Content for TS 29.061 Word version: 18.1.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
3.3 Symbols
4 Network characteristics
5 Interworking Classifications
6 Access reference configuration
7 Interface to Packet Domain Bearer Services
8 Subscription checking
8A Prevention of IP spoofing
9 Message Screening
10 Interworking with PSDN (X.75/X.25)
...
...
1 Scope p. 9
The present document defines the requirements for Packet Domain interworking between a:
- PLMN and PDN;
- PLMN and PLMN.
2 References p. 9
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1] Void.
[2]
TS 22.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service Description; Stage 1".
[3]
TS 23.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service Description; Stage 2".
[4] Void.
[5] Void.
[6] Void.
[7] Void.
[8] Void.
[9] Void.
[10]
TS 27.060: "Packet Domain; Mobile Station (MS) supporting Packet Switched services".
[11]
ITU-T Recommendation E.164: "The international public telecommunication numbering plan".
[12] Void.
[13] Void.
[14] Void.
[15]
RFC 768 (1980): "User Datagram Protocol" (STD 6).
[16]
RFC 791 (1981): "Internet Protocol" (STD 5).
[17]
RFC 792 (1981): "Internet Control Message Protocol" (STD 5).
[18]
RFC 793 (1981): "Transmission Control Protocol" (STD 7).
[19]
RFC 1034 (1987): "Domain names - concepts and facilities" (STD 7).
[20] Void.
[21a]
RFC 1661 (1994): "The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)" (STD 51).
[21b]
RFC 1662 (1994): "PPP in HDLC-like Framing".
[22]
RFC 1700 (1994): "Assigned Numbers" (STD 2).
[23]
TS 44.008: "Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network protocols; Stage 3".
→ to date, withdrawn by 3GPP
[24]
→ to date, withdrawn by 3GPP
TS 29.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) across the Gn and Gp interface".
[25]
RFC 2794 (2000): "Mobile IP Network Address Identifier Extension for Ipv4", P. Calhoun, C. Perkins.
[26]
RFC 2131 (1997): "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol".
[27]
RFC 1542 (1993): "Clarification and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol".
[28] Void.
[29] Void.
[30]
RFC 3344 (2002): "IP Mobility Support", C. Perkins.
[31]
RFC 2486 (1999): "The Network Access Identifier", B. Aboba and M. Beadles.
[32] Void.
[33] Void.
[34] Void.
[35] Void.
[36] Void.
[37]
RFC 2290 (1998): "Mobile-Ipv4 Configuration Option for PPP IPCP", J. Solomon, S. Glass.
[38]
RFC 2865 (2000): "Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)", C. Rigney, S. Willens, A. Rubens, W. Simpson.
[39]
RFC 2866 (2000): "RADIUS Accounting", C. Rigney, Livingston.
[40]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, addressing and identification".
[41]
RFC 3576 (2003): "Dynamic Authorization Extensions to Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)", M.Chiba, M.Eklund, D.Mitton, B.Aboba.
[42]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[43] Void.
[44] Void.
[45]
RFC 3118 (2001): "Authentication for DHCP Messages", R. Droms, W. Arbaugh.
[46]
RFC 3315 (2003) "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for Ipv6 (DHCPv6)", R. Droms, J. Bound, B. Volz, T. Lemon, C. Perkins, M. Carney.
[47]
TS 24.229: "IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on SIP and SDP".
[48]
RFC 2710 (1999): "Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) for Ipv6", S. Deering, W. Fenner, B. Haberman.
[49]
RFC 2460 (1998): "Internet Protocol, Version 6 (Ipv6) Specification", S.Deering, R.Hinden.
[50]
RFC 3162 (2001): "RADIUS and Ipv6", B. Adoba, G. Zorn, D. Mitton.
[51]
RFC 2548 (1999): "Microsoft Vendor-specific RADIUS Attributes", G.Zorn.
[52]
TS 23.228: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2".
[53] Void
[54]
TS 24.008: "Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification; Core Network protocols; Stage 3".
[55] Void.
[56] Void
[57] Void.
[58]
RFC 1035 (1987): "Domain names - implementation and specification" (STD 13).
[59] Void.
[60]
RFC 1771 (1995): "A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4)".
[61]
RFC 1825 (1995): "Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol".
