Content for TS 23.379 Word version: 19.5.0
1…
7…
10…
10.5…
10.6…
10.6.2.3…
10.6.2.4…
10.6.2.5…
10.6.2.6…
10.6.2.9…
10.6.3…
10.7…
10.7.3…
10.7.5…
10.7.6…
10.9…
10.9.1.3.3…
10.9.1.4…
10.9.2…
10.10…
10.12…
10.19…
10.19.3…
10.19.3.1.4…
10.19.3.2…
10.19.3.2.4…
10.19.3.2.6…
A…
10.12 MCPTT media plane transmissions with partner MCPTT systems (on-network)
10.13 Location information (on-network)
10.14 Ambient listening call
10.15 First-to-answer call setup
10.16 Remotely initiated MCPTT call
10.17 Support for multiple devices
10.18 Subscription and notification for functional alias
...
...
10.12 MCPTT media plane transmissions with partner MCPTT systems (on-network) p. 207
The MCPTT user is able to receive MCPTT media services (e.g. group communication, private calls) from partner MCPTT systems in normal and roaming conditions. In this service delivery model, the media plane transmissions between the MCPTT UE of the user and the partner MCPTT system can be achieved directly or via the primary MCPTT system, selected by the PLMN operator's policy. The protocol used for media plane signalling is non-SIP like RTCP.
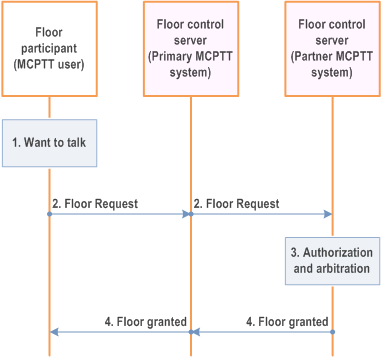
Figure 10.12-1 provides the procedure for media related signalling.
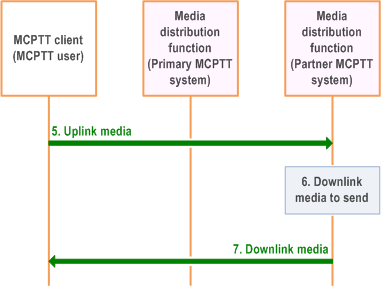
Figure 10.12-2 provide the procedure for the media transmission (directly) between MCPTT UE of the user and the partner MCPTT system.
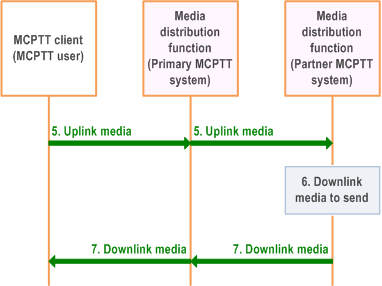
Figure 10.12-3 provides the procedure for the media transmission (via the primary MCPTT system) between MCPTT UE of the user and the partner MCPTT system.
Pre-conditions:
- The MCPTT group is defined in the partner MCPTT system, where the MCPTT client of user receives the MCPTT service.
- An MCPTT group call is set up and active.
- The partner MCPTT system is the group host MCPTT server that is hosting the MCPTT group. The corresponding floor control server manages the media corresponding to the group call.
- Protocol used for signalling of media plane is non-SIP, it can be protocol like RTCP.
- Media related signalling is sent via the primary MCPTT system.
- The path for media between the MCPTT UE and partner MCPTT system has been selected to be sent directly to the partner MCPTT system or via the primary MCPTT system based on PLMN operator's policy.
For media related signalling communication:
Step 1.
For media communication:
An MCPTT user wants to talk.
Step 2.
The floor participant corresponding to the MCPTT user sends a floor request message to floor control server (partner MCPTT system) to get the authorization and/or permission to talk.
Step 3.
The floor control server (partner MCPTT system) performs the authorization and arbitrates between requests that are in contention (i.e., floor control).
Step 4.
If the floor control server (partner MCPTT system) allows the floor participant to talk, a floor granted is provided with permission granted to talk.
Step 5.
