Content for TS 23.548 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.3
5…
6…
6.2.2.3…
6.2.3…
6.2.3.2.3…
6.2.3.2.5…
6.2.3.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6
6.7…
6.7.2.4…
6.7.2.6…
6.7.3…
6.8…
6.10…
7…
A
B…
F…
6.7 Support of the local traffic routing in VPLMN for Home Routed PDU Session for roaming (HR-SBO)
6.7.1 General
6.7.2 Procedure
6.7.2.1 General
6.7.2.2 PDU Session establishment for supporting HR-SBO in VPLMN
6.7.2.3 EAS Discovery Procedure with V-EASDF for HR-SBO
...
...
6.7 Support of the local traffic routing in VPLMN for Home Routed PDU Session for roaming (HR-SBO) |R18| p. 54
6.7.1 General p. 54
When roaming, the UE establishes a Home Routed Session that is capable of supporting session breakout in V-PLMN based on the subscription. In this scenario, the Home PLMN and Visited PLMN have an agreement on the support of the local traffic routing (i.e. session breakout performed by V-SMF also called HR-SBO) in VPLMN for the home routed session.
After establishing the HR-SBO PDU Session, the UE can access EAS deployed in EHE in VPLMN while the UE can also access the data network in the Home PLMN.
The reference architecture supporting this scenario is depicted in Figure 4.2-5 in clause 4.2.
6.7.2 Procedure p. 54
6.7.2.1 General p. 54
This clause describes the authorization procedure of the local traffic offloading using HR PDU Session and EAS discovery procedure supporting HR-SBO.
6.7.2.2 PDU Session establishment for supporting HR-SBO in VPLMN p. 55
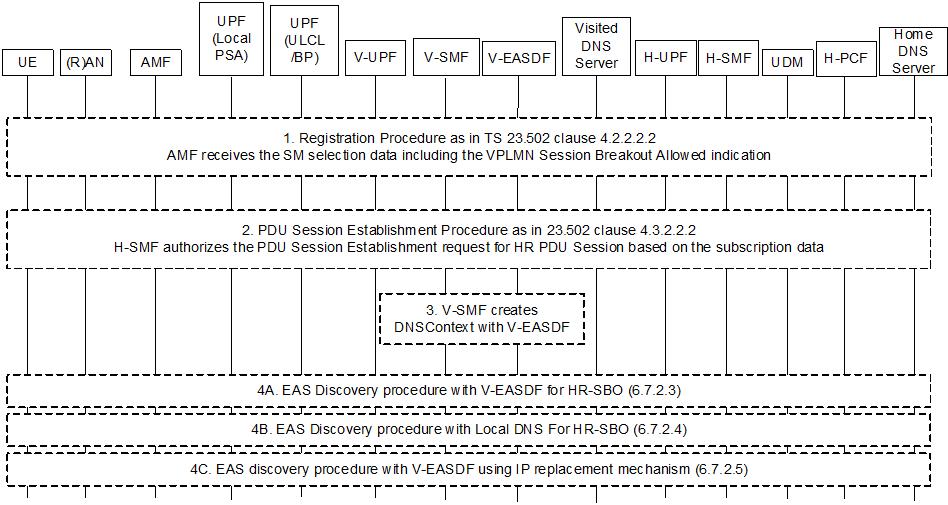
Step 1.
During the Registration procedure, the AMF receives the HR-SBO allowed indication per DNN/S-NSNAI from the UDM in the step 14b of the procedure in the clause 4.2.2.2.2 of TS 23.502.
Step 2.
During the PDU Session Establishment procedure for Home-routed roaming as in clause 4.3.2.2.2 of TS 23.502, if the UE is roaming and if the AMF had received in SMF Selection Subscription data from UDM the HR-SBO allowed indication for the DNN/S-NSSAI in the step 1, the AMF selects a V-SMF supporting HR-SBO and sends an HR-SBO allowed indication to the V-SMF in the step 2 and the step3a of the procedure in Figure 4.3.2.2.2-1 in clause 4.3.2.2.2 of TS 23.502.
