Content for TS 23.334 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.11…
5.12…
5.14…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
6…
6.1.6…
6.1.11…
6.2…
6.2.10…
6.2.10.3.1.2
6.2.10.3.2
6.2.10.4…
6.2.10.4.3…
6.2.10.5
6.2.10.6…
6.2.10A…
6.2.13…
6.2.14…
6.2.14.3
6.2.14.4…
6.2.15…
6.2.17…
6.2.17.3…
6.2.17.5…
6.2.18…
6.2.20
6.2.21…
6.2.22…
6.2.22.3…
6.2.22.3.2
6.2.23
6.2.24
6.2.25
7
8…
8.3
8.4
8.5…
8.23…
6.2 Call Related Procedures
6.2.1 Gate Control & Local NA(P)T procedure
6.2.2 IP realm indication procedure
6.2.3 Remote NA(P)T traversal support procedure
6.2.4 Remote Source Address/Port Filtering
6.2.5 Traffic Policing
6.2.6 Hanging Termination Detection
6.2.7 QoS Packet Marking
6.2.8 Media Inactivity Detection
6.2.9 Handling of RTCP streams
...
...
6.2 Call Related Procedures p. 102
6.2.1 Gate Control & Local NA(P)T procedure p. 102
The session establishment and session release procedures are specified in TS 23.228 Annex G.4.3 and G.4.4.
Figure 6.2.1.2 depicts the signalling flow for a session setup from the IMS access network towards the IMS core network when the P CSCF invokes the IMS-ALG function for a session. The same signalling flow applies for a session setup from the IMS core network towards the IMS access network with the exception that terminations T1 and T2 are then exchanged.
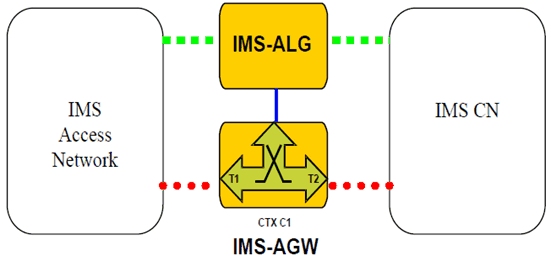
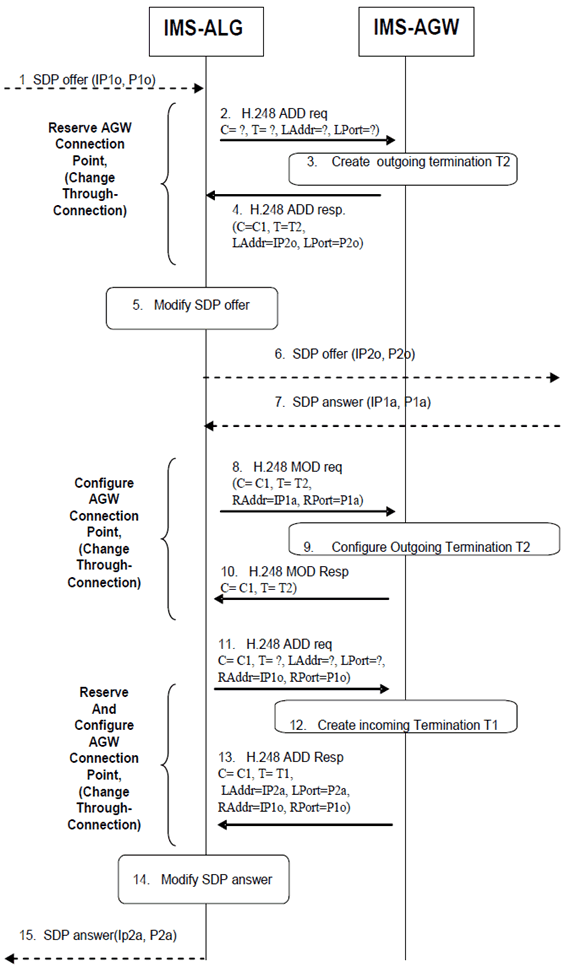
Figure 6.2.1.2: IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW interaction at session establishment
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Upon receipt of a session initiation request, the IMS-ALG shall extract the offerer's destination network address(es) and port number(s) from the signalling message body received from the calling party endpoint. It shall then request the IMS-AGW to allocate transport resources (T2) via the Reserve AGW Connection Point procedure. Upon receipt of the response from the IMS-AGW, the IMS-ALG shall modify the offerer's destination address(es) and/or port(s) contained in the application signalling message body and propagate the session establishment toward the terminating party.
