TS 32.293
Charging Management –
Proxy Function
V18.0.0 (PDF)
2024/03 19 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 18 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 18 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 18 p.
V14.0.0
2017/03 18 p.
V13.0.0
2016/01 18 p.
V12.0.1
2014/09 18 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Törnkvist, Robert
Ericsson LM
Content for TS 32.293 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
4 Required functionality of the Proxy Function
5 Architectural concept
6 Functionalities and message flows
7 Definition of charging information
$ Change History
1 Scope p. 5
The present document is part of a series of documents that specify charging functionality and charging management in GSM/UMTS networks. The GSM/UMTS core network charging architecture and principles are specified in TS 32.240, which provides an umbrella for other charging management TSs that specify:
- the content of the Charging Data Records (CDRs) per domain / subsystem / service (offline charging);
- the content of real-time charging messages per domain / subsystem / service (online charging);
- the functionality of online and offline charging for those domains / subsystems / services;
- the interfaces that are used in the charging framework to transfer the charging information (i.e. CDRs or charging events).
- The common 3GPP charging architecture is specified in TS 32.240;
- Voice Call Service (VCS) charging is specified in TS 32.276.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 32.240: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Architecture and Principles".
[2]-[9] Void.
[10]
TS 32.250: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Circuit Switched (CS) domain charging".
[11]-[29] Void.
[30]
TS 32.270: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) charging".
[31]
TS 32.271: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Location Services (LCS) charging".
[32]
TS 32.272: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Push-to-Talk over Cellular (PoC) charging".
[33]
TS 32.273: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS) charging".
[34]
TS 32.274: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Short Message Service (SMS) charging".
[35]
TS 32.275: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; MultiMedia Telephony (MMTel) charging".
[36]
TS 32.276: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Voice Call Service Charging".
[37]-[49] Void.
[50]
TS 32.299: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Diameter charging application".
[51]
TS 32.298: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) parameter description".
[52]
TS 32.297: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) file format and transfer".
[53]
TS 32.296: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Online Charging System (OCS) applications and interfaces".
[54]
TS 32.295: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; Charging Data Record (CDR) transfer".
[55]-[99] Void.
[100]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[101] Void.
[102] Void.
[103]
TS 23.002: "Network Architecture".
[104]-[199] Void.
[200]-[206] Void.
[207]
TS 22.078: "Customized Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL); Service description; Stage 1".
[208]-[211] Void.
[212]
TS 23.078: "Customized Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase X; Stage 2".
[213]-[217] Void.
[218]
TS 29.078: "Customized Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase X; CAMEL Application Part (CAP) specification".
[219]-[297] Void.
[298]
EU Roaming regulation III; Structural Solutions; High Level Technical Specifications
[299]
EU Roaming regulation III; Interface & Protocol; Detailed Technical Specifications
[300]-[399] Void.
[400]-[499] Void.
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 8
3.1 Definitions p. 8
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
alternative roaming provider:
A roaming provider different from the domestic provider.
CAMEL:
network feature that provides the mechanisms to support operator specific services even when roaming outside HPLMN.
CAMEL subscription information:
identifies a subscriber as having CAMEL services.
chargeable event:
activity utilizing telecommunication network resources and related services for:
charged party:
- user to user communication (e.g. a single call, a data communication session or a short message); or
- user to network communication (e.g. service profile administration); or
- inter-network communication (e.g. transferring calls, signalling, or short messages); or
- mobility (e.g. roaming or inter-system handover); and
- that the network operator may want to charge for.
user involved in a chargeable event who has to pay parts or the whole charges of the chargeable event, or a third party paying the charges caused by one or all users involved in the chargeable event, or a network operator.
charging:
function within the telecommunications network and the associated OCS/BD components whereby information related to a chargeable event is collected, formatted, transferred and evaluated in order to make it possible to determine usage for which the charged party may be billed (offline charging) or the subscriber's account balance may be debited (online charging).
charging event:
set of charging information forwarded by the CTF towards the CDF (offline charging) or towards the OCS (online charging). Each charging event matches exactly one chargeable event.
charging function:
entity inside the core network domain, subsystem or service that is involved in charging for that domain, subsystem or service.
