Content for TS 32.278 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Symbols
3.3 Abbreviations
4 Architecture considerations
4.1 High level monitoring event architecture
4.2 Monitoring Event offline charging architecture
4.3 Monitoring Event online charging architecture
...
...
1 Scope p. 5
The present document is part of a series of documents that specify charging functionality and charging management in GSM/UMTS/LTE networks. The GSM/UMTS/LTE core network charging architecture and principles are specified in TS 32.240, which provides an umbrella for other charging management TSs that specify:
- the content of the CDRs per domain / subsystem / service (offline charging);
- the content of real-time charging messages per domain / subsystem / service (online charging);
- the functionality of online and offline charging for those domains / subsystems / services;
- the interfaces that are used in the charging framework to transfer the charging information (i.e. CDRs or charging events).
- The common 3GPP charging architecture is specified in TS 32.240.
- The parameters, abstract syntax and encoding rules for the CDRs are specified in TS 32.298.
- A transaction based mechanism for the transfer of CDRs within the network is specified in TS 32.295.
- The file based mechanism used to transfer the CDRs from the network to the operator's billing domain (e.g. the billing system or a mediation device) is specified in TS 32.297.
- The 3GPP Diameter application that is used for Monitoring Event offline charging is specified in TS 32.299.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 32.240: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging architecture and principles".
[2] - [9] Void.
[10]
TS 32.250: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Circuit Switched (CS) domain charging".
[11]
TS 32.251: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Packet Switched (PS) domain charging".
[12] - [19] Void.
[20]
TS 32.260: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) charging".
[21] - [29]
Void.
[30]
TS 32.270: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) charging".
[31]
TS 32.271: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Location Services (LCS) charging".
[32]
TS 32.272: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Push-to-Talk over Cellular (PoC) charging".
[33]
TS 32.273: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS) charging".
[34]
TS 32.274: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Short Message Service (SMS) charging".
[35]
TS 32.275: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; MultiMedia Telephony (MMTel) charging".
[36]
TS 32.276: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Voice Call Service (VCS) charging".
[37]
TS 32.277: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Proximity-based Services (ProSe) charging".
[38] - [49] Void.
[50]
TS 32.299: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Diameter charging application".
[51]
TS 32.298: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) parameter description".
[52]
TS 32.297: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) file format and transfer".
[53]
TS 32.296: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Online Charging System (OCS) applications and interfaces".
[54]
TS 32.295: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) transfer".
[55] Void.
[56]
TS 32.293: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Proxy Function".
[57] - [99] Void.
[100]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[101]
TS 22.101: "Service aspects; Service Principles".
[102]
TS 22.115: "Service aspects; Charging and billing".
[103]
TS 23.002: "Network Architecture".
[104]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, addressing and identification".
[105]
TS 27.001: "General on Terminal Adaptation Functions (TAF) for Mobile Stations (MS)".
[106] - [199] Void.
[200] - [212] void
[213]
TS 24.002: "GSM - UMTS Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) access reference configuration".
[214] - [242] Void.
[243]
TS 23.682: "Architecture enhancements to facilitate communications with packet data networks and applications".
[244] - [299] Void.
[300]
Recommendation ITU-T D.93: "Charging and accounting in the international land mobile telephone service (provided via cellular radio systems)".
[301] - [309] Void.
[310]
Recommendation ITU-T E.164: "The international public telecommunication numbering plan".
[311] - [329] Void.
[330]
Recommendation ITU-T Q.767: "Application of the ISDN user part of CCITT signalling System No.7 for international ISDN interconnections".
[331] - [349] Void.
[350]
Recommendation ITU-T X.25: "Interface between Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) for terminals operating in the packet mode and connected to public data networks by dedicated circuit".
[351]
Recommendation ITU-T X.121: "International numbering plan for public data networks".
[352] - [399] Void.
[400]
RFC 959 (1985): "File Transfer Protocol".
[401] Void.
[402]
RFC 4006 (2005): "Diameter Credit-Control Application".
[403] - [499] Void.
[500] - [599] Void.
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 7
3.1 Definitions p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
2G / 3G:
prefixes 2G and 3G refer to functionality that supports only GSM or UMTS, respectively, e.g. 2G SGSN refers only to the GSM functionality of an SGSN.
accounting:
process of apportioning charges between the Home Environment, Serving Network and Subscriber.
application data:
information / data specific to an application other than the MMS User Agent / VASP which is intended to be transported without alteration by using MMS.
billing:
function whereby CDRs generated by the charging function(s) are transformed into bills requiring payment.
Billing Domain:
part of the operator network, which is outside the telecommunication network, that receives and processes CDR files from the core network charging functions.
CDR field categories:
the CDR fields are defined in the present document. CDR fields may be operator provisionable and are divided into the following categories:
-
- Mandatory (M): field that shall always be present in the CDR.
- Conditional (C): field that shall be present in a CDR if certain conditions are met.
- Operator Provisionable: Mandatory (OM): field that, if provisioned by the operator, shall always be present in the CDR.