On receipt of the terminating end SDP in the session establishment response, the IMS-ALG shall pass the information to the IMS-AGW in the Configure AGW Connection Point procedure and shall request the IMS-AGW to allocate transport resources (T1) via the Reserve and Configure AGW Connection Point. Upon receiving the response from the IMS-AGW, the IMS-ALG shall modify the answerer's destination address(es) and/or port(s) contained in the application signalling message body and pass the information to the originating party.
On session termination, the IMS-ALG shall request the IMS-AGW to release its transport resources via the Release AGW Termination procedure.
6.2.2 IP realm indication procedure p. 105
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally specifying the required IP Realm to the IMS-AGW when requesting the allocation of transport resources on the IMS-AGW.
6.2.3 Remote NA(P)T traversal support procedure p. 105
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally indicating to the IMS-AGW that the remote media address/port information (supplied by the IMS-ALG) shall not be used as the destination address for outgoing media. Instead, the IMS-AGW shall "latch" or "relatch" onto the required destination address via the source address/port of the incoming media. The IMS-ALG may command the IMS-AGW to latch once (on the first received packet) or to re-latch (i.e. to check for a change of source address on the incoming media stream and latch once on this new address).
6.2.4 Remote Source Address/Port Filtering p. 105
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally specifying the required IP address and/or port to be used to screen received media packets on a termination.
This clause considers when the IMS-ALG is acting as an Entry point and remote source transport address filtering is required towards the external network.
As a security related option, on request from the IMS-ALG, filtering may be enabled to check/validate the source address or source address and port number of incoming packets from the external network. If the IMS-ALG requests address filtering, it may additionally provide an address specification, which may identify either a single address or a range of addresses, against which filtering is to be performed. The absence of such an address specification in the request shall implicitly request filtering against the IP address of the remote connection address. In addition to address filtering, the IMS-ALG may also request port filtering. If the IMS-ALG requests port filtering, it may additionally include either a port or a range of ports, against which filtering is to be performed. The absence of a port specification in the request shall implicitly request filtering against the port of the remote connection address.
If the IMS-AGW is requested to apply source IP address and possibly source port filtering, it shall only pass incoming IP packets from the identified source, and discard IP packets from other sources.
If remote source address filtering is required for the created termination, then the IMS-ALG shall include the information element "Remote source address filtering" in the request sent to the IMS-AGW. In addition, it may also include the information element "Remote source address mask" in order to request filtering of a range of addresses.
If remote source port filtering is required for the created termination (in addition to remote source address filtering), then the IMS-ALG shall include the information element "Remote source port filtering" in the request sent to the IMS-AGW. It may also include one of the information elements "Remote source port" or "Remote source port range".
Subsequently, the IMS-AGW shall apply filtering as requested to the packets arriving from the external network. Any packet arriving, which does not meet the filtering requirement, shall be discarded.
6.2.5 Traffic Policing p. 106
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally requesting the IMS-AGW to police the media stream flow according to one or more of the following media policing(s) through the IMS-AGW, in accordance with RFC 2216.