Circuit Switched (CS) domain:
domain within GSM / UMTS in which information is transferred in CS mode.
credit control:
mechanism which directly interacts in real-time with an account and controls or monitors the charges, related to the service usage. Credit control is a process of: checking if credit is available, credit reservation, deduction of credit from the end user account when service is completed and refunding of reserved credit not used.
domain:
part of a communication network that provides network resources using a certain bearer technology.
domestic service provider:
An undertaking that provides a roaming customer with domestic mobile communications services, either a Mobile Network Operator or a Mobile Virtual Network Operator.
GSM only:
qualifier indicating that this clause or paragraph applies only to a GSM system. For multi-system cases this is determined by the current serving radio access network.
in GSM,...:
qualifier indicating that this paragraph applies only to GSM System.
in UMTS,...:
qualifier indicating that this paragraph applies only to UMTS System.
"middle tier" (charging) TS:
term used for the 3GPP charging TSs that specify the domain / subsystem / service specific, online and offline, charging functionality. These are all the TSs in the numbering range from TS 32.250 to TS 32.279, e.g. TS 32.250 for the CS domain, or TS 32.270 for the MMS service. Currently, there is only one "tier 1" TS in 3GPP, which is TS 32.240 that specifies the charging architecture and principles. Finally, there are a number of top tier TSs in the 32.29x numbering range ([50] ff) that specify common charging aspects such as parameter definitions, encoding rules, the common billing domain interface or common charging applications.
online charging:
charging mechanism where charging information can affect, in real-time, the service rendered and therefore a direct interaction of the charging mechanism with bearer/session/service control is required.
Online Charging System:
the entity that performs real-time credit control. Its functionality includes transaction handling, rating, online correlation and management of subscriber account balances.
real-time:
real-time charging and billing information is to be generated, processed, and transported to a desired conclusion in less than 1 second.
roaming customer:
a customer of a roaming provider of regulated roaming services, by means of a terrestrial public mobile communications network situated in the Union, whose contract or arrangement with that roaming provider permits Union-wide roaming.successful call: connection that reaches the communication or data transfer phase e.g. the "answered" state for speech connections. All other connection attempts are regarded as unsuccessful.
tariff period:
part of one (calendar) day during which a particular tariff is applied. Defined by the time at which the period commences (the switch-over time) and the tariff to be applied after switch-over.
tariff:
set of parameters defining the network utilisation charges for the use of a particular bearer / session / service.
3.2 Symbols p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
CAP
Reference point for CAMEL between a network element with integrated SSF and the OCS.
Ro
Online charging reference point between a Proxy Function and the OCS.
3.3 Abbreviations p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
3G
3rd Generation
3GPP
3rd Generation Partnership Project
ARP
Alternative Roaming Provider
CAMEL
Customized Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic
CAP
CAMEL Application Part
CCA
Credit Control Answer
CCR
Credit Control Request
CGF
Charging Gateway Function
CI
Cell Identity
CS
Circuit Switched
CSE
CAMEL Service Environment
CTF
Charging Trigger Function
DCCA
Diameter Credit Control Application
DSP
Domestic Service Provider
EU
European Union
FCI
Furnish Charging Information
GMSC
Gateway MSC
gsmSCF
GSM Service Control Function
gsmSSF
GSM Service Switching Function
GSM
Global System for Mobile communication
HLR
Home Location Register
HPLMN
Home PLMN
ICA
Initiate Call Attempt
IMEI
