Content for TS 23.284 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3…
5
6…
6.3…
6.3.2
6.3.3
6.3.4
6.3.5
7…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.2
7.2.4.3
7.2.4.4
7.2.4.5
7.2.4.6
7.3…
7.3.4…
7.3.4.2
7.3.4.3
7.3.4.4
8…
8.2.3
8.3…
8.3.2
8.4…
8.4.1.1.7…
8.4.1.2…
8.4.2…
8.4.2.2…
8.4.5…
8.4.5.6
8.4.5.7
8.4.5.8…
9…
13…
13.4…
13.4.3…
13.4.4…
13.5…
13.6…
13.7…
14…
16…
A…
A.2…
6.3.3 LCLS not established, Basic Call Example with BICC based CS core network p. 35
The Figure 6.3.3.1 shows the message sequence example for the basic call establishment for LCLS when the call could not be locally switched. In this example the CN permits LCLS but the oUE and the tUE belong to different BSS's (marked as oBSS and tBSS). The example is based on examples from TS 23.205 for the basic mobile originating call, forward bearer establishment and the basic mobile terminating call, forward bearer establishment.
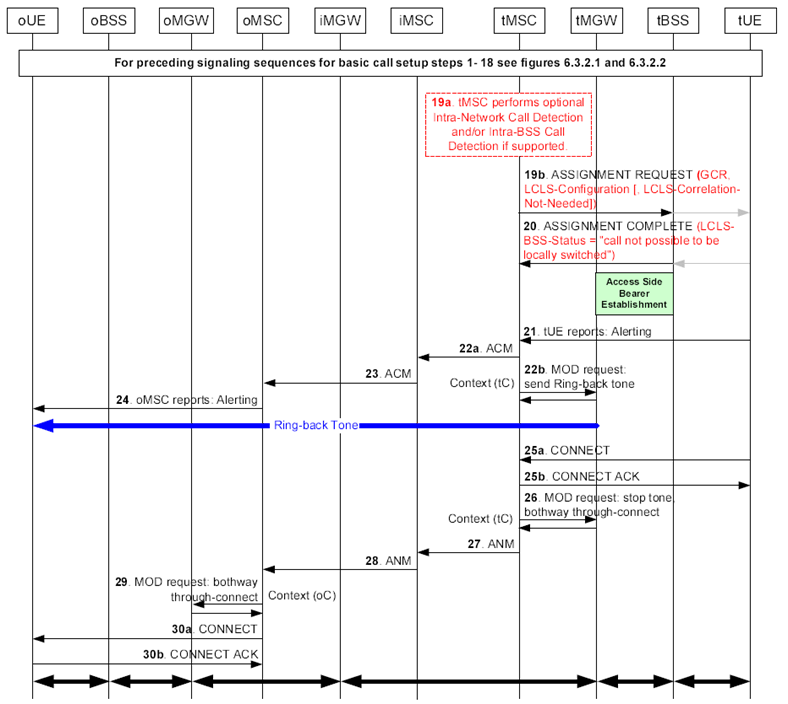
Figure 6.3.3.1: Basic Call Establishment Flow when call is not locally switched
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1 - 18.
The basic call establishment procedure between the UE-1 and the UE-2 is the same as specified in steps 1-18 of Figure 6.3.2.1.
Step 19a.
If the tMSC server supports the optional "Intra-Network Call Detection" procedure it may compare its own Network ID with the Network ID received within the Global Call Reference (GCR) IE.
If the tMSC server supports the optional "Intra-BSS Call Detection" procedure it may compare the BSS ID of the selected terminating BSS with the value of the originating BSS ID received within the GCR IE at this step.
In this case, the result of the "Intra-Network Call Detection" procedure or "Intra-BSS Call Detection" procedure is that the call is not an intra-Network or an intra-BSS call.
Step 19b.
The tMSC server performs the terminating access bearer assignment and sends the ASSIGNMENT REQUEST message containing the GCR IE and the LCLS-Configuration IE if LCLS is permitted in the core network.
If the tMSC server performed the "Intra-Network Call Detection" procedure in step 19a and/or the tMSC server performed the "Intra-BSS Call Detection" procedure in step 19a, then the tMSC server includes the "LCLS-Correlation-Not-Needed" IE in the ASSIGNMENT REQUEST message since the oUE and the tUE belong to the different BSS's.
Step 20.
The tBSS returns the ASSIGMENT COMPLETE message with the LCLS-BSS-Status IE indicating "Call Not Possible to be Locally Switched".
Step 21 - 30.
The basic call establishment procedure between the UE-1 and the UE-2 continues as for the normal, non-LCLS call.