The MCPTT client can now send uplink media data to the media distribution function of the MCPTT server (partner MCPTT system).
Step 6.
The media distribution function of the MCPTT server (partner MCPTT system) has downlink media data to transfer.
Step 7.
The media distribution function of the MCPTT server (partner MCPTT system) transfers the downlink media to the MCPTT client of the MCPTT user.
10.13 Location information (on-network) p. 209
The MCPTT system makes use of all of the procedures for location management as specified in TS 23.280, utilising the CSC-14 reference point between the location management client and location management server and the CSC-15 reference point between the MCPTT server and location management server.
- The MC service client is the MCPTT client;
- The MC service server is the MCPTT server;
- The MC service group is the MCPTT group;
- The MC service ID is the MCPTT ID; and
- The MC service group ID is the MCPTT group ID.
10.14 Ambient listening call p. 209
10.14.1 General p. 209
The ambient listening call is a type of a private MCPTT call that only allows a "listened to" user to transmit media to a "listening" user such that there is no indication on the MCPTT UE of the "listened to" user about the call and the media transmission.
There are two types of ambient listening call as below:
- Remotely initiated ambient listening is initiated by the authorized user (e.g., dispatcher) who wants to listen to another user. In this case, the "listened to" user is the called party, and shall automatically accept the call without causing any indication about the call and transmit the media to the "listening" user.
- Locally initiated ambient listening is initiated by an authorized user who wants another user to listen to the MCPTT UE communication. In this case, the "listened to" user is the calling party and shall automatically transmit the media to the "listening" user without causing any indication about the call processing and media transmission.
10.14.2 Information flows for ambient listening call p. 209
10.14.2.1 Ambient listening call request p. 209
Table 10.14.2.1-1 describes the information flow ambient listening call request from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listening" user |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listened to" user |
| SDP offer | M | Media parameters of MCPTT client. |
| Ambient listening type | M | The ambient listening type indicates remotely initiated ambient listening call or locally initiated ambient listening call. |
10.14.2.2 Ambient listening call response p. 210
Table 10.14.2.2-1 describes the information flow ambient listening call response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listening" user |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listened to" user |
| SDP answer | M | Media parameters selected. |
10.14.2.3 Ambient listening call release request p. 210
Table 10.14.2.3-1 describes the information flow ambient listening call release request from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listening" user |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listened to" user |
| Ambient listening type | M | The ambient listening type indicates a remotely initiated ambient listening call or a locally initiated ambient listening call. |
10.14.2.4 Ambient listening call release response p. 210
Table 10.14.2.4-1 describes the information flow ambient listening call release response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listening" user |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listened to" user |
| Ambient listening type | M | The ambient listening type indicates a remotely initiated ambient listening call or a locally initiated ambient listening call. |
10.14.2.5 Ambient listening call release notification p. 211
Table 10.14.2.5-1 describes the information flow ambient listening call release notification from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listening" user |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the "listened to" user |
| Call release reason | M | The reason for call release by the MCPTT server. |
| Ambient listening type | M | The ambient listening type indicates a remotely initiated ambient listening call or a locally initiated ambient listening call. |
10.14.3 Ambient listening call procedures p. 211
10.14.3.1 Remotely initiated ambient listening call setup p. 211
The MCPTT service provides the capability for an authorised user to initiate a remotely initiated ambient listening call at an MCPTT client.
Figure 10.14.3.1-1 illustrates the information flow for remotely initiated ambient listening call setup.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 1 is the client of the authorized user who is authorized to invoke a remotely initiated ambient listening call to be set up at the requested MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT user 1 is the "listening" user at MCPTT client 1, and MCPTT user 2 is the "listened to" user at MCPTT client 2.
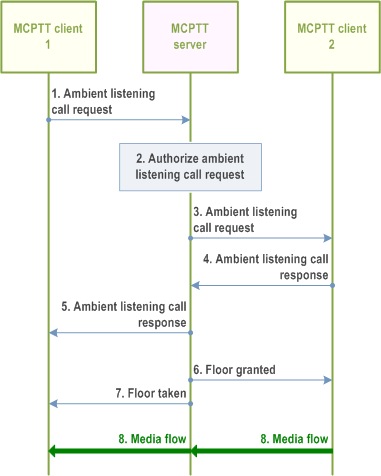
Step 1.