Operator Provisionable: Conditional (OC): field that, if provisioned by the operator, shall be present in a CDR if certain conditions are met.
chargeable event:
activity utilizing telecommunication network resources and related services for:
charged party:
- user to user communication (e.g. a single call, a data communication session or a short message); or
- user to network communication (e.g. service profile administration); or
- inter-network communication (e.g. transferring calls, signalling, or short messages); or
- mobility (e.g. roaming or inter-system handover); and
- that the network operator may want to charge for.
user involved in a chargeable event who has to pay parts or the whole charges of the chargeable event, or a third party paying the charges caused by one or all users involved in the chargeable event, or a network operator.
charging:
function within the telecommunications network and the associated OCS/BD components whereby information related to a chargeable event is collected, formatted, transferred and evaluated in order to make it possible to determine usage for which the charged party may be billed (offline charging) or the subscriber's account balance may be debited (online charging).
Charging Data Record (CDR):
formatted collection of information about one or more chargeable event(s) (e.g. time of call set-up, duration of the call, amount of data transferred, etc) for use in billing and accounting.
charging event:
set of charging information forwarded by the CTF towards the CDF (offline charging) or towards the OCS (online charging).
charging function:
entity inside the core network domain, subsystem or service that is involved in charging for that domain, subsystem or service.
delivery report:
feedback information provided to an originator MMS User Agent by an MMS Relay/Server about the status of the delivery of an MM.
domain:
part of a communication network that provides network resources using a certain bearer technology.
GSM only:
qualifier indicating that this clause or paragraph applies only to a GSM system.
in GSM,...:
qualifier indicating that this paragraph applies only to GSM System.
in UMTS,...:
qualifier indicating that this paragraph applies only to UMTS System.
inter-system change:
change of radio access between different radio access technologies such as GSM, UMTS and LTE.
"middle tier" (charging) TS:
term used for the 3GPP charging TSs that specify the domain / subsystem / service specific, online and offline, charging functionality.
offline charging:
charging mechanism where charging information does not affect, in real-time, the service rendered.
online charging:
charging mechanism where charging information can affect, in real-time, the service rendered and therefore a direct interaction of the charging mechanism with bearer/session/service control is required.
online charging system:
the entity that performs real-time credit control. Its functionality includes transaction handling, rating, online correlation and management of subscriber account balances.
packet switched domain:
domain within GSM/UMTS/LTE in which data is transferred in packet switched mode. Corresponds to the term "GPRS".
partial CDR:
CDR that provides charging information on part of a subscriber session. A long session may be covered by several partial CDRs.
settlement:
payment of amounts resulting from the accounting process.
subscriber:
entity (associated with one or more users) that is engaged in a subscription with a service provider.
successful call:
connection that reaches the communication or data transfer phase e.g. the "answered" state for speech connections.
target UE:
UE being positioned.
tariff period:
part of one (calendar) day during which a particular tariff is applied. Defined by the time at which the period commences (the switch-over time) and the tariff to be applied after switch-over.
tariff:
set of parameters defining the network utilisation charges for the use of a particular bearer / session / service.
UMTS only:
qualifier indicating that this clause or paragraph applies only to a UMTS system.
user:
entity, not part of the 3GPP System, that uses network resources by means of a subscription.
User Equipment (UE):
device allowing a user access to network services.
3.2 Symbols p. 10
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
Bmn
Reference point for the CDR file transfer from the Monitoring Event CGF to the BD.
Ga
Reference point for CDR transfer between a CDF and the CGF.
Ns
Reference point between the SCEF and the RCAF.
Rf
Offline charging reference point between a MME/SGSN/IWK-SCEF and the CDF.
S6t
Reference point between the SCEF and the HSS.
T6a
Reference point between the SCEF and the s erving MME.
T6ai
Reference point between the IWK-SCEF and the serving MME.
T6b
Reference point between the SCEF and the serving SGSN.
T6bi
Reference point between the IWK-SCEF and the serving SGSN.
T7
Reference point between the IWK-SCEF and the serving SCEF.
3.3 Abbreviations p. 10
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply.