If the V-SMF supporting the HR-SBO receives the HR-SBO allowed indication from AMF, the V-SMF may:
PDUSession_Create Response in the step 13 of the procedure in Figure 4.3.2.2.2-1 in clause 4.3.2.2.2 of TS 23.502 with the following information:
Step 3.
- select UL CL/BP UPF and L-PSA UPF based on UE location information and this indication in the step 4 of the Figure 4.3.2.2.2-1 of TS 23.502.
- select a V-EASDF;
-
obtain the V-EASDF IP address based on local configuration, or invoke Neasdf_
DNSContext_ Request including the DNN, S-NSSAI, HPLMN ID and the UE IP address set to unspecified address or to a mapped address as specified in clause 7.1.2.2 to obtain the V-EASDF IP address;Create - may obtain V-EASDF DNS security information based on local configuration or via interaction with EASDF; and
-
send the request for the establishment of the PDU Session supporting HR-SBO in VPLMN and optionally send the IP address and (if exists) DNS security information of V-EASDF/Local DNS Server/Resolver to the H-SMF in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request in the step 6 of the procedure in Figure 4.3.2.2.2-1 in clause 4.3.2.2.2 of TS 23.502.Create
-
optionally, VPLMN Specific Offloading Information that may include FQDN range, IP range, session AMBR for the local part of DN and charging policy.
The VPLMN specific Offloading Information may refer to either allowed or not allowed traffic for HR-SBO (the latter is being used when the HPLMN would like to ensure that certain traffic are not allowed for HR-SBO). The VPLMN Specific Offloading Information for the allowed and not allowed traffic should be mutually exclusive, i.e., either a list of allowed or a list of not allowed traffic descriptors should be sent, but not both. The VPLMN Specific Offloading Policy can be configured in the H-SMF and tagged with Offload Identifier(s), and which VPLMN Specific Offloading Information to be sent to V-SMF can be indicated by these Offload Identifier(s) received from H-PCF.
H-SMF may send the Offload Identifier(s) alone or together with the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information:
- If the given V-SMF has already received the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information corresponding to certain Offload Identifier(s), this could be indicated to the H-SMF in any subsequent request to another HR-PDU Session from the same V-SMF, and the H-SMF will in this case send only the Offload Identifier(s) as a response;
- If the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information for a given Offload Identifier is changed, for each V-SMF using the Offload Identifier, the H-SMF chooses one existing HR-SBO PDU Session using the Offload Identifier to update VPLMN Specific Offloading Information and corresponding Offload Identifier to the V-SMF via PDU Session Modification procedure as described in clause 4.3.3.3 of TS 23.502;
- During PDU Session Release procedure as described in clause 4.3.4.3 of TS 23.502, if the PDU Session is the last HR-SBO PDU Session using a given Offload Identifier on the V-SMF, the V-SMF may remove the Offload Identifier and corresponding VPLMN Specific Offloading Information based on roaming agreements.
- the V-EASDF IP address (corresponding to clause 6.7.2.3) or Local DNS Server/Resolver IP address (corresponding to clause 6.7.2.4) or DNS server IP address of HPLMN (corresponding to clause 6.7.2.5) as DNS server address to be sent to the UE via PCO; and
- the DNS security information of V-EASDF/Local DNS Server/Resolver to be sent to the UE via PCO, if the UE indicate DNS server security information indicator in PDU Session Establishment Request and if supported in V-EASDF/Local DNS Server/Resolver (see TS 24.501 and TS 33.501);
- optionally, the DNS server address provided by HPLMN to be used for DNS requests related with traffic not to be subject to HR-SBO, including to configure V-EASDF corresponding to clause 6.7.2.3, or configure the UPF in VPLMN to perform IP replacement as described in clause 6.7.2.5;
- optionally, the HPLMN address information (e.g. H-UPF IP address on N6) to be used by V-EASDF to build EDNS Client Subnet option for target FQDN of the DNS query which is not authorized for HR-SBO as described in clause 6.7.2.3;
- the HR-SBO authorization result (i.e. whether HR-SBO request is authorized or not).
