A.5.7 Interface between the SMS-GMSC and the IM_MSC (GLg interface) p. 113
This interface is used to forward short messages in the network with the GLR in case of SMS transfer over non-GPRS. Signalling on this interface uses the Mobile Application Part (MAP) (see TS 29.002).
The SMS-GMSC regards the IM_MSC as the MSC via this interface.
A.5.8 Interface between the MSC and the IM_MSC (GLh interface) p. 113
This interface is used to forward short messages in the network with the GLR in case of SMS transfer over non-GPRS. Also this interface is used to exchange data needed by the MSC to perform subscriber authorization and allocate network resources. Signalling on this interface uses the Mobile Application Part (MAP) (see TS 29.002).
A.5.9 Interface between the GMLC and the IM_MSC (GLi interface) p. 113
Also this interface is used to exchange data needed by the MSC to perform subscriber authorization and allocate network resources. Signalling on this interface uses the Mobile Application Part (MAP) (see TS 29.002).
The GMLC regards the IM_MSC as the MSC via this interface.
A.5.10 Interface between the GGSN and the IM_GSN (GLj interface) p. 113
In the network with the GLR when receiving a PDP PDU from the external network the GGSN sends a notification to the IM_GSN by the routing information from the HLR (see TS 29.060). The GGSN regards the IM_GSN as the SGSN via this interface.
A.5.11 Interface between the SGSN and the IM_GSN (GLk interface) p. 113
In the network with the GLR when receiving a PDP notification from the GGSN, the IM_GSN relays the notification to the SGSN by the routing information from the GLR (see TS 29.060). The SGSN regards the IM_GSN as the GGSN via this interface.