Content for TS 23.334 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.11…
5.12…
5.14…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
6…
6.1.6…
6.1.11…
6.2…
6.2.10…
6.2.10.3.1.2
6.2.10.3.2
6.2.10.4…
6.2.10.4.3…
6.2.10.5
6.2.10.6…
6.2.10A…
6.2.13…
6.2.14…
6.2.14.3
6.2.14.4…
6.2.15…
6.2.17…
6.2.17.3…
6.2.17.5…
6.2.18…
6.2.20
6.2.21…
6.2.22…
6.2.22.3…
6.2.22.3.2
6.2.23
6.2.24
6.2.25
7
8…
8.3
8.4
8.5…
8.23…
6.2.18 TCP bearer connection control
6.2.18.1 General
6.2.18.2 Stateless TCP handling
6.2.18.3 State-aware TCP handling without support of modifying the TCP setup direction
6.2.18.4 State-aware TCP handling with support of modifying the TCP setup direction
6.2.19 Application-aware MSRP interworking at the IMS-AGW
...
...
6.2.18 TCP bearer connection control |R12| p. 169
6.2.18.1 General p. 169
All message sequence charts in this clause are examples. The H.248 context model is defined in Figure 6.2.1.1.
6.2.18.2 Stateless TCP handling p. 169
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW applying the requirements specified in clause 5.16.1.
6.2.18.3 State-aware TCP handling without support of modifying the TCP setup direction p. 169
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW applying the requirements specified in clause 5.16.2.2.
Clause 6.2.10.3.1 provides example call flows for TCP bearer connection establishment without modyfing the TCP setup direction.
6.2.18.4 State-aware TCP handling with support of modifying the TCP setup direction p. 169
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW applying the requirements specified in clause 5.16.2.3.
Figure 6.2.18.4.1 shows an example call flow for a terminating session set-up procedure, where the IMS-ALG receives an incoming SDP offer containing media line for a new MSRP media stream with an "a=setup:active" SDP attribute towards a served UE located behind a remote NAT.
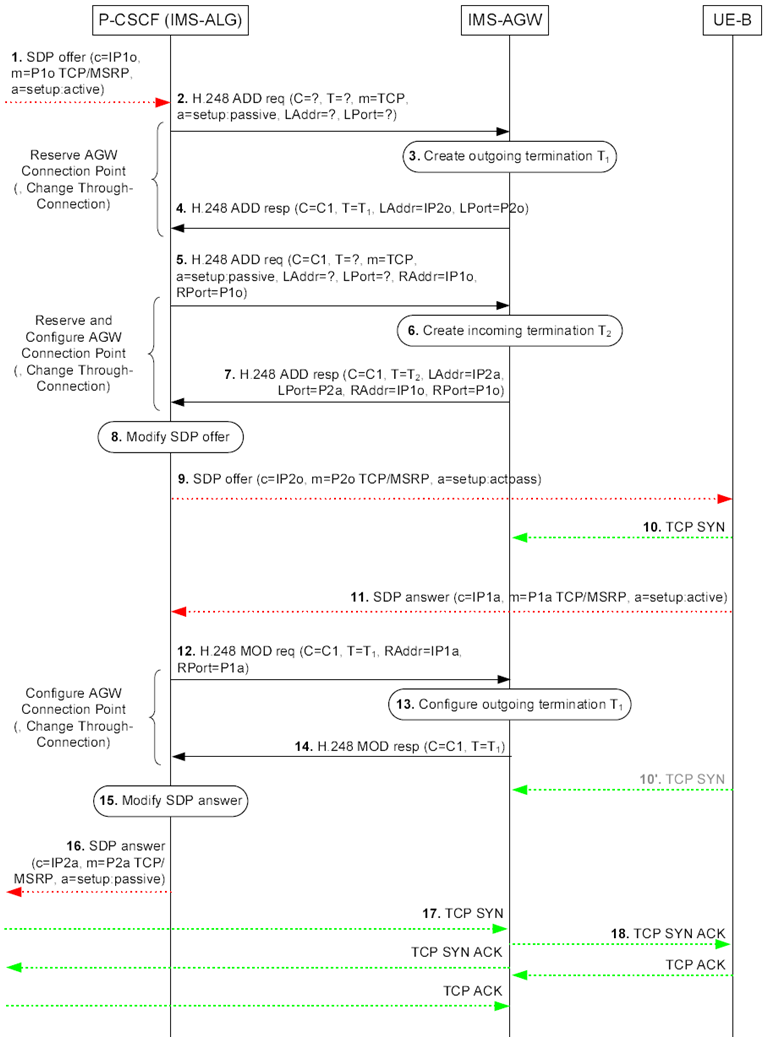
Figure 6.2.18.4.1: Terminating example call flow for MSRP between UEs located behind NAT
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The IMS UE B performs an IMS terminating session set-up according to TS 23.228, with modifications as described in TS 33.328.
The procedure in the above Figure is described step-by-step with an emphasis on the additional aspects for IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW of TCP bearer connection control.
Step 1.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) receives an SDP offer for an MSRP media stream with an "a=setup:active" attribute. For the MSRP media stream offered with transport "TCP/MSRP", the P CSCF (IMS ALG) allocates the required resources, includes the IMS AGW in the media path and proceeds as specified in this clause.
Step 2.-4.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP" media (for application-agnostic interworking) or "TCP/MSRP" media (for application-aware interworking) towards the access network. The IMS-ALG preconfigures the IMS-AGW to operate in TCP merge mode by providing the "a=setup:passive" attribute.
Step 5.-7.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve And Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP" media (for application-agnostic interworking) or "TCP/ MSRP" media (for application-aware interworking) towards the core network. The IMS-ALG preconfigures the IMS-AGW to operate in TCP Merge mode by providing the "a=setup:passive" attribute.
Step 8.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) changes the "a=setup" SDP attribute to "actpass" in the SDP offer and inserts the address information received from the IMS-AGW.
Step 9.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) forwards the SDP offer.
Step 10.
The UE B chooses to become the active party in the TCP connection establishment and sends a TCP SYN to establish the TCP connection. If the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) indicated to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall ignore any incoming TCP connection establishment requests (TCP SYN), e.g. to enable a remote source transport address filtering, or if the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) did not indicate to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall latch onto the required destination address via the source address/port of the incoming media, the IMS-AGW shall drop the TCP SYN received from the UE.
If the TCP SYN is not answered before a timer expiry, the UE will send the TCP SYN a second time (step 10').
Step 11.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) receives the SDP answer. It contains the SDP answer with an "a=setup:active" attribute.
Step 12.-14.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to configure the termination towards the UE B with remote address information.
Step 15.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) modifies the SDP answer before sending it to the core network. The P CSCF (IMS ALG) sets the "a=setup:passive" SDP attribute.
Step 16.
The P-CSCF (IMA-ALG) then sends the updated SDP answer to core network.
Step 17.
The IMS-AGW answers the TCP SYN and the remote peer completes the TCP connection establishment.
Step 18.
The IMS-AGW answers the TCP SYN and UE B completes the TCP connection establishment.
6.2.19 Application-aware MSRP interworking at the IMS-AGW |R12| p. 171
This procedure is identical to that of clause 6.2.1 apart from the IMS-ALG:
- indicating "TCP/MSRP" or "TCP/TLS/MSRP" (if e2ae media security is applied) as transport protocol to the IMS AGW;
- configuring the IMS-AGW to apply application-aware MSRP interworking; and
- providing the SDP "a=path" attribute, as received in SIP/SDP signalling, to the IMS AGW as "MSRP Path" with the remote descriptor of the corresponding call leg.