MCPTT client 1 initiates a remotely initiated ambient listening call by sending the ambient listening call request to the MCPTT server. The remotely initiated ambient listening call type is included.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server performs an authorization check for the authorized user 1 for the remotely initiated ambient listening call. If authorization fails, the MCPTT server provides a failure response to MCPTT client 1. The MCPTT server also performs check whether MCPTT client 2 is engaged in an MCPTT Private Call or an MCPTT Group Call. If MCPTT client 2 is engaged in an MCPTT call, then the ambient listening call set up fails and response is provided to MCPTT client 1.
Step 3.
The MCPTT server sends the ambient listening call request to MCPTT client 2.
Step 4.
MCPTT client 2 returns the ambient listening call response to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
MCPTT server provides an ambient listening call response to MCPTT client 1, indicating whether the call is set up successfully or not.
Step 6.
The floor control server of the MCPTT server then sends a floor granted to MCPTT client 2 according to the ambient listening type received in step 1.
Step 7.
Accordingly, the floor control server of the MCPTT server sends a floor taken to MCPTT client 1.
Step 8.
After receiving the floor granted message at the MCPTT client 2, the media is transmitted from MCPTT client 2 to MCPTT client 1.
10.14.3.2 Locally initiated ambient listening call setup p. 212
The MCPTT service provides the capability for an authorised user to initiate a locally initiated ambient listening call at an MCPTT client.
Figure 10.14.3.2-1 illustrates the information flow for locally initiated ambient listening call setup.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 2 is the client of the authorized user who is authorized to invoke a locally initiated ambient listening call to be set up at the requested MCPTT client 1.
- MCPTT user 1 is the "listening" user at MCPTT client 1, and MCPTT user 2 is the "listened to" user at MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT client 2 is not already engaged in an MCPTT Private Call or an MCPTT Group Call.
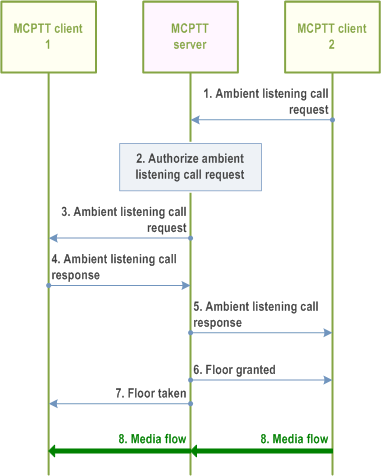
Step 1.
MCPTT client 2 initiates a locally initiated ambient listening call by sending the ambient listening call request to the MCPTT server. The locally initiated ambient listening call type is included.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server performs an authorization check for the authorized user 2 for the locally initiated ambient listening call. If authorization fails, the MCPTT server provides a failure response to MCPTT client 2.
Step 3.
The MCPTT server sends the ambient listening call request to MCPTT client 1.
Step 4.
MCPTT client 1 returns the ambient listening call response to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
MCPTT server provides an ambient listening call response to MCPTT client 2, indicating whether the call is set up successfully or not.
Step 6.
The floor control server of the MCPTT server then sends a floor granted to MCPTT client 2 according to the ambient listening type received in step 1.
Step 7.
Accordingly, the floor control server of the MCPTT server sends a floor taken to MCPTT client 1.
Step 8.
After receiving the floor granted message at the MCPTT client 2, the media is transmitted from MCPTT client 2 to MCPTT client 1.
10.14.3.3 Ambient listening call release - server initiated p. 213
Figure 10.14.3.3-1 illustrates the information flow for ambient listening call release - server initiated when trigger by the MCPTT administrator. This procedure is applied for both remotely initiated ambient listening call and the locally initiated ambient listening call.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 1 is the MCPTT client of the authorized user, who initiated the ambient listening call at MCPTT client 2.
- There is an ongoing ambient listening call between MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 1.
