Content for TS 23.334 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.11…
5.12…
5.14…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
6…
6.1.6…
6.1.11…
6.2…
6.2.10…
6.2.10.3.1.2
6.2.10.3.2
6.2.10.4…
6.2.10.4.3…
6.2.10.5
6.2.10.6…
6.2.10A…
6.2.13…
6.2.14…
6.2.14.3
6.2.14.4…
6.2.15…
6.2.17…
6.2.17.3…
6.2.17.5…
6.2.18…
6.2.20
6.2.21…
6.2.22…
6.2.22.3…
6.2.22.3.2
6.2.23
6.2.24
6.2.25
7
8…
8.3
8.4
8.5…
8.23…
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Symbols
3.3 Abbreviations
...
...
1 Scope p. 9
Annex G of TS 23.228 gives out an IMS Application Level Gateway (IMS-ALG) and IMS Access Media Gateway (IMS-AGW) based reference model to support NAPT-PT, gate control and traffic policing between IP-CAN and IMS domain.
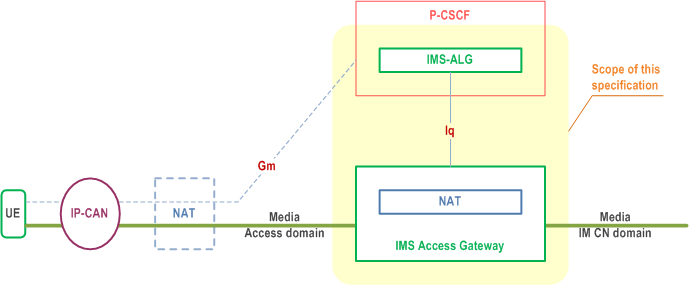
Figure 1.1 illustrates the reference model for Iq:
- the dashed line represents the IP signalling-path with SIP (at Gm) as call/session control protocol between the UE and the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG);
- the bold, horizontal line represents the IP media-path (also known as (IP) bearer-path or (IP) data-path; the notion 'media' is used as generic term for "IP application data"); and
- the vertical line represents the Iq control-path with H.248 as gateway/policy control protocol between the IMS-ALG and the IMS-AGW (H.248 messages are transported over IP).
2 References p. 9
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.228: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), stage 2".
[3]
TS 29.334: "IMS Application Level Gateway (IMS-ALG) - IMS Access Gateway (IMS-AGW) Iq interface, stage 3".
[4]
RFC 2663: "IP Network Address Translator (NAT) Terminology and Considerations".
[5]
TS 32.260: "Telecommunication management; Charging management; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) charging".
[6]
RFC 3556: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Bandwidth Modifiers for RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) Bandwidth".
[7]
RFC 3605: "Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP) attribute in Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[8]
TS 23.205: "Bearer independent circuit-switched core network; Stage 2".
[9]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.1 (05/2002): "Gateway Control Protocol: Version 2" including the Corrigendum1 for Version 2 (03/04).
[10]
RFC 2216: "Network Element Service Template".
[11]
TS 24.229: "IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on SIP and SDP".
[12]
TS 33.328: "IMS Media Plane Security".
[13]
RFC 4568: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Security Descriptions for Media Streams".
[14]
RFC 3711: "The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)".
[15]
RFC 5124: "Extended Secure RTP Profile for Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP)-Based Feedback (RTP/SAVPF)".
[16]
RFC 3168: "The Addition of Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to IP".
[17]
RFC 6679: "Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) for RTP over UDP".
[18]
TS 23.237: "IP Multimedia subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage 2".
[19]
TS 24.237: "IP Multimedia subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage 3".
[20]
TS 29.162: "Interworking between the IM CN subsystem and IP networks".
[21]
TS 26.114: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Multimedia Telephony; Media handling and interaction".
[22]
TS 22.153: "Multimedia Priority Service".
[23]
RFC 5285: "A General Mechanism for RTP Header Extensions".
[24]
RFC 6236: "Negotiation of Generic Image Attributes in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[25]
RFC 4975: "The Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[26]
RFC 6714: "Connection Establishment for Media Anchoring (CEMA) for the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[27]
RFC 4583: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Format for Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP) Streams".
[28] Void.
[29]
RFC 793: "Transmission Control Protocol - DARPA Internet Program - Protocol Specification".
[30]
RFC 4145: "TCP-Based Media Transport in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[31]
RFC 4582: "The Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP)".
