Content for TS 23.554 Word version: 19.3.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.5…
6…
7…
8…
8.2…
8.2.7…
8.2.11
8.3…
8.3.5…
8.4…
8.4.3
8.5…
8.6…
8.7…
8.7.2…
8.7.3…
8.7.4…
8.7.5…
8.7.6…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
8.11…
9…
9.2…
10…
11…
8.6 MSGin5G messaging procedure on Message Gateway
8.6.1 General MSGin5G messaging procedure on Message Gateway
8.6.2 Non-MSGin5G UE receives message from group
8.6.2.1 Legacy 3GPP UE receives message from group
8.6.2.2 Non-3GPP message client receives message from group
...
...
8.6 MSGin5G messaging procedure on Message Gateway p. 86
8.6.1 General MSGin5G messaging procedure on Message Gateway p. 86
Figure 8.6.1-1 shows the MSGin5G message delivery procedure on Message Gateway for Non-MSGin5G UEs.

Step 1.
The MSGin5G Server forwards the MSGin5G message request to recipient Non-MSGin5G UE based on the UE Service ID or to the Broadcast Message Gateway based on the Broadcast Area ID as specified in clause 8.3.3. A Delivery status required IE may be included in the MSGin5G message request.
Step 2.
The Message Gateway records if a message delivery status report is requested in the message. Then it translates the MSGin5G message to a Non-MSGin5G message (e.g. SMS, RCS message as specified in GSMA PRD RCC.07 [3]) with message delivery status report requested and finishes the information exchange procedure with Non-MSGin5G UE (e.g. sends the non-MSGin5G message to the Non-MSGin5G UE and receives the needed response).
Step 3.
The Message Gateway checks if application level message delivery status report is supported by the Non-MSGin5G message delivery mechanism. If not supported, step 4a will be used and steps 4b and 5b will be skipped; otherwise step 4b-5b will be used and step 4a will be skipped.
Step 4a.
Based on the information (e.g. response to the non-MSGin5G message delivery request, transport level information) obtained from the non-MSGin5G message delivery mechanism, the Message Gateway fetches the delivery status from the above information and uses it to create an MSGin5G message delivery status report. If the delivery status is a failure, the Message Gateway also fetches the suitable failure reason from the above information and uses it as reason of failure in the MSGin5G message delivery status report. The Information Elements listed in Table 8.3.4-1 are included in the MSGin5G message delivery status report.
Step 4b.
A non-MSGin5G application level message delivery status report is received by the Message Gateway.
Step 5b.
The Message Gateway translates the non-MSGin5G application level message delivery status report to MSGin5G message delivery status report as specified in clause 8.3.4. The Information Elements listed in Table 8.3.4-1 are also included in this MSGin5G message delivery status report, but the Delivery Status and Failure Cause IEs are fetched from the non-MSGin5G application level message delivery status report.
Step 6.
The Message Gateway sends the MSGin5G message delivery status report to the MSGin5G Server on behalf of the Non-MSGin5G UE or based on the delivery result of the broadcast delivery mechanism, as specified in clause 8.3.4.
8.6.2 Non-MSGin5G UE receives message from group p. 88
8.6.2.1 Legacy 3GPP UE receives message from group p. 88
Figure 8.6.2.1-1 shows the procedure for Legacy 3GPP UE to receive message from group.
Pre-conditions:
- The MSGin5G Server has received the Group message to be sent to a target Legacy 3GPP UE.

Step 1.
The MSGin5G Server sends the MSGin5G message request to the recipient based on the UE Service ID. The Legacy 3GPP Message Gateway receives the MSGin5G message request on behalf of the Legacy 3GPP UE as defined in clause 8.3.3 with following clarifications:
Step 2.
- The MSGin5G message request includes Originating UE Service ID, Recipient Group Service ID, Recipient UE Service ID, Message ID, Payload information elements from Table 8.3.3-1. The MSGin5G message request may include Delivery status required, Application ID and Priority type information elements from Table 8.3.3-1.
The Legacy 3GPP Message Gateway translates the MSGin5G message request to Legacy 3GPP message (e.g. SMS).
Step 3.
The Legacy 3GPP message gateway sends the Legacy 3GPP message (e.g. SMS) to Legacy 3GPP UE.
Step 4.
The Legacy 3GPP UE delivers the payload of the legacy 3GPP message (e.g. SMS) to the targeted Application Client on the Legacy 3GPP UE.
8.6.2.2 Non-3GPP message client receives message from group p. 89
Figure 8.6.2.2-1 shows the procedure for Non-3GPP message client to receive message from group.
Pre-conditions:
- The MSGin5G Server has received the Group message to be sent to target Non-3GPP UE.
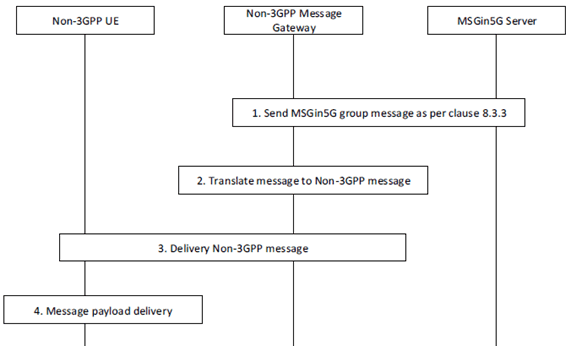
Figure 8.6.2.2-1: Non-3GPP message client receives a message from a group
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The MSGin5G Server sends the MSGin5G message request to the recipient based on the UE Service ID. The MSGin5G Gateway receives the MSGin5G message request on behalf of the Non-3GPP UE as defined in clause 8.3.3 with following clarifications:
Step 2.
- The MSGin5G message request includes Originating UE Service ID, Recipient Group Service ID, Recipient UE Service ID, Message ID, Payload information elements from Table 8.3.3-1. The MSGin5G message request may include Delivery status required, Application ID and Priority type information elements from Table 8.3.3-1.
The Non-3GPP Message Gateway translates the MSGin5G message to Non-3GPP message.
Step 3.
The Non-3GPP Message Gateway sends message to Non-3GPP Message Client.
Step 4.
The Non-3GPP UE delivers the payload of the non-3GPP message (e.g. RCS) to the targeted Application Client on the Non-3GPP UE.