[62]
RFC 1826 (1995): "IP Authentication Header".
[63]
RFC 1827 (1995): "IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)".
[64] Void.
[65]
TS 23.246: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS) Architecture and Functional Description".
[66] Void.
[67] Void.
[68]
TS 23.141: "Presence Service; Architecture and functional description".
[69]
TS 32.422: "Subscriber and equipment trace: Trace Control and Configuration Management".
[70]
TS 48.018: "Base Station System (BSS) - Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN); BSS GPRS Protocol (BSSGP)".
[71]
TS 23.107: "Quality of Service (QoS) Concept and Architecture".
[72]
TS 25.346: "Introduction of the Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) in the Radio Access Network (RAN)".
[73]
RFC 4604 (2006): "Using Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3 (IGMPv3) and Multicast Listener Discovery Protocol Version 2 (MLDv2) for Source-Specific Multicast".
[74]
RFC 4607 (2006): "Source-Specific Multicast for IP".
[75]
TS 29.212: "Policy and Charging Control (PCC); Reference points".
[76]
TS 29.213: "Policy and charging control signalling flows and Quality of Service (QoS) parameter mapping".
[77]
TS 23.401: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) enhancements for Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) access".
[78]
TS 23.402: "Architecture enhancements for non-3GPP accesses".
[79]
RFC 4039 (2005): "Rapid Commit Option for the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4)".
[80]
RFC 3736 (2004): "Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for Ipv6".
[81]
TS 29.274: "Evolved GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for EPS (GTPv2)".
[82]
RFC 4291 (2006): "IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture".
[83]
RFC 4862 (2007): "Ipv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration".
[84]
TS 24.301: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for Evolved Packet System (EPS)".
[85]
RFC 2132 (1997): "DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions".
[86]
RFC 3361 (2002): "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP-for-Ipv4) Option for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers".
[87]
RFC 3646 (2003): "DNS Configuration options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for Ipv6 (DHCPv6)".
[88]
RFC 3319 (2003): "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv6) Options for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers".
[89]
RFC 4861 (2007): "Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (Ipv6)".
[90]
TS 23.203: "Policy and charging control architecture".
[91]
RFC 4739 (2006): "Multiple Authentication Exchanges in the Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol".
[92]
TS 25.413: "UTRAN Iu Interface RANAP Signalling".
[93]
RFC 5176 (2008): "Dynamic Authorization Extentions to Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)".
[94]
TS 36.331: "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Radio Resource Control (RRC); Protocol specification".
[95]
TS 23.380: "IMS Restoration Procedures".
[96]
TS 29.303: "Domain Name System Procedures; Stage 3".
[97]
RFC 4818 (2007): "RADIUS Delegated-Ipv6-Prefix Attribute".
[98]
TS 36.300: "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN); Overall description"
[99]
TS 23.221: "Architectural requirements".
[100]
TS 23.682: "Architecture Enhancements to facilitate communications with Packet Data Networks and Applications".
[101]
TS 29.336: "Home Subscriber Server (HSS) Diameter interfaces for interworking with packet data networks and applications".
[102]
RFC 4282 (2005): "The Network Access Identifier".
[103]
TS 29.275: "Proxy Mobile Ipv6 (PMIPv6) based Mobility and Tunnelling protocols; Stage 3".
[104]
TS 23.007: "Restoration procedures".
[105]
TS 29.229: "Cx and Dx interfaces based on Diameter protocol; Protocol details".
[106]
TS 25.446: "MBMS synchronisation protocol (SYNC)".
[107]
TS 25.323: "Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) specification".
[108] Void.
[109]
RFC 4960 (2007): "Stream Control Transmission Protocol".
[110]
TS 29.128: "Mobility Management Entity (MME) and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) interfaces for interworking with packet data networks and applications ".
[111]
RFC 6733: "Diameter Base Protocol".
[112]
TS 23.285: "Architecture Enhancements for V2X services".
[113]
TS 29.468: "Group Communication System Enablers for LTE (GCSE_LTE); MB2 Reference point; Stage 3".
[114]
TS 29.244: "Interface between the Control Plane and the User Plane of EPC Nodes; Stage 3".
[115]
TS 38.413: "NG Radio Access Network (NG-RAN); NG Application Protocol (NGAP)".
[116]
RFC 2869: "RADIUS Extensions".
