Content for TS 23.273 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.2a…
4.3…
5…
5.5…
6…
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.2
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.4
6.5…
6.7…
6.7.3
6.7.4
6.7.5
6.8
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.19.2…
6.20…
6.20.4…
6.21…
7…
8…
A…
B…
C…
6.11 Common Sub-Procedures
6.11.0 General
6.11.1 UE Assisted and UE Based Positioning Procedure
6.11.2 Network Assisted Positioning Procedure
6.11.3 Obtaining Non-UE Associated Network Assistance Data
6.11.4 Positioning Procedure over User Plane
...
...
6.11 Common Sub-Procedures p. 103
6.11.0 General |R18| p. 103
The procedures defined in clause 6.11 are applicable to both a UE and PRU. Wherever, a UE is referenced in these procedures, a PRU may be used instead.
6.11.1 UE Assisted and UE Based Positioning Procedure p. 103
Figure 6.11.1-1 shows a positioning procedure used by an LMF to support UE based positioning, UE assisted positioning and delivery of assistance data. The procedure is based on use of the LPP protocol defined in TS 37.355 between the LMF and UE.
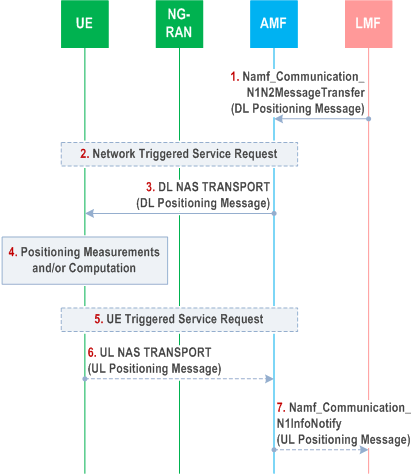
Precondition:
A LCS Correlation identifier and the AMF identity has been passed to the LMF by the serving AMF.
Step 1.
The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a Downlink (DL) Positioning message to the UE. The service operation includes the DL Positioning message. The Session ID parameter of the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation is set to the LCS Correlation identifier. The Downlink Positioning message may request location information from the UE, provide assistance data to the UE or query for the UE capabilities if the UE Positioning Capability is not received from AMF.
Step 2.
If the UE is in CM IDLE state, the AMF initiates a network triggered Service Request procedure as defined in clause 4.2.3.3 of TS 23.502 to establish a signalling connection with the UE.
Step 3.
The AMF forwards the Downlink Positioning message to the UE in a DL NAS TRANSPORT message. The AMF includes a Routing identifier, in the DL NAS TRANSPORT message, which is set to the LCS Correlation identifier. The Downlink Positioning message may request the UE to response to the network, e.g. may request the UE to acknowledge the Downlink Positioning message, to return location information or to return capabilities, as defined in TS 37.355.
Step 4.
The UE stores any assistance data provided in the Downlink Positioning message and performs any positioning measurements and/or location computation requested by the Downlink Positioning message.
Step 5.
If the UE has entered CM-IDLE state during step 4 and needs to responses to the request received in step 3, the UE instigates the UE triggered Service Request as defined in clause 4.2.3.2 of TS 23.502 in order to establish a signalling connection with the AMF.
Step 6.
[Conditional] The UE sends to the AMF the Uplink Positioning message included in a NAS TRANSPORT message, e.g. to acknowledge the Downlink Positioning message, to return any location information obtained in step 4 or returns any capabilities, as requested in step 3. When the UE sends Uplink Positioning message in a NAS TRANSPORT message, the UE shall also include in the UL NAS TRANSPORT message the Routing identifier received in step 3.
Step 7.
[Conditional] The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the routing identifier received in step 6. The service operation includes the Uplink Positioning message received in step 6 and the LCS Correlation identifier. Steps 6 and 7 may be repeated if the UE needs to send multiple Uplink Positioning messages to respond to the request received in Step 3. Steps 1 to 7 may be repeated to send new assistance data, and to request further location information and further UE capabilities.
6.11.2 Network Assisted Positioning Procedure p. 104
Figure 6.11.2-1 shows a procedure that may be used by an LMF to support network assisted and network based positioning. The procedure may be based on an NRPPa protocol in TS 38.455 between the LMF and NG-RAN.
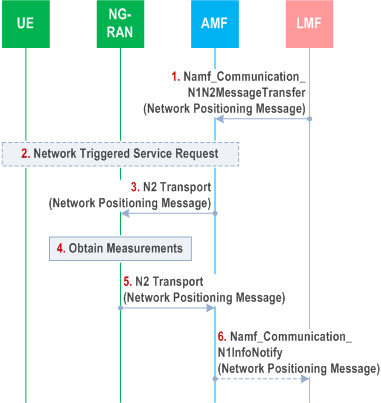
Precondition:
A LCS Correlation identifier and the AMF identity have been passed to the LMF by the serving AMF. In the case of PRU, LCS Correlation identifier is generated by LMF and provided to AMF during PRU Registration Accept message.
Step 1.
