Content for TS 23.548 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.3
5…
6…
6.2.2.3…
6.2.3…
6.2.3.2.3…
6.2.3.2.5…
6.2.3.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6
6.7…
6.7.2.4…
6.7.2.6…
6.7.3…
6.8…
6.10…
7…
A
B…
F…
6.2.3.2.5 Common EAS discovery with EASDF for a set of UEs
6.2.3.2.6 EAS discovery corresponding to Common DNAI with EASDF for a set of UEs
6.2.3.2.7 Coordination among SMFs for Common EAS/DNAI determination
...
...
6.2.3.2.5 Common EAS discovery with EASDF for a set of UEs |R18| p. 29
The following is the procedure for common EAS discovery for a set of UEs accessing the same application. Different UEs can be served by different SMFs.
The common EAS IP address for the set of UEs may either be provided by AF or determined by 5GC. AF may provide the common EAS IP via AF Traffic influence procedure as defined in clause 4.3.6.2 of TS 23.502, for this purpose, AF may determine the common EAS IP address based on candidate DNAI(s) reported by SMF as described in clause 4.3.6.3 of TS 23.502. Alternatively, if AF did not provide a common EAS IP address, the common EAS IP address may be determined by NEF as defined in clause 6.2.3.2.7 and is stored in UDR as part of AF traffic influence request information.
Step 1.
The AF request in step 1 of Figure 4.3.6.2-1 in TS 23.502 is used to request selecting the common EAS for a set of UEs accessing the application as identified in the AF Request.
AF may use External/Internal Group ID(s) or a list of UEs or any UE accessing the combination of DNN, S-NSSAI and DNAI as Target UE Identifier(s) and additionally Spatial Validity Condition to identify the set of UEs for correlated selection of common EAS.
The following information may be included in AF request as defined in clause 5.6.7.1 of TS 23.501:
Step 2.
- An EAS Correlation indication may be provided for indication of selecting the same EAS for the set of UEs accessing the same application.
- A Traffic Correlation ID may be provided for identification of the set of UEs accessing the application identified by the Traffic Description in AF request.
- A Common EAS IP address to be accessed by the set of UEs may be included in AF request, if it is determined by AF.
- FQDN(s) may be included which is corresponding to the application traffic identified by Traffic Description in AF request.
- Spatial Validity Condition could be provided for limiting the location of the UEs, and also "any UE" or a UE list or group ID can be provided for defining the set of UEs accessing the same EAS.
Based on steps 1-19 in Figure 6.2.3.2.2-1, with the following updates:
In step 9:
If FQDN in Neasdf_DNSContext_Notify Request is corresponding to the application indicated in PCC rule, e.g. the FQDN is included in the FQDN(s) in the PCC rule and if EAS Correlation indication is set, SMF determines the UE belongs to the set of UEs identified by Traffic Correlation ID and accessing the application and determines the UE connects to the common EAS for the set of UEs. If FQDN(s) is included in PCC rule, the SMF can use the FQDN(s) in PCC rule and the FQDN in Neasdf_DNSContext_Notify Request to match the FQDN with the PCC rule, i.e. the matched PCC rule includes the FQDN(s) containing the FQDN in Neasdf_DNSContext_Notify Request.
If the common EAS is not present in PCC rule or SMF decides to trigger the EAS discovery procedure to select a new EAS for the set of UEs (e.g. due to UE mobility):
Steps 10-15 are used for discovering of common EAS. After step 15, the procedure defined in clause 6.2.3.2.7 may be performed for common EAS IP coordination.
Else, if the common EAS is available (e.g. common EAS IP address is presented in PCC rule) and to be used for the set of UEs:
Steps 10-15 are skipped.
In step 16:
SMF may determine the DNAI based on the common EAS.
In step 17:
SMF sends DNS message handling rule including IP address for the common EAS and the Forwarding Action "Respond directly to the DNS request" for instructing EASDF to return the Common EAS IP address in a DNS response to UE directly.
In step 19:
If received IP address of the common EAS and instructed to respond directly in step 17, EASDF sends DNS response with the IP address of the common EAS to UE.
6.2.3.2.6 EAS discovery corresponding to Common DNAI with EASDF for a set of UEs |R18| p. 31
The common DNAI for the set of UEs can be provided either by AF or determined by 5GC. When the AF determines the common DNAI, the AF provides the common DNAI for the set of UEs via AF Traffic influence procedure as defined in clause 4.3.6.2 of TS 23.502. The AF may determine the common DNAI based on candidate DNAI(s) reported by SMF as described in clause 4.3.6.3 of TS 23.502.
In the case that the AF did not provide a common DNAI, the 5GC determines the common DNAI. For this case, the common DNAI is determined by NEF and the NEF stores the common DNAI in UDR as part of AF traffic influence request information, as described in clause 6.2.3.2.7.
The following is the procedure for discovery EAS corresponding to a Common DNAI for set of UEs accessing the same application.
Step 1.
The AF request in step 1 of Figure 4.3.6.2-1 in TS 23.502 is used to request selecting the common DNAI for a set of UEs accessing the application as identified in the AF Request.
AF may use External/Internal Group ID(s) or a list of UEs or any UE as Target UE Identifier(s) and additionally Spatial Validity Condition to identify the set of UEs for correlated selection of common DNAI.
The following information may be included in AF request as defined in clause 5.6.7.1 in TS 23.501:
Step 2.
