Content for TS 29.116 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 xMB reference point
4.1 Overview
4.2 Reference model
4.3 Functional elements
4.3.1 BM-SC
4.3.2 Content Provider / Multicast Broadcast Source
4.4 Procedures over xMB reference point
4.4.1 Introduction
4.4.2 Authentication Procedures
4.4.3 Authorization Procedures
4.4.4 Service Management Procedures
4.4.5 Session Management Procedures
...
...
1 Scope p. 6
The present document describes the REST-based protocol for the xMB reference point between the Content Provider and the BM-SC. The xMB reference point and related stage 2 protocol procedures are defined in TS 23.246 and in TS 26.346.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.246: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS) Architecture and Functional Description".
[3]
TS 26.346: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS); Protocols and Codecs".
[4] Void.
[5] Void.
[6]
RFC 7231: "Hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content".
[7]
TS 33.210: "3G security; Network Domain Security (NDS); IP network layer security".
[8]
RFC 7235: "Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Authentication".
[9]
RFC 4918: "HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)".
[10]
TS 26.234: "Transparent end-to-end Packet-switched Streaming Service (PSS); Protocols and codecs".
[11]
RFC 3711: "The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)".
[12] Void.
[13] Void
[14] Void.
[15] Void.
[16] Void.
[17] Void.
[18]
TS 26.247: "Transparent end-to-end Packet-switched Streaming Service (PSS); Progressive Download and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (3GP-DASH)".
[19]
RFC 3926: "FLUTE - File Delivery over Unidirectional Transport".
[20]
TS 29.061: "Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) supporting packet based services and Packet Data Networks (PDN)".
[21]
TS 26.347: "MBMS URLs and APIs".
[22]
Open API Initiative, "OpenAPI 2.0 Specification": https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/2.0.md .
[23]
TS 23.285: "Architecture Enhancements for V2X services".
[24]
TS 33.246: "3G Security; Security of Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS)".
[25]
TS 24.116: "Stage 3 aspects of system architecture enhancements for TV services".
[26]
RFC 2617: "HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication".
[27]
RFC 5795: "The Robust Header Compression (ROHC) Framework".
[28]
RFC 3095: "Robust Header Compression (ROHC): Framework and four profiles: RTP, UDP, ESP, and uncompressed".
[29]
RFC 6363: "Forward Error Correction (FEC) Framework".
[30] Void.
[31]
RFC 1166: "Internet Numbers".
[32]
RFC 5952: "A recommendation for IPv6 address text representation".
[33]
TS 26.348: "Northbound Application Programming Interface (API) for Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS) at the xMB reference point".
[34]
RFC 8259: "The JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Data Interchange Format".
[35]
RFC 7396: "JSON Merge Patch".
[36]
TS 23.280: "Common functional architecture to support mission critical services; Stage 2".
[37]
TS 24.008: "Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network protocols; Stage 3".
[38]
RFC 7232: "Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Conditional Requests".
[39]
TS 23.222: "Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs; Stage 2".
[40]
TS 29.222: "Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs; Stage 3".
[41]
TS 33.122: "Security Aspects of Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs".
[42]
RFC 6749: "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework".
[43]
RFC 7616: "HTTP Digest Access Authentication".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 7
3.1 Definitions p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
Content Provider:
Entity/Entities which supplies/supply content in the form of streaming media or non-real-time (NRT) files to be delivered to UEs over the 3GPP network, via MBMS Bearer and/or unicast bearer services. Also referred to in this document as the Multicast Broadcast Source. The Content Provider may reside either inside or outside the operator's network.
Service:
One of the resource types exposed by the RESTful xMB API and operated on by a Content Provider using HTTP methods. It corresponds to a Content Provider's service offering for delivery over the MBMS network to UEs. Each service instance created over the xMB API maps to an MBMS User Service as specified by TS 26.346. The delivery of the contents of a created service is performed during one or more sessions associated with that service.
Session:
One of the resource types exposed by the RESTful xMB API and operated on by a Content Provider using HTTP methods. It represents one or more time intervals during which the MBMS Bearer is active for the transmission of service contents from the BM-SC to the UE. Each session instance, besides the activity times, may contain various properties pertaining to transport, media and application level information (session type, session state, data rate, permitted delay, user plane ingestion mode, targeted delivery area, reporting parameters, identification of content components delivered during the session, etc.).
3.2 Abbreviations p. 8
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
5GMS
5G Media Streaming
ARP
Allocation and Retention Priority
API
Application Programming Interface
BM-SC
Broadcast Multicast Service Center
CAPIF
Common API Framework
CDN
Content Delivery Network
CP
Content Provider
DASH
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
FEC
Forward Error Correction
FLUTE
File Delivery over Unidirectional Transport
GBR
Guaranteed Bitrate
HTTP
HyperText Transfer Protocol
IS
Initialization Segment
JSON
JavaScript Object Notation
MPD
Media Presentation Description
MSA
MBMS Service Area
PKI
Public Key Infrastructure
PSK
Pre-Shared Key
REST
Representational State Transfer
ROHC
Robust Header Compression
QCI
QoS Class Identifier
QoS
Quality of Service
SACH
Service Announcement Channel
SAF
Service Announcement Function
SLA
Service Level Agreement
TLS
Transport Layer Security
TMGI
Temporarily Mobile Group Identity
TSI
Transport Session Identifier
URI
Universal Resource Identifier
WebDAV
Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning
V2X
Vehicle-to-Everything
4 xMB reference point p. 8
4.1 Overview p. 8
Void
4.2 Reference model p. 8
The xMB reference point resides between the BM-SC and the Content Provider as depicted in Figure 4.2.1. Control- and user-plane procedures are operated over the xMB-C and xMB-U reference points, respectively. The overall xMB reference model is depicted in clause 4.1 of TS 26.348.