[32] Void.
[33]
RFC 7345: "UDP Transport Layer (UDPTL) over Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)".
[34] Void
[35]
GSM Association RCC.07: "Rich Communication Suite 5.1 Advanced Communications Services and Client Specification, Version 2.0, 03 May 2013".
[36]
GSM Association RCC.07: "Rich Communication Suite 5.1 Advanced Communications Services and Client Specification, Version 3.0, 25 September 2013".
[37] Void
[38]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248.84 (07/2012): "Gateway control protocol: NAT-traversal for peer-to-peer services".
[39] Void.
[40] Void.
[41] Void.
[42]
RFC 5763: "Framework for Establishing a Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) Security Context Using Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)".
[43]
RFC 5764: "Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) Extension to Establish Keys for the Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)".
[44]
TS 24.371: "Web Real-Time Communications (WebRTC) client access to the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification".
[45]
RFC 6135: "An Alternative Connection Model for the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[46]
OMA-TS-CPM_Conversation_Function-V2_0-20150113-C: "CPM Conversation Functions, Candidate Version 2.0 - 13 Jan 2015".
[47]
RFC 5746: "Transport Layer Security (TLS) Renegotiation Indication Extension".
[48]
TS 33.310: "Network Domain Security (NDS); Authentication Framework (AF)".
[49]
RFC 7675: "Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) Usage for Consent Freshness".
[50]
RFC 6716: "Definition of the Opus Audio Codec".
[51]
TS 26.441: "Codec for Enhanced Voice Services (EVS); General Overview".
[52]
TS 26.445: "Codec for Enhanced Voice Services (EVS); Detailed Algorithmic Description".
[53]
RFC 4566: "SDP: Session Description Protocol".
[54]
RFC 4867: "RTP Payload Format and File Storage Format for the Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) and Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB) Audio Codecs".
[55]
RFC 4566: "SDP: Session Description Protocol".
[56]
RFC 7587: "RTP Payload Format for the Opus Speech and Audio Codec".
[57]
RFC 6544: "TCP Candidates with Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)".
[58]
RFC 4571: "Framing Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) Packets over Connection-Oriented Transport".
[59]
RFC 6947: "The Session Description Protocol (SDP) Alternate Connectivity (ALTC) Attribute".
[60]
RFC 5761: "Multiplexing RTP Data and Control Packets on a Single Port".
[61]
RFC 8831: "WebRTC Data Channels".
[62]
RFC 8873: "Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)".
[63]
RFC 4960: "Stream Control Transmission Protocol".
[64]
RFC 8841: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Procedures for Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) over Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) Transport".
[65]
RFC 8864: "Negotiation Data Channels Using the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[66]
RFC 5939: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Capability Negotiation".
[67]
RFC 6871: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Media Capabilities Negotiation".
[68]
RFC 4573: "MIME Type Registration for RTP Payload Format for H.224".
[69]
ITU-T Recommendation H.224 (01/2005): "A real time control protocol for simplex applications using the H.221 LSD/HSD/MLP channels".
[70]
ITU-T Recommendation H.281 (11/1994): "A far end camera control protocol for videoconferences using H.224".
[71]
RFC 8858: "Indicating Exclusive Support of RTP and RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) Multiplexing Using the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[72]
RFC 8035: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Clarifications for RTP/RTCP Multiplexing".
[73]
ITU-T Recommendation T.140 (02/98): "Text conversation presentation protocol".
[74]
RFC 4103: "RTP Payload for Text Conversation".
[75]
RFC 8865: "T.140 Real-Time Text Conversation over WebRTC Data Channels".
[76] Void.
[77]
RFC 4585: "Extended RTP Profile for Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP)-Based Feedback (RTP/AVPF)".
[78]
RFC 5104: "Codec Control Messages in the RTP Audio-Visual Profile with Feedback (AVPF)".
[79]
RFC 7728: "RTP Stream Pause and Resume".
[80]
RFC 8122: "Connection-Oriented Media Transport over the Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol in the Session Description Protocol (SDP)".
[81]
RFC 8842: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Considerations for Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)".
[82]
RFC 8445: "Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): A Protocol for Network Address Translator (NAT) Traversal".
[83]
RFC 8839: "Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer/Answer Procedures for Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)".
[84]
RFC 8489: "Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN)".
[85]
RFC 8656: "Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN): Relay Extensions to Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN)".
