Content for TS 26.348 Word version: 18.0.0
0 Introduction
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Architecture
4.1 General
4.2 xMB reference point
...
...
0 Introduction p. 5
The present document defines a northbound interface between the BM-SC and the content provider. The interface is called xMB. Both external (3rd party) content providers and 3GPP defined API invokers e.g. GCS AS can use the xMB reference point to access BM-SC provided delivery services.
The xMB reference point supports different session types, such as generic file delivery e.g. for MCData, application streaming, including DASH streaming, RTP ingest and ingest for transparent delivery. The xMB reference point supports unicast delivery of content, e.g. for devices outside of the MBMS coverage area.
The xMB reference point is fully integrated into the Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs (CAPIF).
1 Scope p. 6
The present document provides interaction methods and interfaces between a BM-SC and a content provider. The purpose of the document is the definition of enablers for the usage of MBMS delivery.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 26.346: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS); Protocols and codecs".
[3]
TS 26.234: "Transparent end-to-end Packet-switched Streaming Service (PSS); Protocols and codecs".
[4]
TS 26.247: "Transparent end-to-end Packet-switched Streaming Service (PSS); Progressive Download and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (3GP-DASH)".
[5]
TS 33.310: "Network Domain Security (NDS); Authentication Framework (AF)".
[6]
RFC 6347: "Datagram Transport Layer Security Version 1.2", E. Rescorla, N. Modadugu.
[7]
RFC 4918: "HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)", L. Dusseault.
[8]
RFC 5795: "The Robust Header Compression (ROHC) Framework".
[9]
RFC 3095: "RObust Header Compression (ROHC): Framework and four profiles: RTP, UDP, ESP, and uncompressed".
[10]
TS 23.222: "Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs".
[11]
draft-wright-json-schema-01: "JSON Schema: A Media Type for Describing JSON Documents", April 15, 2017.
[12]
TS 23.280: "Common functional architecture to support mission critical services; Stage 2".
[13]
TS 29.061: "Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) supporting packet based services and Packet Data Networks (PDN)".
[14]
TS 29.468: "Group Communication System Enablers for LTE (GCSE_LTE); MB2 reference point; Stage 3".
[15]
RFC 5234 (January 2008): "Augmented BNF for Syntax Specifications: ABNF", D. Crocker and P. Overell.
[16]
TS 23.246: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS); Architecture and functional description".
[17]
TS 26.501: "5G Media Streaming (5GMS); General description and architecture".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 7
3.1 Definitions p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
5GMS
5G Media Streaming
ARP
Allocation and Retention Priority
BM-SC
Broadcast-Multicast - Service Centre
DASH
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
DTLS
Datagram Transport Layer Security
FEC
Forward Error Correction
GBR
Guaranteed Bitrate
HLS
HTTP Live Streaming
MPD
Media Presentation Description
QCI
QOS Class Identifier
QOS
Quality of Service
QOE
Quality of Experience
ROM
Receive Only Mode
RTSP
Real-Time Streaming Protocol
RTP
Real Time Transport Protocol
RTCP
Real Time Transport Control Protocol
SACH
Service Announcement Channel
SAI
Service Area Identity
SCEF
Service Capability Exposure Function
SDP
Session Description protocol
TLS
Transport Layer Security
TV
Television
UE
User Equipment
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
URL
Uniform Resource Locator
UTC
Universal Time Coordinated
4 Architecture p. 7
4.1 General p. 7
As shown in Figure 4.1-1, the reference point between Content Provider and BM-SC is called the xMB interface. Using the xMB reference point, content provider can invoke procedures supported by BM-SC(s) to set up and manage MBMS user service from BM-SC to the MBMS Clients. BM-SC defines an endpoint with all supported procedures on the xMB interface, which can then be converted to SGmb procedures for the interface between BM-SC and MBMS GW (not depicted).
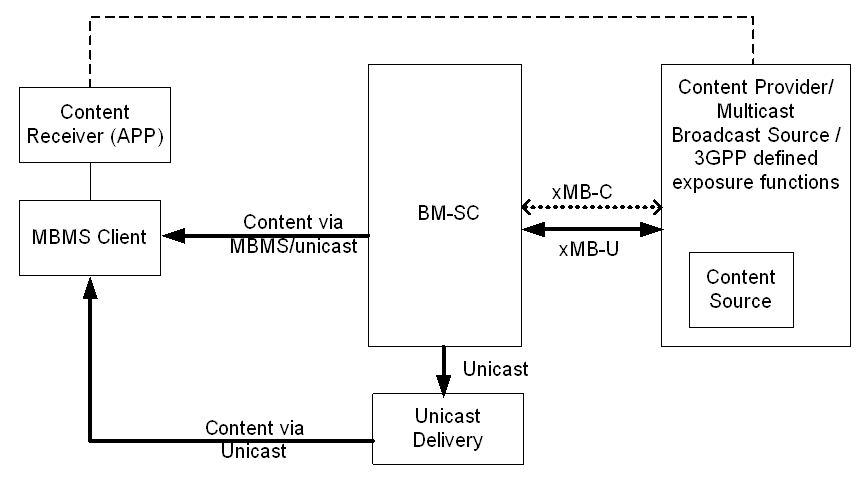
The BM-SC may forward the received content for unicast delivery for appropriate functions (e.g., MBMS user service fallback).
The control plane (xMB-C) and the user plane (xMB-U) may be optionally terminated by 3GPP defined enabler / exposure functions such as an SCEF, which exposes the same or a different interface to content providers. The exposed API such as by SCEF is not specified in the present document.
The content provider may optionally exchange application level information like service metadata (e.g. serviceIds or URL(s) of USD(s) or other service identifier(s)) directly with the application.
The BM-SC may support CAPIF [10]. When CAPIF is supported, then:
- the BM-SC shall support the CAPIF API provider domain functions (i.e. CAPIF-2/2e (xMB), CAPIF-3, CAPIF-4 and CAPIF-5 as specified in TS 23.222);
- the BM-SC xMB authentication and authorization functions (as defined in Clause 5.2) are replaced by CAPIF equivalent core domain functions (i.e. CAPIF-1/1e).
- additional properties within the control plane procedures (Table 5.4-6),
- specific semantic and syntax for the geographical area (Clause 5.4.7).
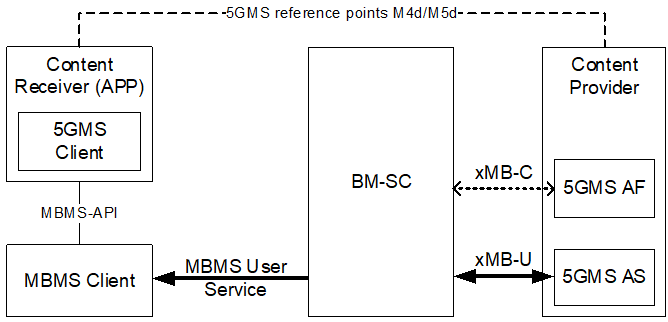
4.2 xMB reference point p. 9
The xMB reference point exists between the content provider and the BM-SC directly or via 3GPP defined enabler / exposure functions such as SCEF. When the BM-SC connects to content provider via a 3GPP defined enabler / exposure function, the xMB-C interface (and optionally also the xMB-U) is terminated at the 3GPP defined enabler / exposure function.
The xMB reference point provides the ability for the content provider to:
- authenticate and authorize BM-SC(s).
- create, modify and terminate a service.
- create, modify and terminate a session.
- query information.
- deliver content to the BM-SC(s)
- authenticate and authorize a content provider.
- notify the content provider of the status of an MBMS user service usage.
- retrieve content from the content provider.