The V-SMF configures the V-EASDF with the DNS handling rules using the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information received from H-SMF or corresponding to Offload Identifier(s) received from H-SMF.
The V-SMF optionally configures the V-EASDF with the DNS server address provided by the HPLMN as default DNS server (corresponding to clause 6.7.2.3), after the step 13 of the procedure in Figure 4.3.2.2.2-1 in clause 4.3.2.2.2 of TS 23.502 if they are received from H-SMF in the step 2. If V-SMF has not received the DNS server address provided by HPLMN from H-SMF in step 2, a default DNS server may be configured to V-EASDF.
If HPLMN address information is received, the V-SMF may also configure the V-EASDF to build EDNS Client Subnet option based on this HPLMN address information for target FQDN of DNS query which is not authorized for HR-SBO.
If the V-SMF has interacted with the V-EASDF in step 2, then the V-SMF invokes Neasdf_DNSContext_Update Request including UE IP address to complete the configuration of the context in the V-EASDF.
The V-SMF configures the UL CL UPF and PSA UPF selected in the step 2 to forward DNS messages to V-EASDF.
If the Authorized DL Session AMBR for Offloading is provided from the H-SMF, the V-SMF configures the Authorized DL Session AMBR for Offloading on the UL CL UPF in the VPLMN and additionally local PSA(s) terminating the N6 interface toward the local part of DN in the VPLMN.
At N4 session establishment for a PDU Session working in HR SBO mode, the SMF in VPLMN provides to any UPF in VPLMN acting as (local) PSA for that PDU Session and capable of enforcing NAT on N6 traffic: the HPLMN ID of UE, andthe DNN/S-NSSAI of the PDU Session in HPLMN for the PDU Session.
Step 4A.
EAS Discovery procedure with V-EASDF is performed as described in clause 6.7.2.3.
Step 4B.
EAS Discovery procedure with Local DNS Server/Resolver is performed as described in clause 6.7.2.4.
Step 4C.
EAS discovery procedure with V-EASDF using IP replacement mechanism as described in clause 6.7.2.5.
6.7.2.3 EAS Discovery Procedure with V-EASDF for HR-SBO p. 58
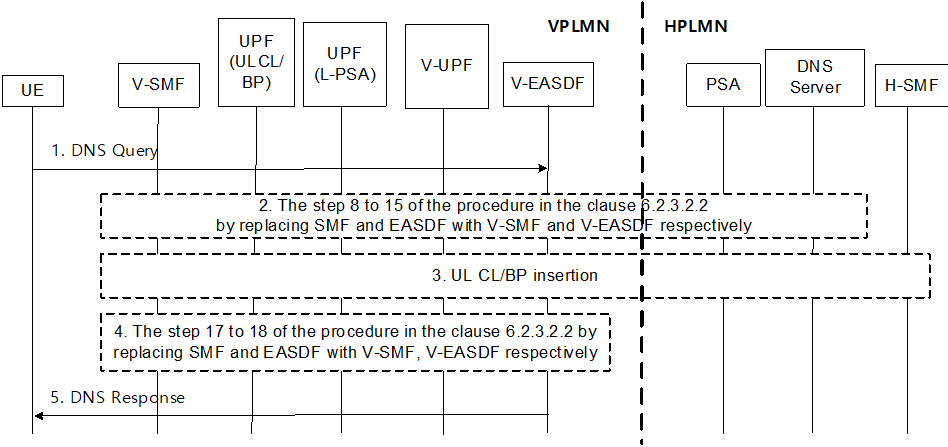
Step 1.
The rest of the procedure assumes the target FQDN of the DNS query is part of the FQDN authorized by the H-SMF in step 2 of clause 6.7.2.2.
The DNS query sent by the UE reaches the UL CL UPF in VPLMN selected in step 2 of clause 6.7.2.2. The UL CL UPF forwards it to Local PSA UPF then V-EASDF, or to H-UPF as described below.
