Content for TS 33.180 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4…
4.3.4
4.3.5
5…
5.1.3
5.1.4…
5.2…
5.2.3
5.2.4
5.2.5
5.2.6…
5.3…
5.4…
6…
7…
7.3…
8…
9…
9.4…
10…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
J…
L…
5.1.4 Inter-domain MC user service authorization
5.1.5 MC user migration service authentication and authorisation
...
...
5.1.4 Inter-domain MC user service authorization p. 35
5.1.4.1 General p. 35
When a MC User requires service authorisation to a service that is located in a different Identity Management Domain, coordination between the identity management services of the primary Identity Management Domain and the partner Identity Management Domain is required. For example, a MC User from Identity Management Domain A may be a member of a group that is home to Identity Management Domain B within the same system or an MC user may migrate from their primary MC domain to a partner MC domain.
While inter-domain user service authorisation is not used for authorising users to services across interconnected MC systems (MC clients always connect directly to MC servers in their primary system with interconnection services provided via MC server to MC server communications), inter-domain user service authorisation shall be used for authorising migration of MC users.
This sub-clause shall be used for authenticating and authorizing a user that is home to Identity Management Domain A with a group service that is located in Identity Management Domain B or when a user from Identity Management Domain A migrates to a MC domain within Identity Management Domain B..
5.1.4.2 Inter-domain identity management functional model p. 35
The inter-domain identity management functional model is shown in Figure 5.1.4.2-1.
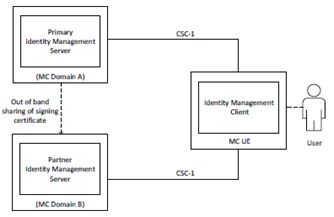
Figure 5.1.4.2-1: Functional Model for Inter-Domain Identity Management
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
In Figure 5.1.4.2-1, the IdMS located in the primary Identity Management Domain (MC Domain A) is the home identity management server for the user. The partner IdMS is located in a second Identity Management Domain (MC Domain B) and provides identity mangement services for the primary user when authorising to partner group services or when the MC user is attempting to migrate.
The CSC-1 reference point between the UE IdM client and the partner IdM server endpoints shall be a direct connection and shall be protected with HTTPS (TLS).
The primary IdMS certificate(s) used to validate the user credentials at the partner IdMS are provisioned into the partner IdMS using an out of band mechanism beyond the scope of this document.
As defined in Clause 5.1.2 an access token is required for user service authorisation. The same principle applies for inter-domain user service authorisation, in that the MC client must present a valid access token issued from the partner IdMS in MC Domain B for authorisation to services located in MC Domain B.
The inter-domain identity management procedure shall be triggered when an MC client, after performing user service authorisation within the primary Identity Management Domain, determines that the user is a member of a group service that is located in a partner IdMS domain (as indicated in the user profile).
Additionally, the inter-domain identity management procedure shall be triggered when a user attempts to migrate from their primary MC system to a partner MC system.
In order for the MC client to obtain the MC Domain B authorisation access token(s), the token exchange procedure with the primary IdM service (MC Domain A) shall be used to obtain a security token that identifies the user to the partner IdM service. This security token shall be specific to the partner IdM service and signed by the primary IdM service per RFC 7515. Upon validation of the security token, the partner IdM service shall provide the access token(s) to the MC client specifically scoped for that user. The access token(s) shall provide the user with authorisation to the service(s) in the partner Identity Management Domain (MC Domain B) which may include services related to migration.
Figure 5.1.4.2-2 shows the token exchange and authentication procedure.
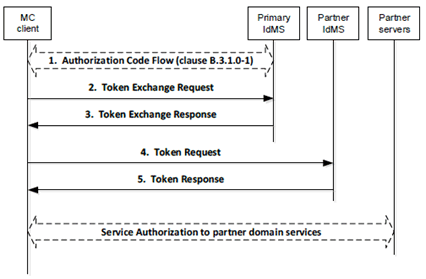
The token exchange profile for accessing the partner identity management service (steps 1-5 in Figure 5.1.4.2-2) shall consist of [45] and [46] and shall be profiled as defined in Annex B.7.
Within a single MC System with interconnected MC domains, once the MC client obtains the access token specific to the partner group service(s) (step 5 in Figure 5.1.4.2-2), the MC client shall follow the user service authorisation procedure defined in clause 5.1.3 to access the group service(s) within the partner domain.
For migration of an MC user from their primary MC domain to a partner MC domain, once the MC client obtains the access token specific to the partner MC system (step 5 in Figure 5.1.4.2-2), the MC client shall follow the user service authorisation procedure defined in clause 5.1.5.
The token exchange procedure shall be repeated for each partner identity management domain where the MC client requires access and authorisation to group service(s) within that partner MC domain or when the user migrates from their primary MC system to a partner MC system.
Annex C.2 shows the detailed flow for inter-domain MC user service authorization using the OAuth 2.0 token exchange procedure.
5.1.5 MC user migration service authentication and authorisation |R15| p. 37
When an MC user migrates from their primary MC domain to a partner MC domain, MC user migration service authentication and MC user migration service authorisation shall be carried out prior to the migrated MC user receiving services at the partner MC domain.
Figure 5.1.5-1 shows the MC user migration service authentication and authorisation procedure.
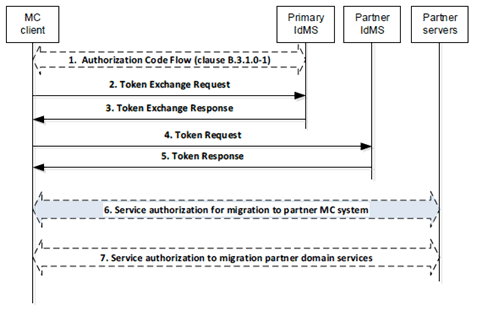
Figure 5.1.5-1: Service authorization for migration to partner MC system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1-5.
Figure 5.1.5-2 shows the 'Service authorisation for migrating to a partner MC system' procedure. Details of this procedure can be found in clause 10.6.3 of TS 23.280.
MC user migration service authentication shall be the inter-domain identity management steps 1-5 in Figure 5.1.4.2-2 of clause 5.1.4.2.
Step 6.
Upon receiving a successful Token Response message, the MC client shall initiate the 'Service authorisation for migrating to a partner MC system' procedure as shown in Figure 5.1.5-2.
Step 7.
Following successful execution of step 6, service authorisation to services in the migration partner MC system shall be performed as defined in clause 5.1.3.
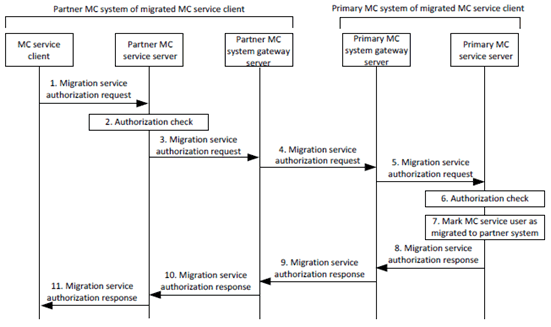
Figure 5.1.5-2: Service authorization for migration to partner MC system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The 'Migration service authorization request' message is sent by the MC service client to the partner MC service server and includes the access token obtained in step 5 of Figure 5.1.5-1.
Step 2.
The partner MC service server performs an initial authorization check to verify that the MC service user is permitted to migrate to the partner MC system. This step includes validation of the access token received in step 1 and shall be performed as defined in Annex B.11.
Step 3-11.
These steps are as defined in clause 10.6.3 of TS 23.280.