Content for TS 23.273 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.2a…
4.3…
5…
5.5…
6…
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.2
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.4
6.5…
6.7…
6.7.3
6.7.4
6.7.5
6.8
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.19.2…
6.20…
6.20.4…
6.21…
7…
8…
A…
B…
C…
6.18 Procedures of User Plane Connection between UE and LMF
6.18.0 General
6.18.1 LMF initiated User Plane Connection
6.18.2 UE initiated User Plane Connection
6.18.3 Modification of User Plane Connection between UE and LMF
...
...
6.18 Procedures of User Plane Connection between UE and LMF |R18| p. 130
6.18.0 General p. 130
Clause 6.18 describes the management of the user plane connection between UE and LMF. LMF or UE may trigger the establishment of the user plane connection.
UE and LMF may maintain the established user plane connection. LMF may modify or terminate the established user plane connection between UE and LMF.
Precondition:
The LMF can send its user plane information (i.e. IP address or FQDN) to the UE via a DL NAS TRANSPORT message of the AMF. If LMF sends its FQDN to the UE, a DNS server/resolver is used to resolve the IP address of LMF (e.g. EASDF or local DNS for local LMF address resolution). UE uses URSP which includes user plane positioning related PDU session parameters (e.g. a dedicated DNN and S-NSSAI) to establish a PDU session used for user plane positioning. SMF should select a PSA UPF (located in central site or local site) connecting with the LMF for this PDU session, based on S-NSSAI, DNN and UE location information, etc.
Session break out for local LMF service for user plane positioning can be supported by preconfiguring SMF with local LMF(s) IP address(es)/network prefix(es) and their DNAIs for positioning dedicated PDU session in certain service area(s) for local PSA and UL CL/BP insertion.
6.18.1 LMF initiated User Plane Connection p. 130
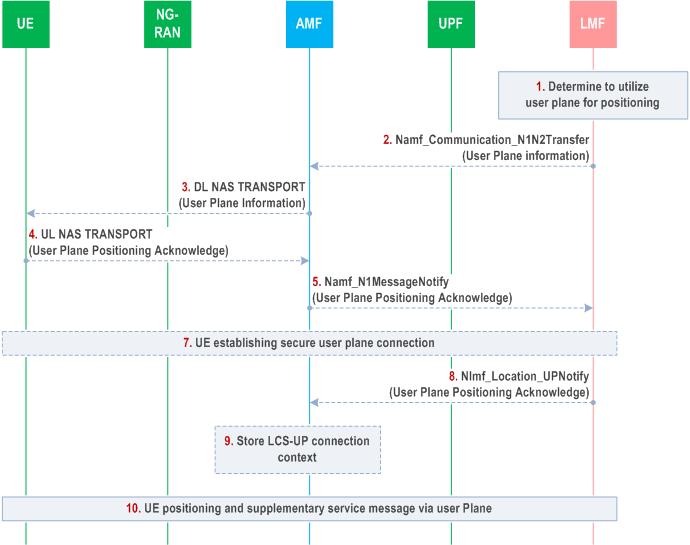
LMF may trigger the user plane connection establishment after receiving a location request from AMF if target UE does not have user plane connection with LMF. AMF may subscribe from LMF the status of LCS user plane connection for the target UE, using a Nlmf_Location_UP Subscribe message if the UE supports user plane positioning. Figure 6.18.1-1 shows a procedure triggered by LMF to support positioning over the user plane connection between UE and LMF.
Step 1.
Based on UE user plane positioning capability, control plane congestion status (e.g. AMF load status) and other implementation factors, LMF decides whether to use the positioning procedure via a user plane connection between UE and LMF.
LMF may invoke Nnrf_NFDiscovery service operation to retrieve control plane congestion status (e.g. AMF load information). LMF may also invoke Nnrf_NFManagement_NFStatusSubscribe service to subscribe specific AMF load information. Based on AMF load information, LMF may determine to use user plane positioning, if there is available user plane connection between UE and LMF.
Steps 2-8 are skipped if there is already a user plane connection context of the target UE in LMF and LMF determines to utilize the user plane connection for positioning.
Step 2.
[Conditional] If LMF decides to utilize user plane for positioning and there is no established secure user plane connection between the UE and LMF, LMF invokes Namf_communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation to send the user plane information to AMF in a NAS container to indicate UE to utilize user plane over TLS for positioning. The user plane information includes the user plane positioning address of the LMF. The LMF allocates LCS-UP binding ID to be used to associate the user plane connection to be established with the target UE and includes this LCS-UP binding ID in the user plane information. The LMF associates the target UE identity (SUPI and/or GPSI) with this LCS-UP binding ID.
If the UE supports the user plane positioning capability and AMF has not subscribed the status of LCS user plane connection, the AMF may subscribe from LMF the status of LCS user plane connection.
Step 3.