If the target FQDN of the DNS query is not part of the FQDN authorized by the H-SMF in step 2 of clause 6.7.2.2, the following a) or b) may be performed:
- Based on SMF instruction in step 3 of clause 6.7.2.2, the V-EASDF proceeds to step 12 of clause 6.2.3.2.2 where it sends the DNS query which may include the HPLMN address information as the EDNS Client Subnet option. The DNS query is sent to the DNS server address according to the DNS message handling rules provided by the V-SMF or to the default DNS server configured in the V-EASDF. Upon receiving the DNS response, the procedure proceeds immediately to step 5.
- The UL CL/BP UPF sends the DNS query to the DNS server address provided by HPLMN via V-UPF (if exists) and H-UPF (through N9), by modifying the packet's destination IP address (corresponding to V-EASDF) to the DNS server address provided by HPLMN on UL CL or H-UPF. For the corresponding DNS response received by H-UPF, the H-UPF or UL CL modifies the packets' source IP address to that of the V-EASDF. This assumes that the UL CL is able to detect FQDN(s) in traffic sent to the IP address of the EASDF. It is thus incompatible with usage of DoT (DNS over TLS) or DoH to protect the DNS traffic exchanged between the UE and the PLMN. If the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information only includes IP range, the V-SMF can configure the V-EASDF to resolve all DNS queries using a VPLMN address (e.g. an IP address associated with the L-PSA UPF in the VPLMN) as EDNS Client Subnet option.
Step 2.
The steps 8 to 15 of the procedure in the clause 6.2.3.2.2 by replacing SMF and EASDF with V-SMF and V-EASDF respectively.
If VPLMN Specific Offloading Information does not include FQDN range and the EAS IP address of the DNS response is not part of the IP range(s) authorized in step 2 of clause 6.7.2.2, the following may be performed:
Step 3.
- If the V-EASDF is not configured with the DNS server address provided by the HPLMN as default DNS server, The V-SMF indicates the V-EASDF to construct and to send another DNS query with the same FQDN and the HPLMN address information as the EDNS Client Subnet option, to the DNS server address as described in step 1) bullet a). Otherwise V-SMF indicates the V-EASDF to construct and send another DNS query with the same FQDN to the DNS server provided by HPLMN.
The V-SMF selects UL CL/BP and local PSA in VPLMN based on the V-EASDF notification, EAS Deployment Information in the VPLMN, VPLMN Specific Offloading Information and UE location. The V-SMF may perform insertion or change of UL CL/BP and local PSA in VPLMN.
The V-SMF configures the UL CL/BP and local PSA for the traffic to be offloaded to the local part of DN based on the VPLMN Specific Offloading Information received from H-SMF.
If the Authorized DL Session AMBR for Offloading is provided from the H-SMF, the V-SMF configures the Authorized DL Session AMBR for Offloading on the UL CL/BP in the VPLMN and additionally the local PSA(s) terminating the N6 interface toward the local part of DN in the VPLMN.
In the case of UL CL, the V-SMF configures the traffic detection rules and traffic routing rules on the UL CL UPF based on the EAS Deployment Information and the EAS addresses included in VPLMN Specific Offloading Information.
If there is no other V-UPF between the selected UL CL/BP in this step and H-UPF, the V-SMF sets up user plane between this UL CL/BP and H-UPF via the interaction with H-SMF. Otherwise, the V-SMF sets up user plane between this ULCL/BP and the existing V-UPF.
The V-SMF sets up user plane between the selected UL CL/BP in this step and RAN (if no other V-UPF exists between RAN and this UL CL/BP) or the V-UPF (if exists between this UL CL/BP and RAN).
If the EAS IP address is not part of the IP address authorized by H-SMF, the UL CL/BP V-UPF is instructed by V-SMF to send the packet from UE to the H-UPF.
Step 4.
The steps 17 to 18 of the procedure in clause 6.2.3.2.2 by replacing SMF and EASDF with V-SMF and V-EASDF respectively.
Step 5.
V-EASDF sends the DNS Response to the UE.