- MCPTT user 1 is the current user at MCPTT client 1 who is listening, and MCPTT user 2 is the current user at MCPTT client 2 who is being listened to.
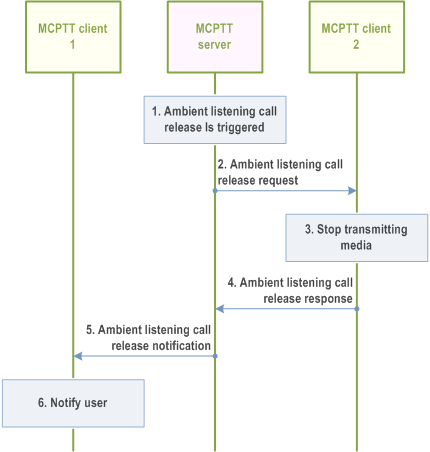
Step 1.
The ambient listening call release is triggered by the MCPTT administrator or by one of the following events:
Step 2.
- the MCPTT server receives MCPTT call requests towards MCPTT client 2; or
- the MCPTT client 2 initiates MCPTT call requests;
The MCPTT server sends an ambient listening call release request to MCPTT client 2.
Step 3.
MCPTT client 2 stops transmitting media to MCPTT client 1.
Step 4.
MCPTT client 2 provides an ambient listening call release response to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server sends an ambient listening call release notification to MCPTT client 1 together with a reason code identifying that the call was released.
Step 6.
MCPTT client 1 notifies the authorized user 1.
10.14.3.4 Remotely initiated ambient listening call release - "listening" user initiated p. 214
Figure 10.14.3.4-1 illustrates the information flow for ambient listening call release - "listening" user initiated. This procedure is applied for both remotely initiated ambient listening call and the locally initiated ambient listening call.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 1 is the MCPTT client of the authorized user, who is authorized to release the ambient listening call at MCPTT client 2.
- There is an ongoing ambient listening call between MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 1.
- MCPTT user 1 is the "listening" user at MCPTT client 1, and MCPTT user 2 is the "listened to"user at MCPTT client 2.
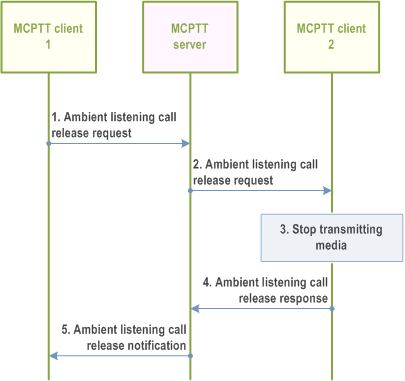
Step 1.
The authorized user 1 at MCPTT client 1 initiates the ambient listening call release by sending an ambient listening call release request to the MCPTT server.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server provides an ambient listening call release request to MCPTT client 2.
Step 3.
MCPTT client 2 stops transmitting media to MCPTT client 1.
Step 4.
MCPTT client 2 provides an ambient listening call release response to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server provides the ambient listening call release response to MCPTT client 1.
10.14.3.5 Ambient listening call release - "listened to" user initiated p. 215
Figure 10.14.3.5-1 illustrates the information flow for ambient listening call release - "listened to" user initiated. This procedure is only applied for the locally initiated ambient listening call.
Pre-conditions:
- There is an ongoing ambient listening call between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT user 1 is the "listening" user at MCPTT client 1, and MCPTT user 2 is the "listened to" user at MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT client 2 is the MCPTT client of the authorized user, who is authorized to release the locally initiated ambient listening call at MCPTT client 2.
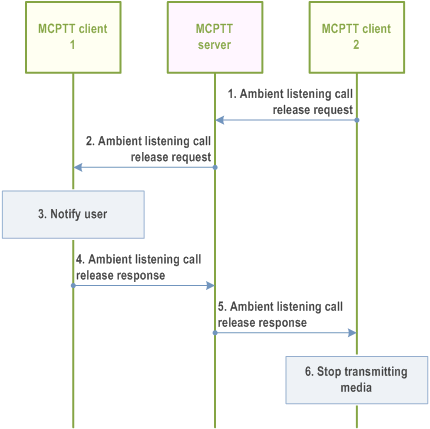
Step 1.