[86]
TS 26.250: "Codec for Immersive Voice and Audio Services - General Overview".
[87]
TS 26.253: "Codec for Immersive Voice and Audio Services - Detailed Algorithmic Description incl. RTP payload format and SDP parameter definitions".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 13
3.1 Definitions p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
End-to-access edge security:
media protection extending between an IMS UE and the first IMS core network node in the media path without being terminated by any intermediary node.
End-to-end security:
media protection between two IMS UEs without being terminated by any intermediary node.
Full ICE:
The full implementation of the Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) specified in RFC 8445.
ICE lite:
The lite implementation of the Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) specified in RFC 8445.
Local (near-end) NAPT control:
the operation of providing network address mapping information and NAPT policy rules to a near-end NAT in the media flow.
NAT-PT/NAPT-PT:
see definition in TS 23.228.
NAPT control and NAT traversal:
controls network address translation for both near-end NA(P)T and far-end NA(P)T
Network Address Translation (NA(P)T):
see definition in TS 23.228.
Remote (far-end) NAT traversal:
the operation of adapting the IP addresses so that the packets in the media flow can pass through a far-end (remote) NAT.
RTP / RTCP transport multiplexing:
a single IP transport (L4) port for RTP and RTCP packets.
TLS-client:
the entity that initiates a TLS session establishment to a server.
TLS-server:
the entity that responds to requests for TLS session establishment from clients.
TLS endpoint:
either a TLS-client or a TLS-server.
Convention:
Wherever the term NAT is used in this specification, it may be replaced by NA(P)T or NA(P)T-PT.
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions given in TS 23.237 apply:
Access Leg
Access Transfer Control Function (ATCF)
Access Transfer Gateway (ATGW)
Remote Leg
Target Access Leg
Source Access Leg
3.2 Symbols p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
Iq
Interface between the IMS Application Level Gateway and the IMS Access Media Gateway
3.3 Abbreviations p. 14
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
ALTC
Alternate Connectivity
AMR
Adaptive Multi-Rate
AMR-WB
Adaptive Multi-Rate - WideBand
AMR-WB IO
Adaptive Multi-Rate - WideBand Inter-operable Mode, included in the EVS and IVAS codecs
APP
APPlication-defined RTCP packet
ATCF
Access Transfer Control Function
ATGW
Access Transfer Gateway
BFCP
Binary Floor Control Protocol
CCM
Codec Control Messages
CVO
Coordination of Video Orientation
DBI
Delay Budget Information
DC
Data Channel
DTLS
Datagram Transport Layer Security
DTX
Discontinuous Transmission
e2ae security
End-to-access-edge security
e2e security
End-to-end security
ECN
Explicit Congestion Notification
ECN-CE
ECN Congestion Experienced
eIMS-AGW
IMS Access Gateway enhanced for WebRTC
eP-CSCF
P-CSCF enhanced for WebRTC
EVS
Enhanced Voice Services
FECC
Far End Camera Control
FIR
Full Intra Request
GTT
Global Text Telephony
ICE
Interactive Connectivity Establishment
IMS-AGW
IMS Access Media Gateway
IMS-ALG
IMS Application Level Gateway
IM CN
IMS Core Network
IVAS
Immersive Voice and Audio Services
MSRP
Message Session Relay Protocol
MTSI
Multimedia Telephony Service for IMS
NA(P)T
Network Address and optional Port Translation
NAPT
Network Address Port Translation
NAT
Network Address Translation
NA(P)T-PT
NAT Address (and optional Port-) Translation and Protocol Translation
P-CSCF
Proxy-CSCF
PI
Processing Information
ROI
Region of Interest
RTCP
RTP Control Protocol
RTP
Real-time Transport Protocol
SDPCapNeg
SDP Capability Negotiation
SRTP
Secure Real-time Transport Protocol
SRVCC
Single Radio Voice Call Continuity
STUN
Session Traversal Utilities for NAT
TLS
Transport Layer Security
TMMBN
Temporary Maximum Media Stream Bit Rate Notification
TMMBR
Temporary Maximum Media Stream Bit Rate Request
TURN
Traversal Using Relay NAT
UDPTL
User Datagram Protocol Transport Layer
URN
Uniform Resource Name
WebRTC
Web Real-Time Communication
WIC
WebRTC IMS Client
WWSF
WebRTC Web Server Function