- An indication of traffic correlation may be provided for indication of selecting the same DNAI (i.e. selecting EAS corresponding to the same DNAI) for the set of UEs accessing the same application.
- A Traffic Correlation ID may be provided for identification of the set of UEs accessing the application identified by the FQDN(s) in AF request.
- A Common DNAI to be accessed by the set of UEs can be included in Potential locations of applications of the AF request, if it is determined by AF.
- FQDN(s) may be included which is corresponding to the application identified by Traffic Description in AF request.
- Spatial Validity Condition could be provided for limiting the location of the UEs, and also "any UE" or a UE list or group ID can be provided for defining set of UEs accessing the same DNAI.
Based on steps 1~19 in Figure 6.2.3.2.2-1, with the following changes:
In step 10:
If FQDN in Neasdf_DNSContext_Notify Request is corresponding to the application indicated in PCC rule, e.g. the FQDN is included in the FQDN(s) in the PCC rule and if indication of traffic correlation is set, SMF determines the UE belongs to set of UEs identified by Traffic Correlation ID and accessing the application and determines the UE connects to EAS corresponding to the common DNAI for the set of UEs. If FQDN(s) is included in PCC rule, the SMF can use the FQDN(s) in PCC rule and the FQDN in Neasdf_DNSContext_Notify Request to match the FQDN with the PCC rule, i.e. the matched PCC rule includes the FQDN(s) containing the FQDN.
If the common DNAI is not available in the PCC Rule received in step 1, the SMF invokes the NEF to determine the common DNAI as described in clause 6.2.3.2.7.
Once the common DNAI is available, for Option A, SMF provisions EASDF with the information to build EDNS Client Subnet option that refers to a location that is topologically close to the common DNAI; for Option B, SMF provisions EASDF with Local DNS server related to the common DNAI.
6.2.3.2.7 Coordination among SMFs for Common EAS/DNAI determination |R18| p. 32
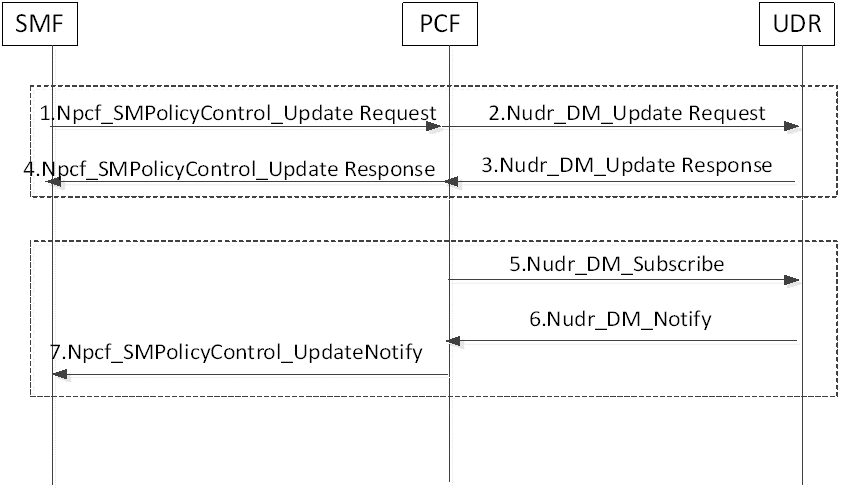
Step 1.
SMF sends Nsmf_TrafficCorrelation_Notify to the NEF with Notification Endpoint received in the PCC rule as described in clauses 6.2.3.2.5 and 6.2.3.2.6 and provides: EAS IP address(es) based on EASDF procedure and/or list of candidate DNAI(s), SMF ID, number of PDU sessions it is serving for the set of UEs, Traffic Correlation ID.
Step 2.
If the NEF determines that there is currently no common EAS IP address and/or common DNAI available for the set of UEs identified by Traffic Correlation ID, it selects a common DNAI and/or common EAS using the list of DNAI(s), EAS IP address and number of PDU sessions each SMF is serving for the set of UEs received in step 1. Then the NEF updates traffic influence data with the 5GC determined common EAS/DNAI for the set of UEs.
The update of traffic influence data triggers notifications to PCF(s) that in turn trigger associated PCC rule updates to the SMF(s), if any, with PDU Session(s) associated with the traffic correlation ID.
The NEF maintains a list of SMFs serving the set of UEs and the associated data including common DNAI, common EAS, number of PDU sessions each SMF is serving for the set of UEs, Traffic Correlation ID.
Step 3.
NEF responds by acknowledging the notification to the SMF.
Step 4.
The update in UDR triggers notification to the PCF(s) that have subscribed for notification. The PCF(s) sends PCC rule(s) with NEF information, Traffic correlation ID and common EAS IP address and/or Common DNAI, as part of traffic influence data to the SMF(s) with PDU Session(s) associated with the Traffic Correlation ID.
SMF(s) may select other candidate DNAI(s) for the PDU session(s) or a candidate new EAS IP address via the EASDF procedure e.g. due to UE(s) mobility. In this case, the SMF notifies to the NEF as in the above step 1, with the list of candidate DNAI(s) and/or EAS IP address. This may trigger NEF to re-select common DNAI and/or common EAS. NEF determines common EAS and/or common DNAI based on received EAS IP, list of candidate DNAI(s), number of PDU sessions SMF(s) serving for the set of UEs.
If another DNAI/EAS IP address is selected by the NEF, it updates the common DNAI or common EAS in the UDR in the Traffic Influence data.