The authorized user 2 at MCPTT client 2 initiates the ambient listening call release by sending an ambient listening call release request to the MCPTT server.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server provides an ambient listening call release request to MCPTT client 1.
Step 3.
The user 1 at MCPTT client 1 is notified about the ambient listening call release.
Step 4.
MCPTT client 1 provides an ambient listening call release response to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server provides the ambient listening call release response to MCPTT client 2.
Step 6.
MCPTT client 2 stops transmitting media to MCPTT client 1.
10.15 First-to-answer call setup p. 216
10.15.1 Description p. 216
Figure 10.15.3-1 describes the basic procedure for the MCPTT client initiating MCPTT first-to-answer call. The flow may use a floor request in the MCPTT call request indicating that the originator will be given the floor when the call starts and eliminates the need for a separate initial floor request message during media plane establishment. Alternatively, the call initiation may be sent without the floor request, which allows the called party to request the floor first. For a MCPTT first-to-answer call without floor control, floor control is not established.
Figure 10.15.3-1 also describes the handling of private calls when a functional alias replaces the MCPTT ID as target address. A functional alias can be simultaneously used by more than one MCPTT user, i.e. multiple MCPTT clients can activate the same functional alias.
10.15.2 Information flows for first-to-answer call p. 216
10.15.2.1 MCPTT first-to-answer call request (MCPTT client to MCPTT server) |R16| p. 216
Table 10.15.2.1-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call request from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID list (see NOTE) | O | The list of MCPTT IDs of the called party. |
| Functional alias (see NOTE) | O | The functional alias of the called party. |
| Use floor control indication | M | This element indicates whether floor control will be used for the private call. |
| SDP offer | O | Media parameters of MCPTT client. |
| Implicit floor request | O | An indication that the user is also requesting the floor. |
| Location information | O | Location of the calling party. |
|
NOTE:
At least one identity shall be present. If both are present the MCPTT ID list shall be used to route the call request and the functional alias is just for information.
|
||
10.15.2.2 MCPTT first-to-answer call request (MCPTT server to MCPTT client) |R16| p. 217
Table 10.15.2.2-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call request from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the called party. |
| Use floor control indication | M | This element indicates whether floor control will be used for the private call. |
| SDP offer | M | Media parameters of MCPTT client. |
| Implicit floor request | O | An indication that the user is also requesting the floor. |
10.15.2.3 MCPTT first-to-answer call response (MCPTT client to MCPTT server) |R16| p. 217
Table 10.15.2.3-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the called party. |
| SDP answer | M | Media parameters selected. |
10.15.2.4 MCPTT first-to-answer call response (MCPTT server to MCPTT client) |R16| p. 218
Table 10.15.2.4-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call response from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the called party. |
| SDP answer | M | Media parameters selected. |
10.15.2.5 MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel request (MCPTT server to MCPTT client) |R16| p. 218
Table 10.15.2.5-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel request from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
10.15.2.6 MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel response (MCPTT client to MCPTT server) |R16| p. 218
Table 10.15.2.6-1 describes the information flow MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
10.15.3 Procedure p. 219
All clients are served by the primary MCPTT service provider in Figure 10.15.3-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The calling MCPTT user has selected first-to-answer call.
- MCPTT clients 1 to n are registered and their respective users, MCPTT user 1 to MCPTT user n, are authenticated and authorized to use the MCPTT service, as per procedure in subclause 10.2.
- MCPTT clients 2 to n have activated the same functional alias.
