Content for TS 28.104 Word version: 18.4.0
5 MDA functionality and service framework
5.1 General framework
5.2 Interaction with CN and RAN domains
5.3 Deployment of multiple MDAs
5.4 Network Context
5.5 Historical data handling for MDA
5.6 AI/ML support for MDA
...
...
5 MDA functionality and service framework p. 13
5.1 General framework p. 13
MDA MnS (also referred to as MDAS) in the context of SBMA enables any authorized consumer to request and receive analytics as illustrated in Figure 5.1-1.

A management function (MDAF) may play the roles of MDA MnS producer, MDA MnS consumer, other MnS consumer, NWDAF consumer and LMF service consumer, and may also interact with other non-3GPP management systems.
The internal business logic related to MDA leverages the current and historical data related to:
- Performance Measurements (PM) as per TS 28.552 and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) as per TS 28.554.
- Trace data, including MDT/RLF/RCEF, as per TS 32.422 and TS 32.423.
- QoE and service experience data as per TS 28.405 and TS 28.406.
- Analytics data offered by NWDAF as per TS 23.288 including 5GC data and external web/app-based information (e.g. web crawler that provides online news) from AF.
- Alarm information and notifications as per TS 28.532.
- CM information and notifications.
- UE location information provided by LMF as per TS 23.273.
- MDA reports from other MDA MnS producers.
- Management data from non-3GPP systems.
5.2 Interaction with CN and RAN domains p. 14
The MDA MnS producer provides analytics data for management purposes based on input data related to different types of NFs or entities in the network, e.g. data reported from gNB and/or specific core network function(s). Depending on the use case and when needed, the MDA MnS producer may use the analytics results produced by NWDAF as input.
Management Data Analytics Function (MDAF) may act as 3GPP domain-specific (e.g. RAN or CN) or as 3GPP cross-domain MDA MnS producer. Figure 5.2-1 illustrates the example of coordination between NWDAF, gNB and MDA MnS producer(s) for data analytics purpose.

Figure 5.2-1: Example of coordination between NWDAF, gNB and MDAS (MDA MnS) producer
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Any authorized MnS consumers get access to MDA reports by interacting with MDA MnS producers. These scenarios include but are not limited to the following:
- The NWDAF, leveraging MDA reports (e.g. for control purposes and other 5GC NFs), interacts with MDA MnS producers.
- The gNB may consume the MDA MnS for RAN control purpose.
- The 3GPP cross domain MDA MnS Producer may consume (acting as Domain MDA MnS consumer) MDA MnS provided by domain-specific (RAN and/or CN) MDA MnS producer(s) and produce MDA MnS that may be consumed by 3GPP cross-domain MDA MnS consumer(s).
- The CN Domain MDA MnS producer may consume the service provided by NWDAF and other 5GC NFs for MDA purpose.
- The RAN Domain MDA MnS producer may consume the MnS provided by/for gNB for MDA purpose.
- The cross domain MDA MnS producer may consume the MDA MnS provided by RAN and/or CN domains.
- The cross domain MDA MnS producer may consume MnS provided by RAN and/or CN domains, and produce MDA MnS that may be consumed by 3GPP cross-domain MDA MnS consumer(s).
5.3 Deployment of multiple MDAs p. 16
Multiple MDA instances may be deployed according to deployment needs.
The 3GPP cross domain management may consume MDA MnS provided by core network management as shown in Figure 5.3-1.

The management function (MDAF) playing the role of 3GPP cross domain MDA MnS producer interacts with CN domain MDA per each MDA use case/capability as follows:
- The cross-domain MDA MnS producer may consume the CN domain MDA MnS.
- The cross-domain MDA MnS producer may consume MnS provided by CN domains, and produce MDA MnS that may be consumed by 3GPP cross-domain MDA MnS consumer(s).
- The CN domain MDA MnS producer may consume analytics results produced by NWDAF, MnS provided by CN domain management, other MDA MnS producers, management data derived by subnetwork management function(s), and management data derived by element management function(s).
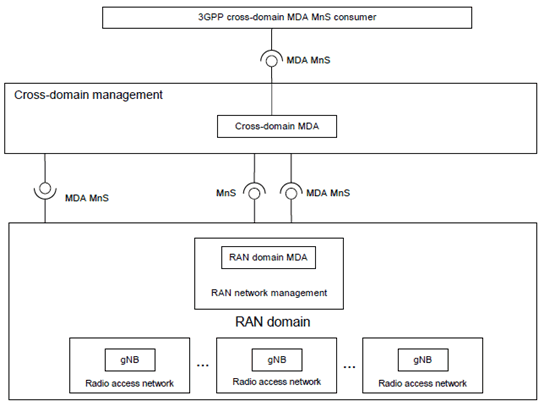
Figure 5.3-2: Example of coordination cross-domain MDA and RAN domain MDA
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The management function (MDAF) playing the role of 3GPP cross domain MDA MnS producer interacts with RAN domain MDA per each MDA use case/capability as follows:
- The cross domain MDA MnS producer may consume the RAN domain MDA MnS.
- The cross domain MDA MnS producer may consume MnS provided by RAN domains, and produce MDA MnS that may be consumed by 3GPP cross-domain MDA MnS consumer(s).
- The RAN domain MDA MnS producer may consume MnS provided by RAN domain management, other MDA MnS producers, management data derived by subnetwork management function(s), and management data derived by element management function(s).
5.4 Network Context p. 17
An MDA MnS producer provides analytics with respect to a particular network context, i.e. network status, under which data is collected to produce analytics. For example, a prediction of load in an area of interest may differ when all gNBs and potential additional RATs are operating compared to case where certain gNBs or other RATs are experiencing a fault or are powered off to save energy. The analytics conducted and produced by the MDA MnS producer for these two example scenarios would be different and directly affected by the specific status of network. Although the network status (context) affects the produced analytics conducted by the MDA producer, awareness of the network context would fall on the consumer side to complement the obtained analytics results. This network context, reflecting network status at the time of enabling data collection, is important for the MDA MnS consumer to understand the network conditions related to the obtained analytics and hence be able to use such analytics more efficiently.
The MDA MnS consumer cannot expect the MDA producer to provide the network context, because the network context interest of each MDA MnS consumer may differ depending on the usage and purpose of analytics. The usage can include a proprietary algorithm that assist a decision-making process. For example, a load balancing algorithm may require the load and mobility information among neighbouring gNB whereas other load balancing algorithms may also require load and mobility information from a greater geographical area.
In addition, the selection of the parameters and their combinations may prove to be impractical for the MDA MnS producer to prepare and provide. Hence, it is efficient for the MDA MnS producer to prepare only the MDA output without including any network context and allow the MDA MnS consumer to obtain the required network context, to complement the obtained analytics, using conventional configuration management procedures as described in TS 28.511 and TS 28.531.
5.5 Historical data handling for MDA p. 18
Historical analytics reports may be saved and retrieved for use at later times by a MDA MnS consumer, and historical analytics input (enabling) data (along with current analytics input data) may be used for analytics by MDA MnS producer. Such a historical data usage may be applicable to both or one of the MDA MnS producer and MDA MnS consumer side.
5.6 AI/ML support for MDA p. 18
The MDA process may utilize AI/ML technologies. An MDA Function may optionally be deployed as one or more AI/ML inference function(s) in which the relevant ML entities are used for inference per the corresponding MDA capability. Specifications for MDA ML model training to enable ML model deployments are given in TS 28.105.