[117]
TS 23.214: "Architecture enhancements for control and user plane separation of EPC nodes; Stage 2".
[118]
RFC 2661: "Layer Two Tunneling Protocol "L2TP".
[119]
RFC 2868: "RADIUS Attributes for Tunnel Protocol Support".
[120]
RFC 7155: "Diameter Network Access Server Application".
[121]
TS 29.214: "Policy and Charging Control over Rx reference point".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 13
3.1 Definitions p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TS 22.060, TS 23.060, TS 23.401, TS 23.402 and the following apply:
2G- / 3G-:
prefixes 2G- and 3G- refers to functionality that supports only A/Gb mode GPRS or Iu mode, respectively, e.g., 2G-SGSN refers only to the A/Gb mode GPRS functionality of an SGSN. When the prefix is omitted, reference is made independently from the A/Gb mode GPRS or Iu mode functionality.
A/Gb mode:
indicates that the text applies only to a system or sub-system which operate in A/Gb mode of operation, i.e. with a functional division that is in accordance with the use of an A or a Gb interface between the radio access network and the core network.
Iu mode:
indicates that the text applies only to a system or a sub-system which operates in Iu mode of operation, i.e. with a functional division that is in accordance with the use of an Iu-CS or Iu-PS interface between the radio access network and the core network.
IP-CAN session:
association between a UE and an IP network. The association is identified by a UE represented by an Ipv4 address and/or an Ipv6 prefix together with a UE identity information, if available, and a PDN identity (e.g. APN). An IP-CAN session incorporates one or more IP-CAN bearers. Support for multiple IP-CAN bearers per IP-CAN session is IP-CAN specific. An IP-CAN session exists as long as the related UE Ipv4 address and/or Ipv6 prefix are established and announced to the IP network.
EPC based Packet Domain:
Packet domain which makes use of EPC nodes (e.g. P-GW, S-GW, etc.).
Packet Domain Bearer:
A transmission path between a UE and a GGSN/P-GW, terminating at the User Plane protocol stack under the IP layers.
NR RedCap:
a 3GPP RAT type Identifier used in the Core Network only, which is a sub-type of NR RAT type, and defined to identify in the Core Network the NR when used by a UE indicating NR Reduced Capability.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 14
Abbreviations used in the present document are listed in TR 21.905. For the purposes of the present document, the following additional abbreviations apply:
5QI
5G QoS Identifier
AMBR
Aggregate Maximum Bit Rate
APN
Access Point Name
ARP
Allocation and Retention Priority
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
APCO
Additional Protocol Configuration Options
BG
Border Gateway
BM-SC
Broadcast/Multicast Service Centre
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CIoT
Cellular Internet of Things
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCPv6
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6
DNS
Domain Name System
DSMIPv6
Dual-Stack MIPv6
DVMRP
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
EPC
Evolved Packet Core
ePDG
Evolved Packet Data Gateway
EPS
Evolved Packet System
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name
GBR
Guaranteed Bit Rate
GFBR
Guaranteed Flow Bit Rate
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node
GTP-U
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for user plane
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force
IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol
IMS
IP Multimedia Subsystem
IP
Internet Protocol
IPCP
IP Control Protocol (PPP NCP for IPv4)
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6
IPV6CP
IPv6 Control Protocol (PPP NCP for IPv6)
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
ISP
Internet Service Provider
L2TP
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol
LAC
L2TP Access Concentrator
LAN
Local Area Network
LNS
L2TP Network Server
MBMS
Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service
MBR
Maximum Bit Rate
MFBR
Maximum Flow Bit Rate
MIP
Mobile IP
MLD
Multicast Listener Discovery
MME
Mobility Management Entity
MOSPF
Multicast Open Shortest Path First
MS
Mobile Station
MT
Mobile Terminal
MTC
Machine Type Communication
MTU
Maximum Transfer Unit
NAI
Network Access Identifier
NCGI
NR Cell Global Identity
PAP
Password Authentication Protocol
PCC
Policy and Charging Control
PCO
Protocol Configuration Options
PCRF
Policy and Charging Rules Function
P-CSCF
Proxy Call Session Control Function
PDCP
Packet Data Convergence Protocol
PDN
Packet Data Network
PDU
Protocol Data Unit
PGW-C
PDN Gateway Control plane function
PGW-U
PDN Gateway User plane function
P-GW
PDN Gateway
PIM-SM
Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol
PS
Packet Switched
QCI
QoS Class Identifier
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
SCEF
Service Capability Exposure Function
SGSN
Serving GPRS Support Node
S-GW
Serving Gateway
SMDS
Switched Multimegabit Data Service
SMF
Session Management Function
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TE
Terminal Equipment
TEID
Tunnel End-point Identifier
TMGI
Temporary Mobile Group Identity
TWAN
Trusted WLAN Access Network
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
3.3 Symbols p. 15
For the purposes of the present document, the following symbols apply:
Gb
Interface between an SGSN and a BSC.