- The MCPTT server has subscribed to the MCPTT functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
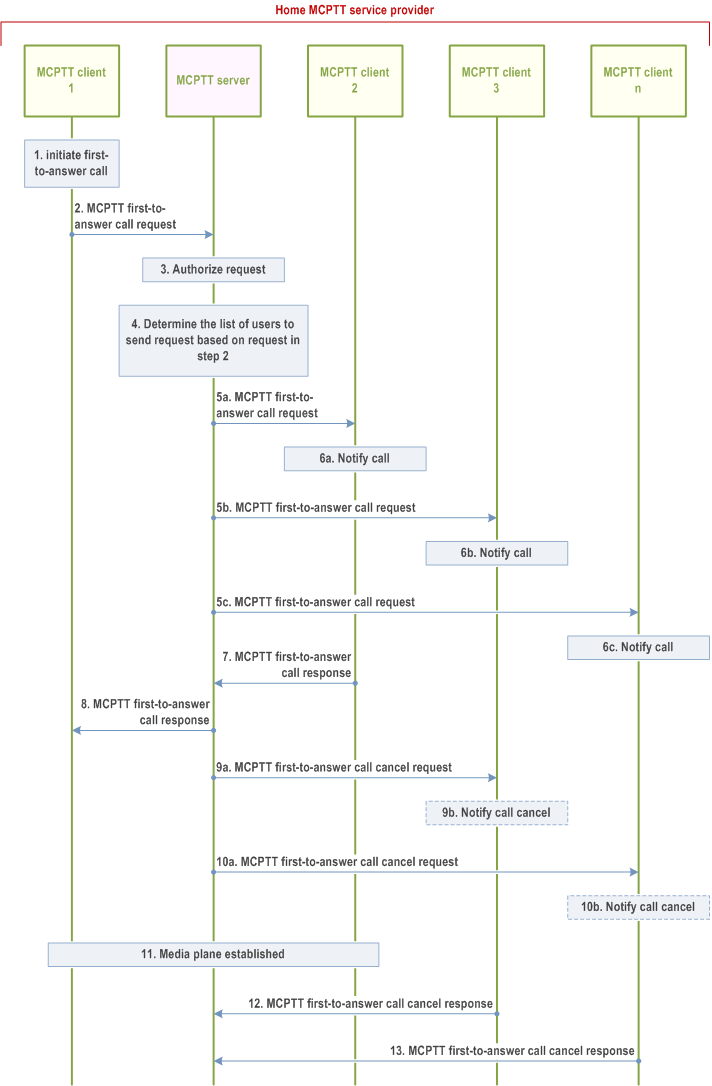
Step 1.
MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1 would like to establish a MCPTT first-to-answer call indicating a set of potential target recipients or by calling a functional alias. For a MCPTT first-to-answer call with floor control, floor control is to be established. For first-to-answer call without floor control, both users will have the ability to transmit without floor arbitration.
Step 2.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT first-to-answer call request including a set of potential target recipients to the MCPTT server (via the SIP core as defined in TS 23.228), using either a list of MCPTT IDs or a functional alias. The MCPTT first-to-answer call request contains the MCPTT ID and may contain the functional alias of originating user and an SDP offer containing one or more media types. The MCPTT first-to-answer call request may also contain a data element that indicates that MCPTT client 1 is requesting the floor, for a first-to-answer call with floor control. The MCPTT client 1 includes a first-to-answer call indication that the call is to be established only to the first answering user.
Step 3.
The MCPTT server confirms that MCPTT users are authorized for the call and whether the MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1 is authorized to initiate a first-to-answer call. The MCPTT server checks whether the provided functional alias of the calling user, if present, can be used and has been activated for the MCPTT user. If a functional alias is present, the MCPTT server shall also check whether MCPTT client 1 is allowed to use the functional alias of MCPTT client 2 (to MCPTT client n) to setup a private call and whether MCPTT client 2 (to MCPTT client n) is (are) allowed to receive a private call from MCPTT client 1 using a functional alias.
Step 4.
The MCPTT server determines the list of MCPTT users to send MCPTT first-to-answer call request, based on a set of allowed potential target recipients obtained from the request from MCPTT client 1. Alternatively, when a functional alias is used as target address, the MCPTT server resolves the functional alias to a corresponding list of related MCPTT IDs of MCPTT client 2 to MCPTT client n who have activated the functional alias. The functional alias must have been activated to identify the MCPTT IDs of the called users.