An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
3G
3rd Generation
3GPP
3rd Generation Partnership Project
ACA
Accounting Answer
ACR
Accounting Request
AMF
Account Balance Management Function
APN
Access Point Name
AVP
Attribute Value Pair
BD
Billing Domain
BS
Billing System
CCF
Charging Collection Function
CDF
Charging Data Function
CDR
Charging Data Record
CG
Charging Gateway
CGF
Charging Gateway Function
CRF
Charging Rules Function
CTF
Charging Trigger Function
DCCA
Diameter Credit Control Application
EBCF
Event Based Charging Function
ECUR
Event Charging with Unit Reservation
FCI
Furnish Charging Information
FQPC
Fully Qualified Partial CDR
FTAM
File Transfer, Access and Management
G-CDR
GGSN (PDP context) generated - CDR
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service
GSM
Global System for Mobile communication
HLR
Home Location Register
HPLMN
Home PLMN
HSS
Home Subscriber Server
IEC
Immediate Event Charging
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force
IMEI
International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
IP
Internet Protocol
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
IWK-SCEF
Interworking SCEF
M-CDR
Mobility management generated - Charging Data Record
MECN
Monitoring Event Charging Node (MME, SGSN, IWK-SCEF)
MNC
Mobile Network Code (part of IMSI)
MSISDN
Mobile Station ISDN number
NE
Network Element
NI
Network Identifier (part of the APN)
OCF
Online Charging Function
OCS
Online Charging System
OMA
Open Mobile Alliance
PLMN
Public Land Mobile Network
PMD
Pseudonym Mediation Device functionality
PS
Packet-Switched
PSPDN
Packet-Switched Public Data Network
PSTN
Public Switched Telephony Network
QoS
Quality of Service
RAB
Radio Access Bearer
RAN
Radio Access Network
RF
Rating Function
SBCF
Session Based Charging Function
SCCP
Signalling Connection Control Part
S-CDR
SGSN (PDP context) generated - CDR
SCEF
Service Capability Exposure Function
SCUR
Session Charging with Unit Reservation
SGSN
Serving GPRS Support Node
TAP
Transferred Account Procedure
TDP
Trigger Detection Point
TPF
Traffic Plane Function
TR
Technical Report
TS
Technical Specification
TV
Type, Value
UA
User Agent
UE
User Equipment
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
UTRAN
Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
VLR
Visitor Location Register
VPLMN
Visited PLMN
4 Architecture considerations p. 11
4.1 High level monitoring event architecture p. 11
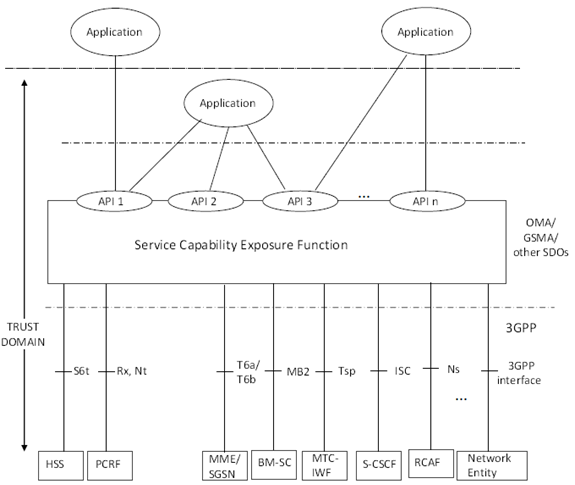
Figure 4.1.1 shows the overall architecture for Service Capability Exposure which enables the 3GPP network to securely expose its services and capabilities provided by 3GPP network interfaces to external 3rd party service provider applications, which includes Monitoring Event functionality, as described in TS 23.682.
For roaming case, the Interworking SCEF (IWK-SCEF) is optionally deployed and located in the VPLMN, as described in Figure 4.1.2.
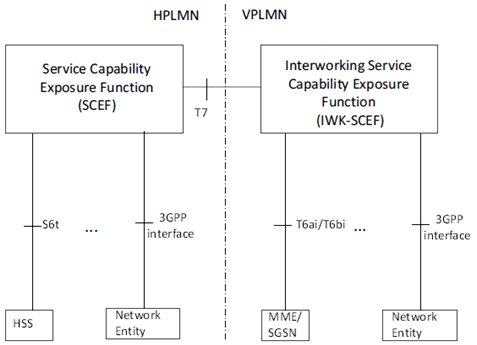
Figure 4.1.2: 3GPP roaming Architecture for Service Capability Exposure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2 Monitoring Event offline charging architecture p. 13
As described in TS 32.240, the CTF (an integrated component in each charging relevant NE) generates charging events and forwards them to the CDF. The CDF, in turn, generates CDRs which are then transferred to the CGF.
Finally, the CGF creates CDR files and forwards them to the BD.
For offline charging the following Monitoring Event Charging Nodes (MECN), functioning as the CTF, may generate accounting metrics sets for Monitoring Event CDRs:
- the MME, to record Monitoring Events;
- the SGSN, to record Monitoring Events;
- the IWK-SCEF, to record Monitoring Events.
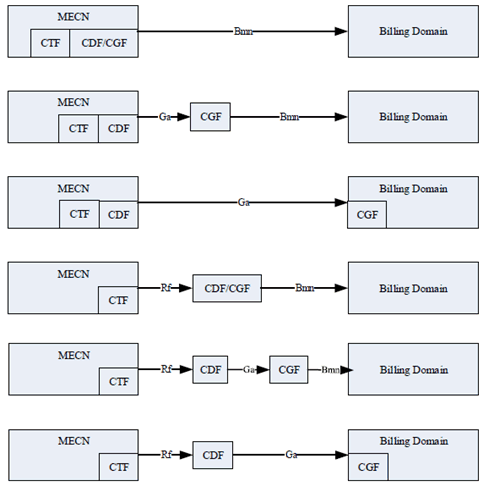
It is mandatory to support at least one of the Rf, Ga or Bmn interfaces from the MECN as described in the present document.
4.3 Monitoring Event online charging architecture p. 14
Not specified in the present document.