Content for TS 23.002 Word version: 18.0.0
5.5 Configuration of IM CN Subsystem entities
5.6 Configuration of Signalling Gateway Function
5.7 Configuration of 3GPP/WLAN Interworking
5.8 Configuration of Presence service
5.9 Configuration of MBMS entities
5.10 Configuration of Short Message Service over generic 3GPP Internet Protocol access (SMSIP) entities
...
...
5.5 Configuration of IM CN Subsystem entities |R5| p. 59
5.5.1 IM CN Subsystem functional entities |R8| p. 59
The configuration of IM CN Subsystem entities is presented in Figure 6. In the Figure, all the functions are considered implemented in different logical nodes. If two logical nodes are implemented in the same physical equipment, the relevant interfaces may become internal to that equipment.
Only the interfaces specifically linked to the IM CN subsystem are shown, i.e. all the SGSN, GGSN, S-GW, PDN-GW and HSS interfaces depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 1b are still supported by these entities even if not shown.
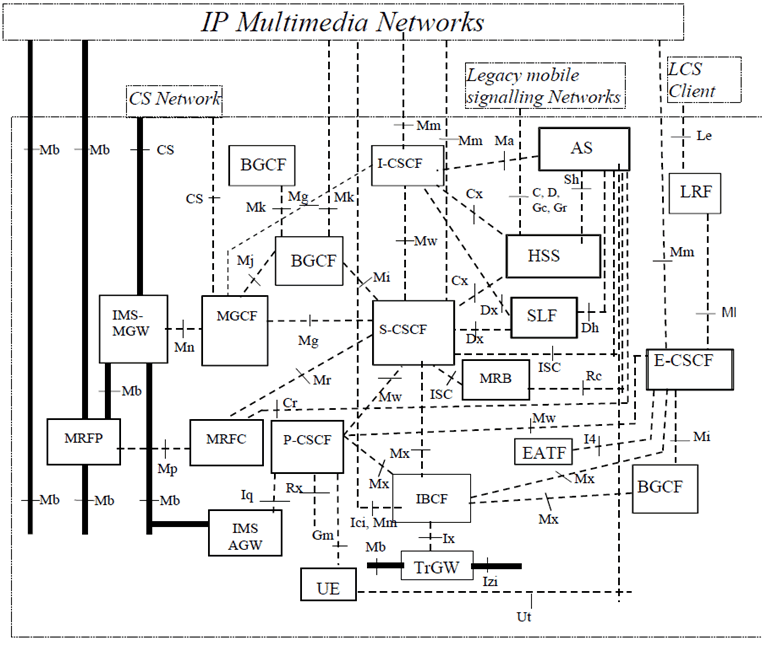
Legend:
Bold lines:
interfaces supporting user traffic;
Dashed lines:
Interfaces supporting only signalling.
5.5.2 IM CN Subsystem Service layer |R8| p. 60
The Figure below depicts an overall view of the functional architecture for services.
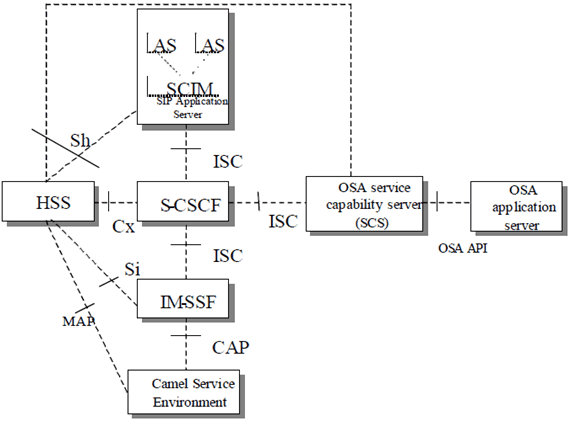
Figure 6a: Functional architecture for the provision of service in the IMS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The purpose of the IM SSF is to host the CAMEL network features (i.e. trigger detection points, CAMEL Service Switching Finite State Machine, etc.) and to interwork with CAP. The IMS-SSF may receive CAMEL subscription data from HSS via Sh reference point in addition to the Si reference point.
The IM SSF and the CAP interface support legacy services only.
The application server may contain "service capability interaction manager" (SCIM) functionality and other application servers. The SCIM functionality is an application which performs the role of interaction management. The internal components are represented by the "dotted boxes" inside the SIP application server. The internal structure of the application server is outside the standards. The Sh interface shall have sufficient functionality to enable this scenario.
The Figure below depicts an overall view of the functional architecture for enabling the management of the user's service related information via the Ut interface.