Step 5a, 5b, 5c.
The MCPTT server includes information that it communicates using MCPTT service, offers the same media types or a subset of the media types contained in the initial received request and sends similar MCPTT first-to-answer call request to each potential target recipient, including the MCPTT ID and, if present, the functional alias of the calling MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1. If one or more called MCPTT users have registered to the MCPTT service with multiple MCPTT UEs and has designated the MCPTT UE for receiving the calls, then the incoming MCPTT first-to-answer call request is delivered only to the designated MCPTT UE. Otherwise MCPTT first-to-answer call request may be delivered to all the registered MCPTT UEs. If a functional alias is present and more than one MCPTT client has activated that functional alias, then the MCPTT server sends an MCPTT first-to-answer call request to each MCPTT client.
Step 6a, 6b, 6c.
The MCPTT users are alerted, regardless of the commencement mode.
Step 7.
MCPTT user at MCPTT client 2 accepted the call which causes MCPTT client 2 to send an MCPTT first-to-answer call response to the MCPTT server.
Step 8.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT first-to-answer call response to MCPTT client 1 indicating that MCPTT user at MCPTT client 2 has accepted the call, including the accepted media parameters.
Step 9a.
The MCPTT server sends a MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel request to MCPTT client 3.
Step 9b.
Optionally, MCPTT client 3 notifies the user.
Step 10a.
The MCPTT server sends a MCPTT first-to-answer call cancel request to MCPTT client n.
Step 10b.
Optionally, MCPTT client n notifies the user.
Step 11.
The media plane for communication is established. Either user can transmit media individually when using floor control. For successful call establishment for first-to-answer call with floor request from MCPTT client 1, the floor participant associated with MCPTT client 1 is granted the floor initially. At the same time the floor participant associated with MCPTT client 2 is informed that the floor is taken. For a first-to-answer call without floor control both users are allowed to transmit simultaneously.
Step 12.
MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT first-to-answer cancel call response.
Step 13.
MCPTT client n sends an MCPTT first-to-answer cancel call response.
10.16 Remotely initiated MCPTT call p. 222
10.16.1 General p. 222
A remotely initiated MCPTT call allows an authorized user to cause a remote MCPTT UE to initiate a call by itself, without its user explicitly initiating the call.
10.16.2 Information flows for remotely initiated MCPTT call p. 222
10.16.2.1 Remotely initiated MCPTT call request p. 222
Table 10.16.2.1-1 describes the information flow remotely initiated MCPTT call request from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and from the MCPTT server to MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party (remote). |
| Notification to remote user of remotely initiated call | M | Use to determine whether the called party (remote) receives any indication of the remotely initiated MCPTT call. |
| MCPTT ID | O (see NOTE) | For a remotely initiated MCPTT private call the MCPTT User ID to be called. |
| MCPTT Group ID | O (see NOTE) | For a remotely initiated MCPTT group call to use. |
| Requested commencement mode | O | Requested commencement mode for the remotely initiated MCPTT private call. |
| Requested priority | O | Requested priority for the remotely initiated MCPTT private call or MCPTT group call. |
|
NOTE:
One and only one of these shall be present.
|
||
10.16.2.2 Remotely initiated MCPTT call response p. 222
Table 10.16.2.2-1 describes the information flow remotely initiated MCPTT call response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and from the MCPTT server to MCPTT client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party. |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party. |
| Result | M | Result of the remotely initiated MCPTT call request - success or fail. |
10.16.3 Procedure p. 223
10.16.3.1 Remotely initiated MCPTT call request p. 223
The remotely initiated MCPTT call request procedure includes the initial remotely initiated MCPTT call request from the MCPTT user to the remote UE and either the MCPTT private call procedures or the MCPTT group call procedures originating at the remote UE.
Procedures in Figure 10.16.3.1-1 show the signalling control plane procedures for the MCPTT client initiating a remotely initiated MCPTT call request with the chosen MCPTT user.