Gi
Reference point between Packet Domain and an external packet data network.
Gmb
Reference point between GGSN and BM-SC.
Gn
Interface between two GSNs within the same PLMN.
Go
Interface between a GGSN and a PDF.
Gp
Interface between two GSNs in different PLMNs. The Gp interface allows support of Packet Domain network services across areas served by the co-operating PLMNs.
Gs
Interface between an SGSN and MSC.
Iu
Interface between the RNS and the core network. It is also considered as a reference point.
Pk
Reference Point between GGSN and Presence Network Agent.
R
The reference point between a non-ISDN compatible TE and MT. Typically this reference point supports a standard serial interface.
S2a
It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between trusted non-3GPP IP access and P-GW.
S2b
It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between ePDG and P-GW.
S2c
It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between UE and P-GW. This reference point is implemented over trusted and/or untrusted non-3GPP Access and/or 3GPP access.
S5
Interface between a S-GW and a P-GW within the same PLMN.
S8
Interface between a S-GW and a P-GW in different PLMNs.
Sgi
The reference point between the EPC based PLMN and the packet data network.
Sgi-mb
The reference point between BM-SC and MBMS GW for MBMS data delivery.
SGmb
The reference point for the control plane between BM-SC and MBMS GW.
T6a
Reference point used between SCEF and serving MME.
T6b
Reference point used between SCEF and serving SGSN.
Um
The interface between the MS and the fixed network part in A/Gb mode. The Um interface is the A/Gb mode network interface for providing packet data services over the radio to the MS. The MT part of the MS is used to access the GSM services through this interface.
Uu
Interface between the mobile station (MS) and the fixed network part in Iu mode. The Uu interface is the Iu mode network interface for providing packet data services over the radio to the MS. The MT part of the MS is used to access the UMTS services through this interface.
4 Network characteristics p. 16
4.1 Key characteristics of PLMN p. 16
The PLMN is fully defined in the 3GPP technical specifications. The Packet Domain related key characteristics are found in TS 23.060 , TS 23.401 and TS 23.402.
4.2 Key characteristics of PSDN p. 16
Void.
4.3 Key characteristics of IP Networks p. 16
The Internet is a conglomeration of networks utilising a common set of protocols. IP protocols are defined in the relevant IETF STD specifications and RFCs. The networks topologies may be based on LANs (e.g. Ethernet), Point to Point leased lines, PSTN, ISDN, X.25 or WANs using switched technology (e.g. SMDS, ATM).
5 Interworking Classifications p. 16
5.1 Service Interworking p. 16
Service interworking is required when the Teleservice at the calling and called terminals are different. For Packet Domain, service interworking is not applicable at the Gi/Sgi reference point.
5.2 Network Interworking p. 16
Network interworking is required whenever a PLMN is involved in communications with another network to provide end-to-end communications. The PLMN shall interconnect in a manner consistent with that of a normal Packet Data Network (type defined by the requirements e.g. IP). Interworking appears exactly like that of Packet Data Networks.
5.3 Numbering and Addressing p. 16
See TS 23.003 and the relevant section for IP addressing below.
6 Access reference configuration p. 17
6.1 General |R8| p. 17
The figures depicted in subclauses 6.2 and 6.3 below are the logical representation of the EPC and the non-EPC based Packet Domains. Physically, an operator's PLMN may consist of both EPC and non-EPC nodes. In other words, for example, an operator's PLMN may have both GGSNs and P-GWs; and a Rel-8 SGSN may initiate PDP context activation procedure via both Gn/Gp and S4/S5/S8 reference points.