International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
ITU-T
International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunications standardization sector
JIP
Jurisdiction Information Parameter
LAC
Location Area Code
LRN
Location Routing Number
MAP
Mobile Application Part
MCC
Mobile Country Code (part of IMSI)
MLC
Mobile Location Center
MNC
Mobile Network Code (part of IMSI)
MO
Mobile Originated
MOC
Mobile Originated Call (attempt)
MO-LR
Mobile Originated Location Request
MS
Mobile Station
MSC
Mobile services Switching Centre
MSISDN
Mobile Station ISDN number
MSRN
Mobile Station Roaming Number
MT
Mobile Terminated
MTC
Mobile Terminated Call (attempt)
MT-LR
Mobile Terminated Location Request
NE
Network Element
NI-LR
Network Induced Location Request
NP
Number Portability
NPDB
Number Portability Data Base
OCF
Online Charging Function
OCS
Online Charging System
O-CSI
Originating CAMEL Subscription Information
PLMN
Public Land Mobile Network
PSTN
Public Switched Telephony Network
RAC
Routing Area Code
RAN
Radio Access Network
RNC
Radio Network Controller
SAC
Service Area Code
SCI
Subscriber Controlled Input or Send Charging Information
SRF
Specialised Resource Function
SS7
Signalling System No. 7
SSF
Service Switching Function
T-CSI
Terminating CAMEL Subscription Information
TDP
Trigger Detection Point
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
UTRAN
Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
VAS
Value Added Service
VCC
Voice Call Continuity
VCS
Voice Call Service
VLR
Visitor Location Register
VMSC
Visited MSC
VPLMN
Visited PLMN
VT-CSI
Visited Terminating CAMEL Subscription Information
4 Required functionality of the Proxy Function p. 11
5 Architectural concept p. 11
5.1 Architecture reference model for Alternative Roaming Provider (ARP) p. 11
5.1.1 Proxy Function for Voice Call Service p. 11
Figure 5.1.1.1 shows the Proxy Function for voice control in the framework of the overall Single IMSI architecture for EU Roaming as defined in the high-level technical specification [298].
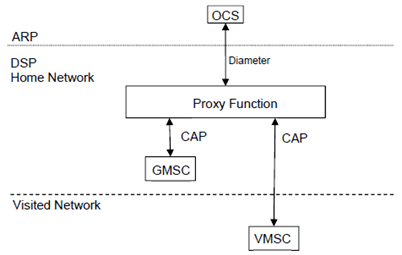
Figure 5.1.1.1: The Proxy Function architecture for Voice Call Service
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The Proxy Function entails a functional entity in the DSP's network that handles CAMEL and Diameter interworking.
The signaling between the CS domain elements and the Proxy Function is implemented by CAMEL techniques as described in TS 23.078 and TS 29.078. The signalling between the ARP OCS and the Proxy Function for online charging is implemented as specified in TS 32.276.
6 Functionalities and message flows p. 12
6.1 Reference point required functionality p. 12
6.2 Message flows p. 12
6.2.1 Mobile Originated Call p. 12
This message flow is for illustrative purpose and depicts a Mobile Originated Call in which charging starts at call attempt.The handling of regulated user, routing and call control as defined in EU Roaming regulation III Interface & Protocol Detailed Technical specifications [299] are out of the 32 series charging specifications.
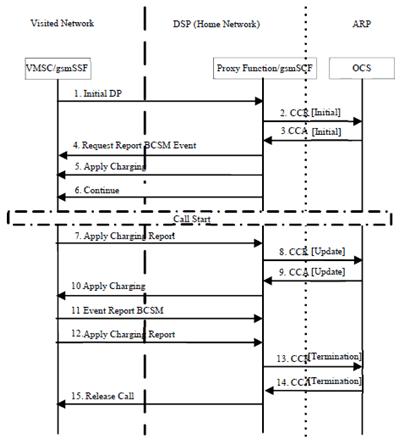
Figure 6.2.1.1: Mobile Originated Call When the ARP subscriber is roaming
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The Proxy Function/ gsmSCF receives the Initial DP of the CAP dialogue that is initiated from the VMSC/gsmSSF in the VPLMN's network.
Step 2.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF initiates a Diameter session towards ARP OCS with CCR [Intial] to request the quotas for voice call service.
Step 3.
ARP OCS sends the CCA [Initial] with the granted quotas, such as the duration of a call 5 minutes.
Step 4.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends Request Report BCSM Event to VMSC/gsmSSF to monitor for a call-related event, and then sends a notification back to the gsmSCF.
Step 5.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF instructs the VMSC/gsmSSF to apply charging mechanisms to control the call duration.
Step 6.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF requests the VMSC/gsmSSF to proceed with call processing.