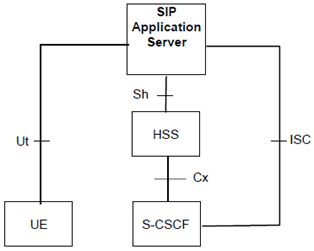
Figure 6b: Functional architecture for the management of the user's service related information
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The Figure below depicts an overall view of the functional architecture for routing SIP requests between I CSCF and Application Server.
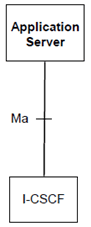
Figure 6c: Functional architecture for the routing of SIP requests between I CSCF and AS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
5.5.3 Service Centralization and Continuity |R8| p. 62
Figure 6d depicts an overall view of the functional architecture for IMS services centralization and continuity.
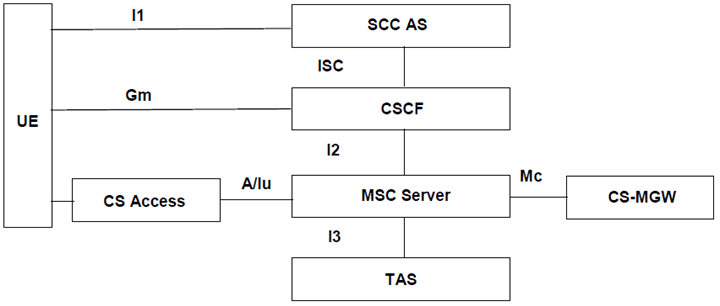
Figure 6d: Functional architecture for IMS Service Centralization and Continuity
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
IMS Service Centralization, defined in TS 23.292 provides communication services such that all services, and service control, are based on IMS mechanisms and enablers. It enables IMS services when using CS access as bearer for the media.
IMS Service Continuity, defined in TS 23.237 provides Session Transfer mechanisms to maintain service continuity in the event of access transfer for the case when such events are not hidden from the IMS session layer and thus service continuity could not otherwise be maintained.
Figure 6e provides the reference architecture for SRVCC using the ATCF enhancements as defined in TS 23.237. The ATCF enhancements provide Session Transfer mechanisms in the serving network to maintain service continuity in the event of access transfer for SRVCC.
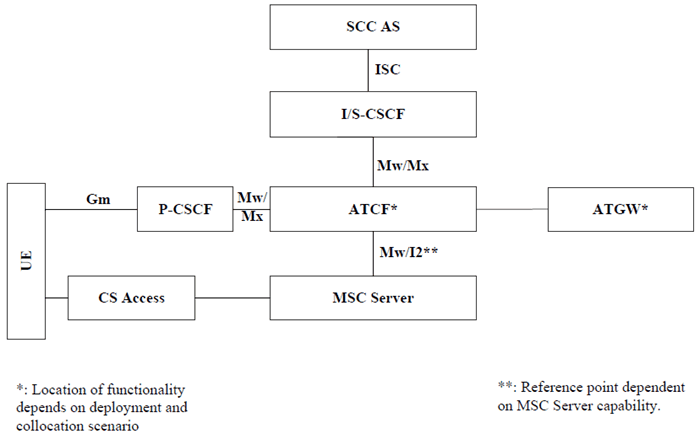
Figure 6e: IMS Service Centralization and Continuity Reference Architecture when using ATCF enhancements
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
If neither the MSC Server is not enhanced for ICS, the interface between MSC Server and ATCF is Mw.
5.5.4 WebRTC access to IMS |R12| p. 63
Figure 5.5.4-1 depicts an overall view of the functional architecture for WebRTC access to IMS.
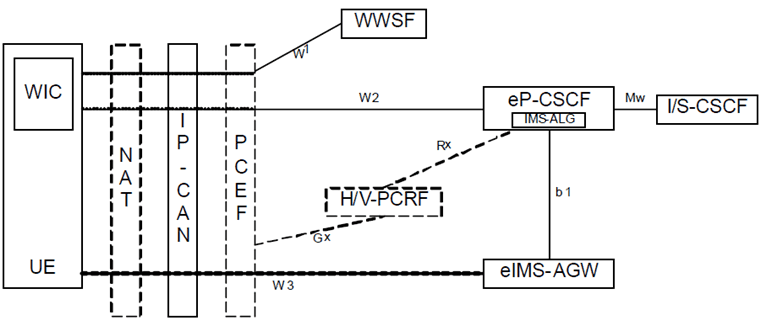
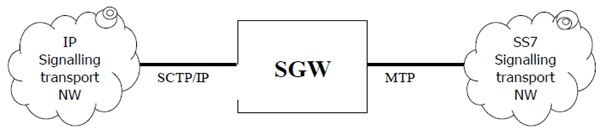
5.6 Configuration of Signalling Gateway Function |R4| p. 64
The Signalling gateway function is used to interconnect different signalling networks i.e. SCTP/IP based signalling networks and SS7 signalling networks. The application layer (e.g. ISUP, BICC, MAP or CAP) is not affected. The signalling gateway function may be implemented as a stand-alone entity or inside another entity.
