Content for TS 23.548 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.3
5…
6…
6.2.2.3…
6.2.3…
6.2.3.2.3…
6.2.3.2.5…
6.2.3.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6
6.7…
6.7.2.4…
6.7.2.6…
6.7.3…
6.8…
6.10…
7…
A
B…
F…
4 Reference Architecture and Connectivity Models
4.1 General
4.2 Reference Architecture for Supporting Edge Computing
...
...
4 Reference Architecture and Connectivity Models p. 8
4.1 General p. 8
Edge Computing enables operator and 3rd party services to be hosted close to the UE's access point of attachment, so as to achieve an efficient service delivery through the reduced end-to-end latency and load on the transport network.
5GS supports Edge Hosting Environment (EHE) deployed in the DN beyond the PSA UPF. An EHE may be under the control of either the operator or 3rd parties.
The Edge Computing features defined in this specification are applicable to PLMN(s) and to SNPN(s).
The Local part of the DN in which EHE is deployed may have user plane connectivity with both a centrally deployed PSA and locally deployed PSA of same DNN. Edge Computing enablers as described in clause 5.13 of TS 23.501, e.g. local routing and traffic steering, session and service continuity, AF influenced traffic routing, are leveraged in this specification.
Edge Computing in the serving network (e.g. for Local Break Out roaming scenario in case of PLMN access or Home Routed with Session Breakout roaming scenario) is supported. For AF guidance to PCF determination of URSP rules in the HR-SBO scenario, the Serving network (e.g. VPLMN or serving SNPN) has no control on URSP, so cannot influence UE in selecting a specific Edge Computing related DNN and S-NSSAI.
4.2 Reference Architecture for Supporting Edge Computing p. 8
The reference architectures for supporting Edge Computing are based on the reference architectures specified in clause 4.2 of TS 23.501. The following reference architectures for non-roaming, LBO roaming and HR with Session Breakout (HR-SBO) roaming scenarios further depict the relationship between the 5GS and a DN where Edge Application Servers (EASs) are deployed in an EHE.
The reference architecture for Local Offloading Management scenario is based on the non-roaming architecture with I-SMF insertion to the PDU Session with UL-CL/BP with an additional reference point N88a between I-SMF and EASDF (see clause 5.34.2.2 of TS 23.501).
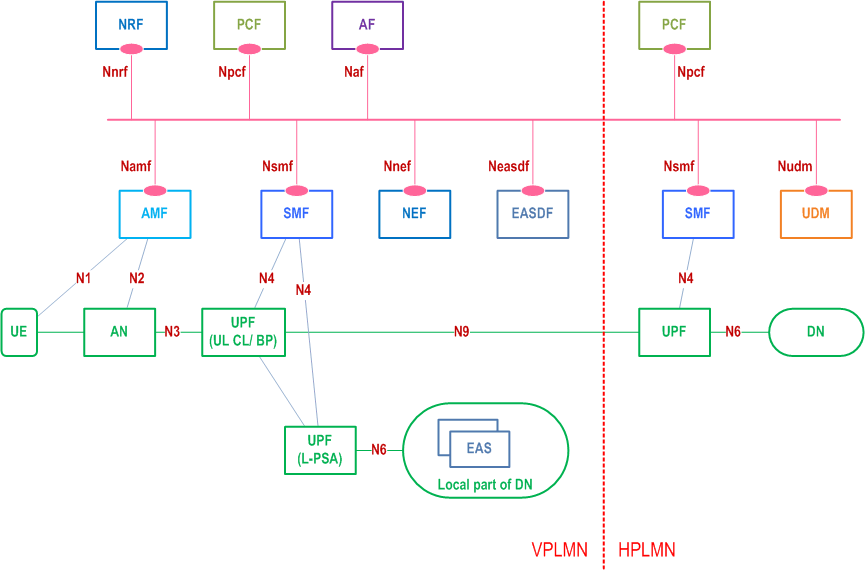
Figure 4.2-1 depicts 5GS architecture for non-roaming scenario supporting Edge Computing with UL CL/BP.
