Content for TS 32.240 Word version: 19.0.0
A Bibliography p. 61
This annex contains guidelines for the references in all the charging specifications.
-
The 3GPP charging specifications
[1] - [99]
One example:
-
Common 3GPP specifications
[100] - [199]
-
other Domain and Service specific 3GPP / ETSI specifications
[200] - [299]
-
Relevant ITU Recommendations
[300] - [399]
One example: [300]ITU-T Recommendation D.93: "Charging and accounting in the international land mobile telephone service (provided via cellular radio systems)".
-
Relevant IETF RFCs
[400] - [499]
-
Others
[500] - [699]
One example: [601]Broadband Forum TR-134: "Broadband Policy Control Framework (BPCF)".
B (Normative) Single IMSI architecture for EU Roaming |R12| p. 62
B.0 General p. 62
To enable the sale of regulated roaming services, an architecture based on 3GPP has been defined in the high-level technical specification EU Roaming regulation III; Structural Solutions; High Level Technical Specifications [298]. A real-time interface has been defined in EU Roaming regulation III; Interface & Protocol; Detailed Technical Specifications [299] for retailing billing of voice calls between a Domestic Service Provider and an Alternative Roaming Provider.
For the purposes of this Annex, the following definitions apply:
Alternative Roaming Provider (ARP):
A roaming provider different from the domestic provider.
Domestic Service Provider (DSP):
An undertaking that provides a roaming customer with domestic mobile communications services, either a Mobile Network Operator or a Mobile Virtual Network Operator.
B.1 Voice Control p. 62
To enable charging of ARP subscribers for voice calls, an online charging interface between the DSP and ARP is established. The concept of voice call shall be interpreted as any Circuit-switched call, whatever the teleservice used (speech, 3.1 kHz audio, Fax, or CS data) except circuit-switched Video Telephony calls (BS 37, 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital info mode). The voice control architecture is shown in Figure B.1.1.
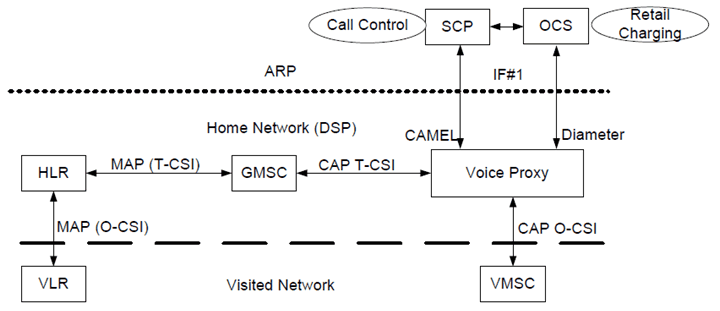
The signaling between the Visited Network and the DSP utilizes CAP for the online CS domain charging as specified in TS 32.250. For the CAMEL option of IF#1, the signaling between the DSP and ARP also utilizes CAP for the online CS domain charging as specified in TS 32.250. For the Diameter option of IF#1, the signaling between the DSP and ARP utilizes Diameter Ro for the Voice Call Service online charging as specified in TS 32.276 and utilizes the Proxy Function for mapping between CAMEL and Diameter as specified in TS 32.293.