The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a Network Positioning message to the serving NG-RAN node (gNB or ng-eNB) for the UE. The service operation includes the Network Positioning message and may indicate if the positioning is initiated towards a PRU and the LCS Correlation identifier. The Network Positioning message may request location information for the UE from the NG-RAN and may include UE unaware indication if it is received by LMF from AMF. LMF may provide an LPHAP Assistance Information to RAN in an NRPPa message, if LPHAP indication is received in step 11 clause 6.1.2.
Step 2.
If the UE is in CM IDLE state and there is no UE unaware indication for the UE in the UE's location context, the AMF initiates a network triggered Service Request procedure as defined in clause 4.2.3.3 of TS 23.502, to establish a signalling connection with the UE. If positioning towards a PRU is indicated in step 1, the AMF verifies the UE is a valid PRU before initiating the procedure.
If the UE is in CM-IDLE state and there is UE unaware indication for the UE in the UE's location context, the AMF should reject the forwarding request of the Network Positioning message with a proper rejection cause value and steps 3-6 are skipped.
Step 3.
The AMF forwards the Network Positioning message to the serving NG-RAN node in an N2 Transport message. The AMF includes a Routing identifier, in the N2 Transport message, identifying the LMF.
Step 4.
The serving NG-RAN node obtains any location information for the UE requested in step 3.
If UE unaware indication is received in the Network Positioning message, and the UE is in RRC_INACTIVE state, the NG-RAN rejects the Network Positioning message with appropriate rejection cause (e.g. UE cannot be paged).
Step 5.
The serving NG-RAN node returns any location information obtained in step 4 to the AMF in a Network Positioning message included in an N2 Transport message. The serving NG-RAN node shall also include the Routing identifier in the N2 Transport message received in step 3.
Step 6.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N2InfoNotify service towards the LMF indicated by the routing identifier received in step 5. The service operation includes the Network Positioning message received in step 5 and the LCS Correlation identifier. Steps 1 to 6 may be repeated to request further location information and further NG-RAN capabilities.
6.11.3 Obtaining Non-UE Associated Network Assistance Data p. 105
Figure 6.11.3-1 shows a procedure which may be used by an LMF to support network assisted and network based positioning. This procedure is not associated with a UE location session. It is used to obtain network assistance data from a NG-RAN node (e.g. gNB or ng-eNB). The procedure may be based on an NRPPa protocol in TS 38.455 between the LMF and NG-RAN.
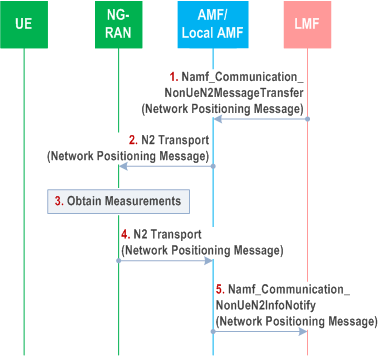
Step 1.
The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a Network Positioning message to a NG-RAN node (gNB or ng-eNB) in the NG-RAN. The service operation includes the Network Positioning message and the target NG-RAN node identity. The Network Positioning message may request position related information from the NG-RAN.
Step 2.
The AMF forwards the Network Positioning message to the target NG-RAN node indicated in step 1 in an N2 Transport message. The AMF includes a Routing identifier, in the N2 Transport message, identifying the LMF.
Step 3.
The target NG-RAN node obtains any position related information requested in step 2.
Step 4.
The target NG-RAN node returns any position related information obtained in step 3 to the AMF in a Network Positioning message included in an N2 Transport message. The target NG-RAN node shall also include the Routing identifier in the N2 Transport message received in step 2.
Step 5.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the routing identifier received in step 4. The service operation includes the Network Positioning message received in step 4. Steps 1 to 5 may be repeated to request further position related information from the NG-RAN.
6.11.4 Positioning Procedure over User Plane |R18| p. 106
The flow below shows a positioning procedure used by an LMF and/or UE over User Plane. The procedure is based on use of the LPP protocol defined in TS 37.355 between the LMF and UE. Prerequisite of this procedures is User Plane establishment between UE and LMF described in in clause 6.18.
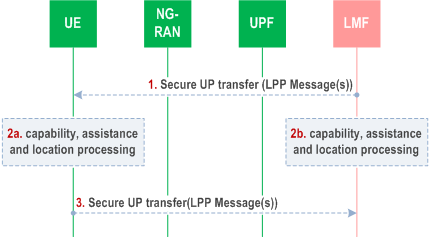
Step 1.
[Optional] The UE or LMF use the Secure UP transfer one or multiple LPP message(s). If LMF starts the procedure the LMF may request location information and/or measurements from the UE, and/or provide assistance data to/from the UE and/or query for the capabilities; if UE starts procedure, UE may request assistance data from LMF and/or providing location data and/or capability information to LMF.
Step 2.
[Optional] The UE or LMF processes capabilities information, assistance data, and/or location measurements/calculations.
Step 3.
[Optional] The UE or LMF may send one or multiple LPP message(s) using the Secure UP transfer.