[Conditional] When AMF receives the user plane information from LMF in step 2, AMF sends it to UE via a DL NAS TRANSPORT message.
Step 4.
[Conditional] If there is no established applicable PDU session for the user plane positioning, the UE uses the URSP as defined in TS 23.503 which includes user plane positioning related PDU session parameters, e.g. a dedicated DNN and S-NSSAI, to establish the PDU session for user plane positioning. UE establishes a secured user plane connection with LMF. If LMF send its FQDN to the UE, a DNS server/resolver is used to resolve the IP address of LMF (e.g. EASDF or local DNS for local LMF address resolution). After the secured user plane connection been established successfully, the UE sends the LCS-UP binding ID received in step 3 to LMF via the secured user plane connection to enable LMF to perform the correlation of the UE with the secured user plane connection. The LCS-UP binding ID will be released once the correlation is complete.
Step 5.
[Conditional] UE sends an acknowledgement to LMF through AMF to indicate a success of user plane connection establishment for positioning service or a failure to utilize the user plane connection as defined in TS 24.572.
Step 6.
[Conditional] AMF sends the acknowledgement received in step 5 to the LMF via Namf_N1messageNotify service.
Step 7.
[Conditional] LMF indicates AMF in the Nlmf_Location_UPNotify message that user plane connection between the UE and LMF has been established.
Step 8.
[Conditional] The AMF stores the LCS-UP connection context as part of UE context.
Step 9.
If LMF or UE determines to utilize the user plane connection for positioning and the secure user plane connection is established, LPP messages are transferred between UE and LMF for UE based positioning, UE assisted positioning and delivery of assistance data. Supplementary services messages including event report messages, periodic triggered invoke messages and MS cancel deferred location messages may also be transferred between LMF and UE via the established user plane connection.
6.18.2 UE initiated User Plane Connection p. 132
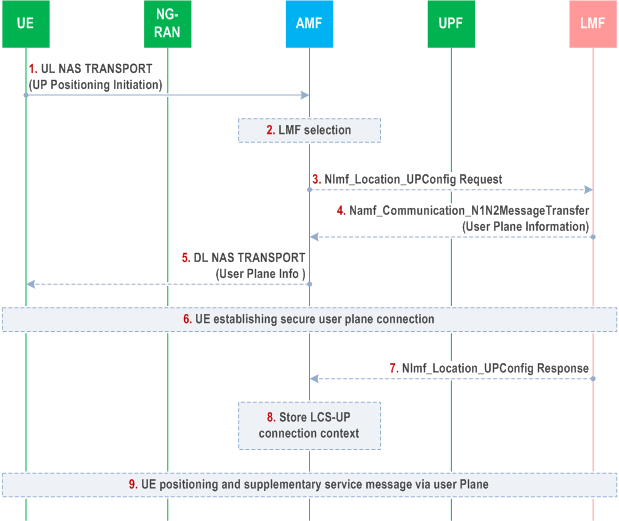
UE may trigger the user plane connection establishment if the UE does not have user plane connection with LMF. Figure 6.18.2-1 shows a procedure triggered by UE to support positioning over the user plane connection between UE and LMF.
Step 1.
UE sends a user plane connection establishment request to AMF via NAS Message, if there is no established secure user plane connection between the UE and LMF and UE decides to request a user plane connection for upcoming positioning requests.
Step 2.
[Conditional] If the UE is authorized based on UE Subscription to use the user plane positioning, AMF selects an LMF which capable to establish a user plane session for positioning with the UE. AMF may either query the NRF or based on local configuration to discover and select a proper LMF.
Step 3.
[Conditional] The AMF sends a Nlmf_Location_UPConfig Request towards LMF to request set up of an LCS-UP connection. The AMF shall include the target UE identity (see TS 29.572) (SUPI and/or GPSI) in the request.
Step 4.
[Conditional] If LMF accepts to utilize user plane for positioning and there is no established secure user plane connection between the UE and LMF, LMF sends a user plane information to AMF to indicate UE to accept and utilize user plane for positioning. The user plane information includes the user plane positioning address of the LMF. The LMF allocates a LCS-UP binding ID to associate the user plane connection to be established with the target UE and includes the LCS-UP binding ID in the user plane information. The LMF associates the target UE identity (SUPI and/or GPSI) with the LCS-UP binding ID.
Step 5.
[Conditional] When AMF receives the user plane information from LMF in step 4, AMF forwards it to UE via a DL NAS TRANSPORT message.
Step 6.
[Conditional] If there is no established secure user plane connection, UE establishes a secured user plane connection with LMF. UE uses the user plane positioning address of the LMF, together with the information in the URSP, to determine the PDU session parameters including DNN+S-NSSAI. UE uses the PDU session parameter to establish PDU session. When SMF receives the request, it selects a proper UPF based on the DNN+S-NSSAI, and establishes the connection between the UPF and LMF.