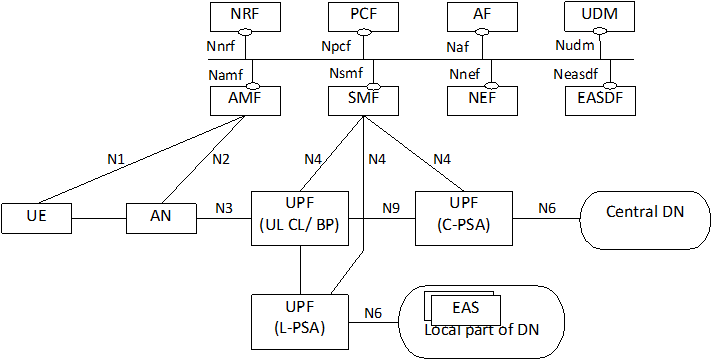
Figure 4.2-2 depicts 5GS architecture for non-roaming scenario supporting Edge Computing without UL CL/BP.
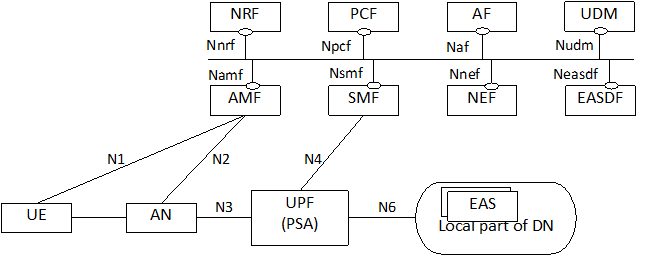
Figure 4.2-3 depicts 5GS architecture for LBO roaming scenario supporting Edge Computing with UL CL/BP.
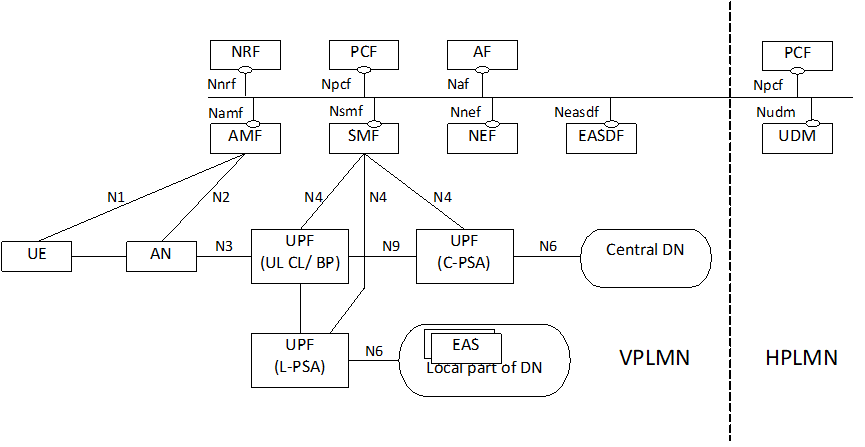
Figure 4.2-4 depicts 5GS architecture for LBO roaming scenario supporting Edge Computing without UL CL/BP.
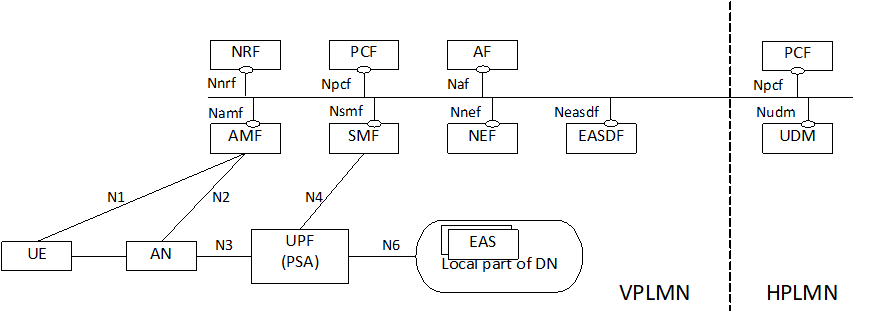
Figure 4.2-5 depicts 5GS architecture for HR-SBO roaming scenario supporting Edge Computing with UL CL/BP.