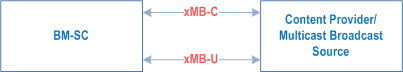
For the V2X Localized User Plane supported feature, the reference model in Clause B.3 of TS 23.285 applies.
4.3 Functional elements p. 9
4.3.1 BM-SC p. 9
The complete functionality of the BM-SC is defined in TS 26.346. In the context of the xMB reference point, the BM-SC represents the peer endpoint to the Content Provider in supporting all procedures on the xMB interface.
In addition to the functions defined in TS 26.346, the BM-SC may support, for V2X services, the V2X Localized User Plane procedures as defined in clause 5.4.2.2 of TS 23.285 for receiving Local MBMS information from the Content Provider acting as a V2X Application Server.
4.3.2 Content Provider / Multicast Broadcast Source p. 9
The functional role of the Content Provider is defined in clause 4.4.1a of TS 26.346. Using the xMB reference point, a Content Provider/Multicast Broadcast Source may provide media, as well as service descriptions and control data, to the BM-SC to set up and manage MBMS User Service(s) from the BM-SC to MBMS clients (the latter is not depicted in Figure 4.2.1).
In addition, the Content Provider which acts as a V2X Application Server may support V2X Localized User Plane procedures as defined in clause 5.4.2.2 of TS 23.285 for requesting the BM-SC to activate an MBMS bearer for Local MBMS based MBMS data delivery.
The content provider may also be a mission critical service provider (TS 23.280) which is arranging MC Services to Mission Critical Organizations and may require additional control of the resource allocation (QoS, coverage area).
The Content Provider may be a 5GMS Application Provider as defined in clause 4.1 of TS 26.348, providing 5G Media Streaming services to a 5GMS System.
4.4 Procedures over xMB reference point p. 9
4.4.1 Introduction p. 9
All procedures that operate across the xMB reference point, as specified in clause 5 of TS 26.348, are summarized in the following clauses.
4.4.2 Authentication Procedures p. 9
Authentication procedures shall be performed via (D)TLS as specified by TS 33.246. The Content Provider shall act as the (D)TLS client and the BM-SC as the (D)TLS server when the Content Provider wants to provision new services or manage existing services. Similarly, the BM-SC shall act as the client when the BM-SC wishes to send reports and notifications to the Content Provider. All of the following procedures require the authentication procedure to be completed successfully.
4.4.3 Authorization Procedures p. 10
The authorization procedure of the Content Provider towards the BM-SC may be based on the (D)TLS connection established as part of the authentication procedure (see clause 4.4.2). In that case, the BM-SC shall check if the Content Provider who sent a request over an authenticated (D)TLS connection is authorized to send that specific request. See clause 7.2 for further details.
The authorization procedure of the BM-SC towards the Content Provider to allow pushing notifications to the Content Provider may be based on the (D)TLS connection established as part of the authentication procedure (see clause 4.4.2). In that case, the Content Provider shall check if the BM-SC who sent the notification over an authenticated (See clause 7.2 for further details)(D)TLS connection is authorized to send that specific notification.
4.4.4 Service Management Procedures p. 10
4.4.4.1 Create Service p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to create a service at the BM-SC and negotiate the supported features for the created service. The Content Provider shall use HTTP POST for this purpose. A successfully created service is associated with a resource identifier which is used by the Content Provider to discover, update and delete the service.
4.4.4.2 Get Service Properties p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to obtain the service properties from the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP GET for this purpose.
4.4.4.3 Update Service Properties p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider for updating the service properties at the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP PUT or HTTP PATCH, corresponding to complete or partial update of service properties, respectively, for this purpose.
4.4.4.4 Delete Service p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to terminate the service at the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP DELETE for this purpose.
4.4.4.5 Service Notifications p. 10
This procedure is used by the BM-SC to send service related notifications to the Content Provider.
4.4.5 Session Management Procedures p. 10
4.4.5.1 Create Session p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to create a session for a previously created service at the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP POST for this purpose. A successfully created session is associated with a resource identifier which is used by the Content Provider to discover, update and delete the session.
4.4.5.2 Get Session Properties p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to obtain the session properties of a service from the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP GET for this purpose.
4.4.5.3 Update Session Properties p. 10
This procedure is used by the Content Provider for updating the session properties of a session at the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP PUT or HTTP PATCH, corresponding to complete or partial update of session properties, respectively, for this purpose.
If the V2X Localized User Plane feature is supported, the Content Provider may wish to update the session properties for Local MBMS based MBMS data delivery. If so, and the BM-SC decides to use the Local MBMS information, the BM-SC shall use the received BM-SC IP address and port for user plane data delivery.
If the MCExtension feature is supported, the content provider acting as a mission critical service provider may include:
- additional properties for resource allocation control (mc-extension in Table 5.2.2.1-1); and
- specific semantic and syntax for the geographical area (clause 5.4.7 of TS 26.348).
4.4.5.4 Delete Session p. 11
This procedure is used by the Content Provider to terminate a session of a service at the BM-SC. The Content Provider shall use HTTP DELETE for this purpose.