After the secured user plane connection has been established successfully, the UE sends the LCS-UP binding ID received in step 4 to LMF via the secured user plane connection to enable LMF to perform the correlation of the UE with this secured user plane connection. The LCS-UP binding ID will be released once the correlation is complete.
Step 7.
[Conditional] UE sends an acknowledgement to LMF through AMF to indicate a success of user plane connection establishment for positioning service or a failure to utilize the user plane connection as defined in TS 24.572.
Step 8.
[Conditional] AMF sends the acknowledgement received in step 7 to the LMF via Namf_N1messageNotify service.
Step 9.
[Conditional] LMF responds to AMF that user plane connection between the UE and LMF has been established.
Step 10.
[Conditional] The AMF stores the LCS-UP connection context as part of UE context
Step 11.
[Conditional] After the secure user plane connection is established, if LMF determines to utilize the user plane connection for positioning after receiving a positioning request from AMF, or UE determines to utilize the user plane connection for positioning, LPP messages are transferred between UE and LMF for UE based positioning, UE assisted positioning and delivery of assistance data. Supplementary services messages including event report messages, periodic triggered invoke messages and MS cancel deferred location messages may also be transferred between LMF and UE via the established user plane connection.
6.18.3 Modification of User Plane Connection between UE and LMF p. 134
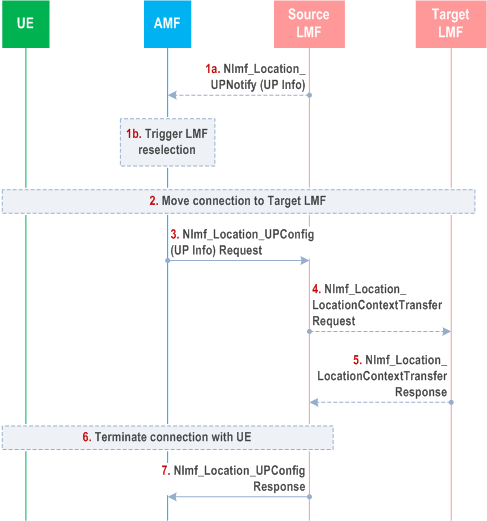
The Figure 6.18.3-1 shows how a secure user plane connection between UE and LMF is modified. The flow describes change of LMF but applies also when source and target LMF is the same. The procedure can also be used to terminate the user plane connection to Source LMF not selecting any Target LMF.
Step 1a.
[Conditional] The LMF discovers a need to change LMF or re-establish the user plane connection between UE and LMF or terminate the user plane connection, e.g. after receiving an event report via user plane from UE or after receiving an AMF relocation information from a target AMF (target AMF obtains from source AMF the UE LCS-UP context which indicates UE has maintained LCS-UP connection with the source LMF, the target AMF may inform the source LMF about the AMF change using the Nlmf_Locatoion_UPConfig request). The LMF sends an Nlmf_Location_UPNotify message that includes connection move (termination and establishment) or termination is required and if connection move is requested then message may include target LMF identification. The address of the AMF was provided to LMF as a "Notification Target Address" in latest Nlmf_Location_UPConfig message or Nlmf_Location_UP Subscribe message. If the LMF is going to terminate the user plane connection, step 1a, step 3, step 6 and step 7 are performed and other steps are skipped.
If the request is to terminate the user plane connection, the AMF releases the LCS-UP context.
Step 1b.
[Conditional] AMF based on target LMF identification received from source LMF for user plane positioning, or AMF may perform LMF reselection if UE moves to a new location (which may be out of serving area of source LMF and in serving area of target LMF) and select the target LMF for the current UE location based on LMF service area, LMF user plane positioning capability information and other information listed in clause 5.1. LMF needs to be capable to establish a user plane session for positioning with the UE. After AMF relocation, the target AMF may tigger the LMF reselection and LCS-UP connection modification procedure, e.g. if the source LMF does not perform LMF reselection.
Step 2.
[Conditional] Steps 3-10 of Figure 6.18.2-1 are performed between AMF (or Target AMF), UE, and Target LMF with addition that UE also terminate connection to Source LMF.
Step 3.
The AMF sends an Nlmf_Location_UPConfig Request towards the source LMF. The message may include a request for the Source LMF to terminate a specific user plane connection to the UE and the Target LMF identification. Alternatively, it may include information about AMF reallocation.
Step 4-5.
[Conditional] The source LMF may invoke an Nlmf_Location_LocationContextTransfer Request service operation towards the target LMF to provide the current location context(s) of the UE, if there is user plane based periodic and triggered UE location events report context(s). The target LMF informs source LMF of the location context transfer operation results.
Step 6.
[Conditional] If the user plane connection to source LMF is still active, the source LMF terminates the connection to the UE.
Step 7.
The LMF sends Nlmf_Location_UPConfig Response message to AMF to confirm connection termination or acknowledge change of AMF. If this procedure is used for termination, the AMF will release the LCS-UP context after receiving the response message.