6.2 Access Interfaces and Reference Points for non-EPC based Packet Domain |R8| p. 17
Figure 1a shows the relationship between the MS, its terminal equipment and the PLMN network in the non-EPC based overall Packet Domain environment.
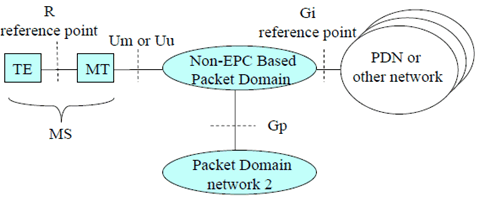
Figure 1a: Non-EPC based Packet Domain Access Interfaces and Reference Points
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
6.3 Access Interfaces and Reference Points for EPC based Packet Domain |R8| p. 17
Figure 1b shows the relationship between the UE and the EPS network for both the 3GPP access and the non-3GPP access in the EPC based Packet Domain environment. The S8/S2a/S2b interface includes GTP-based and PMIP-based.
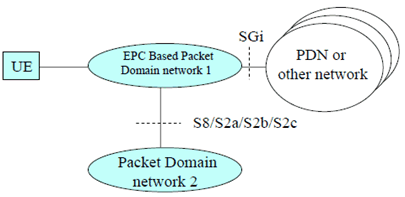
Figure 1b: EPC based Packet Domain Access Interfaces and Reference Points
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
7 Interface to Packet Domain Bearer Services p. 18
7.1 A/Gb mode p. 18
Figure 2a shows the relationship of the non-EPC based Packet Domain Bearer in A/Gb mode terminating at the SNDCP layer to the rest of the A/Gb mode Packet Domain environment. It is shown for reference purposes only and detailed information can be found in TS 23.060.
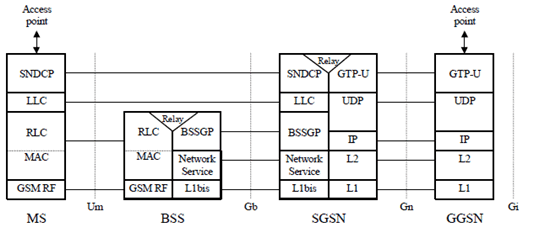
7.2 Iu mode p. 18
Figure 2b shows the relationship of the non-EPC based Packet Domain Bearer in Iu mode, terminating at the PDCP layer, to the rest of the Iu mode Packet Domain environment. It is shown for reference purposes only and detailed information can be found in TS 23.060.
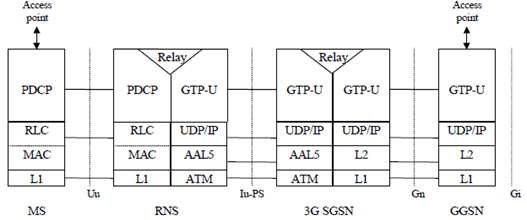
7.3 Interface to EPC-based Packet Domain Bearer Services |R8| p. 18
8 Subscription checking p. 19
The subscription of an MS/UE is checked by the PLMN during IP-CAN session establishment procedure as described in TS 23.060, TS 23.401 and TS 23.402. The GGSN/P-GW implicitly checks its internal context related to the destination address for each mobile terminated packet. For PDN types other than Non-IP, if there is a context IP-CAN session associated with the IP address the packet shall be forwarded towards the MS/UE; otherwise the packet shall be discarded or rejected depending on the implemented protocol. For PDN type "Non-IP", the packet shall be forwarded towards the MS/UE, discarded or rejected depending on the implemented protocol.
8A Prevention of IP spoofing |R6| p. 19
For PDN types other than "Non-IP", if IP spoofing has to be prevented, the GGSN/P-GW shall verify the source IP address of the IP packets issued by the UE and compare it against the address, IPv4 or IPv6, assigned for the IP-CAN session. If the verification fails for a packet,the GGSN/P-GW shall discard the packets and shall be capable to log the event in the security log against the subscriber information (IMSI/MSISDN).
9 Message Screening p. 19
Screening functions reside within the Packet Domain as described in TS 22.060, TS 23.060, TS 23.401 and TS 23.402. Screening may be applicable for only certain protocols. Screening is outside the scope of the present document.
10 Interworking with PSDN (X.75/X.25) p. 19
(no figure)
(no figure)
(no figure)
(no figure)