Step 7.
The VMSC/gsmSSF reports to the gsmSCF the information requested in the Apply Charging.
Step 8.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends CCR [Update] to request the quotas.
Step 9.
ARP OCS sends the CCA [Update] with the granted quatos again, such as more 5 minutes fot the duration of a call.
Step 10.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF instructs the VMSC/gsmSSF to apply charging mechanisms to control the call duration.
Step 11.
The ARP User as the calling party end the call. The VMSC/gsmSSF sends the Event Report BCSM.
Step 12.
The VMSC/gsmSSF reports to the gsmSCF the information requested in the Apply Charging.
Step 13.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends the CCR [Termination] to ARP OCS.
Step 14.
The ARP OCS answers the quest with CCA [Termination].
Step 15.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF tears down the call for all parties involved in the call.
6.2.2 Mobile Terminated Call p. 13
This message flow is for illustrative purpose and depicts a Mobile Terminated call at DSP in which charging starts at call attempt. CAMEL control of Mobile Terminated calls may be done through interaction with the GMSC or through interaction with the VMSC.The MT call based VMSC is out of consideration as defined in EU Roaming regulation III Interface & Protocol Detailed Technical specifications [299]. The handling of regulated user, routing and call control as defined in EU Roaming regulation III Interface & Protocol Detailed Technical specifications [299] are also out of scope of this specification.
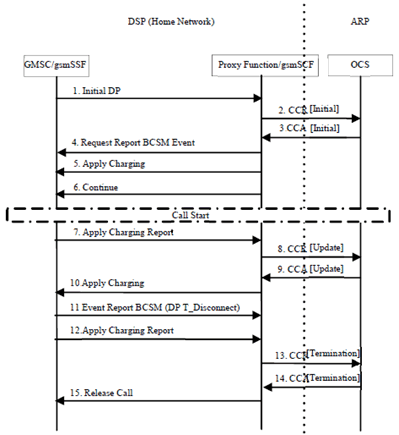
Figure 6.2.2.1: Mobile Terminated Call When the ARP subscriber is roaming
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The Proxy Function/ gsmSCF receive the Initial DP of the CAP dialogue that is initiated from the GMSC/gsmSSF in the Home network.
Step 2.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF initiates a Diameter session towards ARP OCS with CCR [Initial] to request the quotas for voice call service of called party.
Step 3.
ARP OCS sends the CCA [Initial] with the granted quotas, such as the duration of a call 5 minutes.
Step 4.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends Request Report BCSM Event to GMSC/gsmSSF to monitor for a call-related event, and then sends a notification back to the gsmSCF.
Step 5.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF instructs the GMSC/gsmSSF to apply charging mechanisms to control the call duration.
Step 6.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF requests the GMSC/gsmSSF to proceed with call processing.
Step 7.
The GMSC/gsmSSF reports to the gsmSCF the information requested in the Apply Charging.
Step 8.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends CCR [Update] to request the quotas.
Step 9.
ARP OCS sends CCA [Update] with the granted quatos, such as more 5 minutes fot the duration of a call.
Step 10.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF instructs the GMSC/gsmSSF to apply charging mechanisms to control the call duration.
Step 11.
The ARP User as the called party end the call. The GMSC/gsmSSF sends the Event Report BCSM with DP-T-Disconnect.
Step 12.
The GMSC/gsmSSF reports to the gsmSCF the information requested in the Apply Charging.
Step 13.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF sends the CCR [Termination] to ARP OCS.
Step 14.
The ARP OCS answers the request with CCA [Termination].
Step 15.
The Proxy Function/gsmSCF tears down the call for all parties involved in the call.
6.2.3 Mobile Forwarded Call p. 15
For conditionally and unconfitionally call forwarding, the call in different phase would be handled the same as the normal MO call or MT call message flows. For example, the charging provision for B is as normal MT in the call leg between calling-party (A) and the called-party (B), the charging provision for B is as normal MO in the call leg between called-party (B) and the forwarded-to-party(C). In order to avoid the duplication, the detailed message flows of Mobile Forwarded call are not present here.
7 Definition of charging information p. 15
Void