The following media policing shall be supported at the IMS-AGW:
- Sustainable Data Rate (SDR) Policing: To request policing of the sustainable data rate of a media stream, the IMS-ALG shall request media policing for that media stream and shall provide the sustainable data rate, and shall provide a maximum burst size (MBS) indicating the expected maximum size of packet bursts for that media stream. The IMS-AGW shall then measure the data rate for the received packets within that media stream as per RFC 2216 for "Token Bucket", where r = SDR and b = MBS. If the permissible sustainable data rate is exceeded, the IMS-AGW shall discard packets to reduce the data rate to the permissible sustainable data rate.
- Peak Data Rate Policing: To request policing of the peak data rate of a media stream, the IMS-ALG shall request media policing for that media stream and shall provide the peak data rate, and may provide a Delay Variation Tolerance indicating the expected maximum delay variation due to jitter for that media stream. The IMS-AGW shall then measure the data rate for the received packets within that media stream. If the permissible peak data rate is exceeded, the IMS-AGW shall discard packets to reduce the data rate to the permissible peak data rate. If both peak data rate and sustainable data rate have been provided for the same media stream, the IMS-AGW shall discard packets to reduce the data rate to the permissible peak data rate and should discard packets to reduce the data rate to the permissible sustainable data rate.
6.2.6 Hanging Termination Detection p. 106
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG requesting the IMS-AGW to periodically report termination heartbeat indications to detect hanging context and termination in the IMS-AGW that may result e.g. from a loss of communication between the IMS-ALG and the IMS-AGW.
When the IMS-ALG receives a termination heartbeat notification from the IMS-AGW via the Termination heartbeat - Indication procedure, the IMS-ALG shall return a Termination heartbeat -Indication Ack (without an error) if the context id / termination identity combination exists in the IMS-ALG. If it does not exist, the IMS-ALG shall return an error and shall correct the mismatch, e.g. by requesting the IMS-AGW to subtract the indicated termination and to clear any associated context.

6.2.7 QoS Packet Marking p. 107
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally specifying the setting of the DSCP for outgoing packets on a termination. The DSCP value may be explicitly set by the IMS-AGW or else copied from that received in the corresponding received packet.
If differentiated services are required for the created termination, then the IMS-ALG shall include the information elements "DiffServ Code Point" and/or "DiffServ Tagging Behaviour" in the request sent to the IMS-AGW.
Subsequently, for all egress packets, the IMS-AGW shall set the DiffServ Code Point in the IP header as specified by the IMS-ALG:
- If the DiffServ Tagging Behaviour information element was received with a value to indicate that the DiffServ Code Point should be copied, then the DiffServ Code Point in the IP header of the egress packet is copied from the ingress packet.
-
If the Diffserv Tagging Behaviour information element was not received, or was received with a value to indicate that the DiffServ Code Point should be set to a specific value, then:
- If the DiffServ Code Point information element was received, then the DiffServ Code Point in the IP header of the egress packet shall be set to the value received in the DiffServ Code Point information element.
- If the DiffServ Code Point information element was not received, then the DiffServ Code Point in the IP header of the egress packet shall be set to a configured default value.
6.2.8 Media Inactivity Detection p. 107
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally requesting the IMS-AGW to detect inactive media.
If media inactivity detection is required for the created termination, the IMS-ALG may include the information elements "Inactivity detection time" and "Inactivity detection direction" in the request sent to the IMS-AGW. The IMS-ALG may request the detection of media inactivity on a termination or a stream basis.
When the IMS-ALG receives a notification of inactive media from the IMS-AGW via the Media Inactivity Notification procedure, the IMS-ALG shall return a Media Inactivity Notification Ack and shall take appropriate action (e.g. release the termination).

6.2.9 Handling of RTCP streams p. 108
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG optionally requesting the IMS-AGW to allocate or not allocate RTCP resources. Additionally if RTCP handling is requested, the IMS ALG may include:
- the explicit RTCP transport address information element;
- the RTP/RTCP transport multiplexing information element; and
- the bandwidth allocation for RTCP,