Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 18.4.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
6.2 Key hierarchy, key derivation, and distribution scheme p. 58
6.2.1 Key hierarchy p. 58
Requirements on 5GC and NG-RAN related to keys are described in clause 5.1.3. The following describes the keys of the key hierarchy generation in a 5GS in detail.:
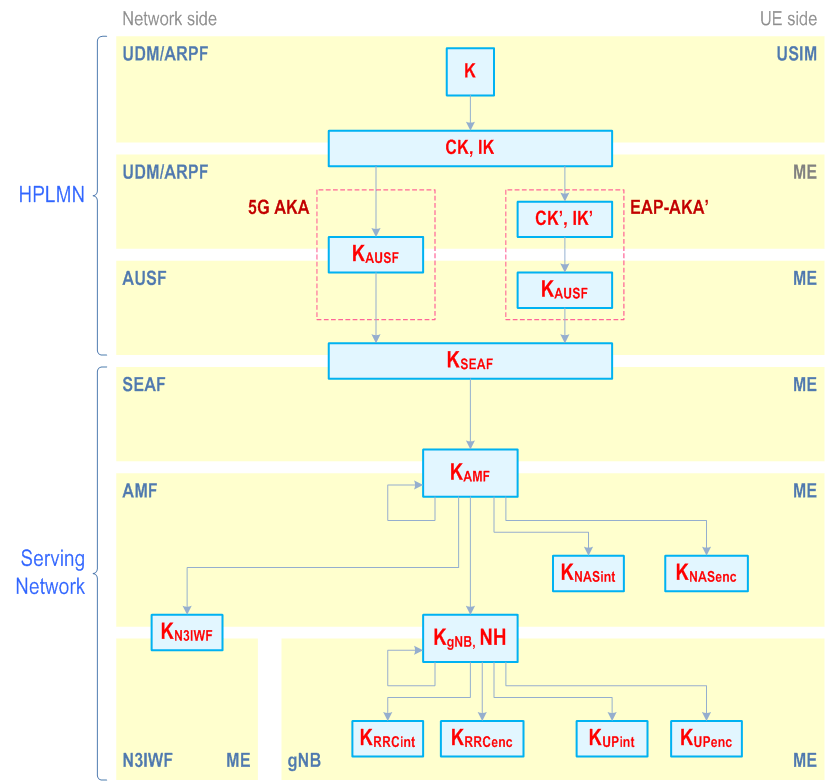
The keys related to authentication (see Figure 6.2.1-1) include the following keys: K, CK/IK. In case of EAP-AKA', the keys CK', IK' are derived from CK, IK as specified in clause 6.1.3.1.
The key hierarchy (see Figure 6.2.1-1) includes the following keys: KAUSF, KSEAF, KAMF, KNASint, KNASenc, KN3IWF, KgNB, KRRCint, KRRCenc, KUPint and KUPenc.
Keys for AUSF in home network:
-
KAUSF is a key derived
- by ME and AUSF from CK', IK' in case of EAP-AKA', CK' and IK' is received by AUSF as a part of transformed AV from ARPF; or,
- by ME and ARPF from CK, IK in case of 5G AKA, KAUSF is received by AUSF as a part of the 5G HE AV from ARPF.
- KSEAF is an anchor key derived by ME and AUSF from KAUSF. KSEAF is provided by AUSF to the SEAF in the serving network.
- KAMF is a key derived by ME and SEAF from KSEAF. KAMF is further derived by ME and source AMF when performing horizontal key derivation.
- KNASint is a key derived by ME and AMF from KAMF, which shall only be used for the protection of NAS signalling with a particular integrity algorithm.
- KNASenc is a key derived by ME and AMF from KAMF, which shall only be used for the protection of NAS signalling with a particular encryption algorithm.
- KgNB is a key derived by ME and AMF from KAMF. KgNB is further derived by ME and source gNB when performing horizontal or vertical key derivation. The KgNB is used as KeNB between ME and ng-eNB.
- KUPenc is a key derived by ME and gNB from KgNB, which shall only be used for the protection of UP traffic with a particular encryption algorithm.
- KUPint is a key derived by ME and gNB from KgNB, which shall only be used for the protection of UP traffic between ME and gNB with a particular integrity algorithm.
- KRRCint is a key derived by ME and gNB from KgNB, which shall only be used for the protection of RRC signalling with a particular integrity algorithm.
- KRRCenc is a key derived by ME and gNB from KgNB, which shall only be used for the protection of RRC signalling with a particular encryption algorithm.
- NH is a key derived by ME and AMF to provide forward security as described in Clause A.10.
- KNG-RAN* is a key derived by ME and NG-RAN (i.e., gNB or ng-eNB) when performing a horizontal or vertical key derivation as specified in Clause 6.9.2.1.1 using a KDF as specified in Clause A.11 / Clause A.12.
- KAMF' is a key that can be derived by ME and AMF when the UE moves from one AMF to another during inter-AMF mobility as specified in Clause 6.9.3 using a KDF as specified in Annex A.13.
- KN3IWF is a key derived by ME and AMF from KAMF for the non-3GPP access. KN3IWF is not forwarded between N3IWFs.