Pre-conditions:
- If the MCPTT user on MCPTT client 1 wants the resulting remotely initiated MCPTT call to be:
- an MCPTT group call, then MCPTT user 2 on MCPTT client 2 is an affiliated MCPTT group member of the MCPTT group that is the target of the remotely initiated MCPTT call.
- an MPCTT private call, then the MCPTT user 2 on MCPTT client 2 is permitted to initiate an MCPTT private call to the identified MCPTT user.
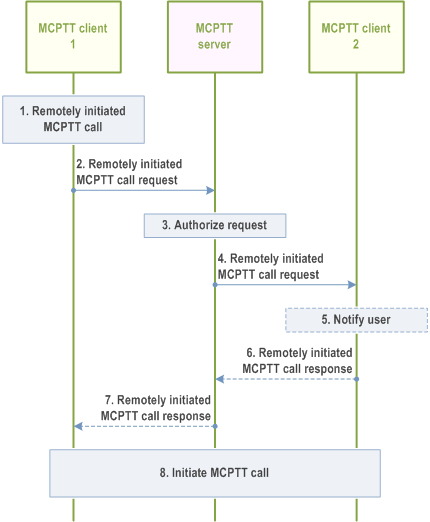
Step 1.
The result of these procedures is an on-going MCPTT (group or private) call which includes MCPTT client 1.
MCPTT user on MCPTT client 1 initiates a remotely initiated MCPTT call request to the MCPTT user of MCPTT client 2.
Step 2.
MCPTT client 1 sends a remotely initiated MCPTT call request towards the MCPTT server.
Step 3.
MCPTT server checks whether the MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1 is authorized to initiate a remotely initiated MCPTT call request. If the resulting of this request is to initiate a group call, MCPTT client 1 is authorized to remotely initiate the MCPTT call request, and if MCPTT client 2 is a member of the group, the MCPTT server implicitly affiliates the MCPTT user 2 on MCPTT client 2 to the MCPTT group if the MCPTT client 2 is not already affiliated and notifies the MCPTT client 2 of this affiliation change.
Step 4.
If authorized, MCPTT server sends the corresponding remotely initiated MCPTT call request towards the MCPTT client 2.
Step 5.
Based on the received information the receiving MCPTT client 2 may notify the user of the remotely initiated MCPTT call request.
Step 6.
Optionally the receiving MCPTT client 2 sends a remotely initiated MCPTT call response to the MCPTT server.
Step 7.
After receiving the remotely initiated MCPTT call response from MCPTT client 2, the MCPTT server informs the MCPTT client 1 about successful remotely initiated MCPTT call request.
Step 8.
Based on the received information the MCPTT client 2 initiates an MCPTT call (either an MCPTT group call or an MCPTT private call) using the normal MCPTT call establishment procedures (clause 10.6.2.3.1.1.2 or clause 10.7.2.2) with implicit floor request and other call set up parameters if received in the remotely initiated call request. The MCPTT call request may include the additional information such as indication of whether the call initiation is due to receiving of remotely initiated call request.
Step 9.
If the remotely initiated call is a group call, then when the ongoing MCPTT group call is terminated, the MCPTT server de-affiliates the MCPTT user 2 on MCPTT client 2 from the MCPTT group if MCPTT client 2 is implicitly affiliated as defined in the step 3 above (the de-affiliation is not shown in the figure for simplicity).
10.17 Support for multiple devices p. 224
10.17.1 General p. 224
An MCPTT user may be authorized to use the MCPTT service from multiple MCPTT UEs as per the procedure in subclause 10.2.
If an MCPTT server receives a service authorization request for an MCPTT user who is previously MCPTT service authorized on another MCPTT UE, then the MCPTT server shall process this service authorization request as described in subclause 10.2. In the MCPTT service authorization response to the MCPTT user, the MCPTT server shall also indicate that the MCPTT user is already MCPTT service authorized from another MCPTT UE.
10.18 Subscription and notification for functional alias |R16| p. 224
10.18.1 General p. 224
The MCPTT service shall support the procedures and related information flows as specified in subclauses 10.13.10 of TS 23.280 with the following clarifications:
- The MC service client is the MCPTT client;
- The MC service server is the MCPTT server;