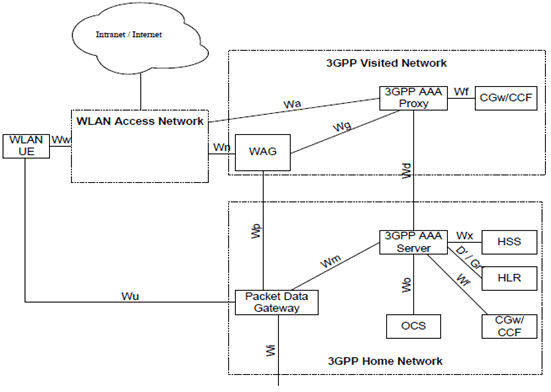
5.7 Configuration of 3GPP/WLAN Interworking |R6| p. 64
The configuration of the 3GPP/WLAN interworking function is presented in Figure 8. The Figure shows all network entities and reference point for the roaming scenario when a WLAN UE accesses PS based services in the home network. PS based services in the visited network are accessed via a Packet Data Gateway in the visited 3GPP network. Reference point Ww between WLAN UE and WLAN is outside the scope of 3GPP and only shown for completeness.
5.8 Configuration of Presence service |R6| p. 65
The reference architecture model, the reference points and the functional entities to support the Presence Service are described in TS 23.141.
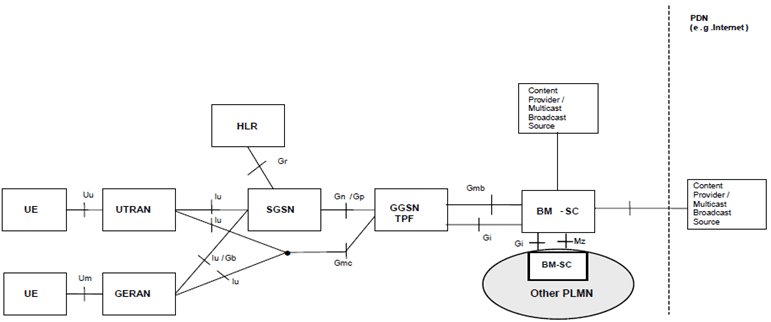
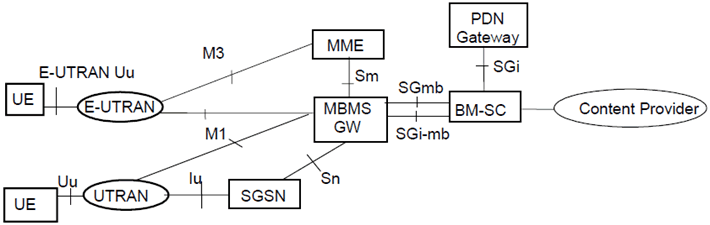
5.9 Configuration of MBMS entities |R6| p. 65
The configuration of the MBMS entities for GPRS and EPS is represented in Figure 9 and Figure 9a respectively. MBMS for GPRS supports UTRAN and GERAN. MBMS for EPS supports E-UTRAN and UTRAN.
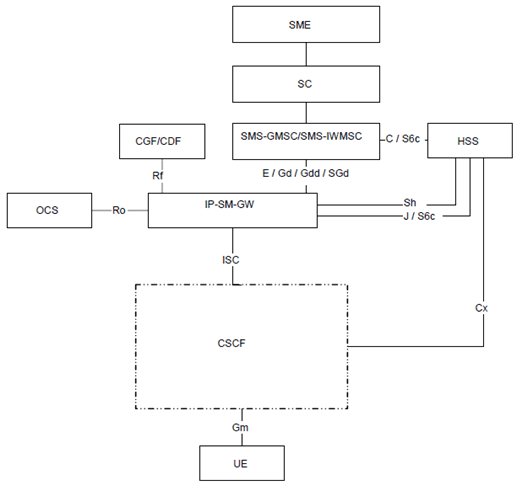
5.10 Configuration of Short Message Service over generic 3GPP Internet Protocol access (SMSIP) entities |R7| p. 67
The configuration of the Short Message Service over generic 3GPP Internet Protocol access (SMSIP) entities are represented in Figure 10.