Content for TS 23.333 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4
5…
5.8…
5.12…
5.14…
5.20…
5.24…
6…
6.1.8…
6.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.4…
6.2.5
6.2.6…
6.2.7…
6.2.8…
6.2.9…
6.2.10…
6.2.10.2.7
6.2.10.3…
6.2.11…
6.2.13…
6.2.13.2.6…
6.2.14…
6.2.15…
6.2.16…
6.2.18…
6.2.19…
6.2.19.3…
6.2.20…
6.2.21…
6.2.22…
6.2.23
6.2.24…
7
8…
8.11…
8.20
8.21
8.22
8.23…
8.30…
8.39…
8.45…
8.56…
6 MRFC-MRFP Procedures
6.1 Non-Call Related Procedures
6.1.1 General
6.1.2 MRFP Unavailable
6.1.3 MRFP Available
6.1.4 MRFP Recovery
6.1.5 MRFC Recovery
6.1.6 MRFP Re-register
6.1.7 MRFP Re-registration Ordered by MRFC
...
...
6 MRFC-MRFP Procedures p. 76
6.1 Non-Call Related Procedures p. 76
6.1.1 General p. 76
The non-call related procedures are based on corresponding procedures of TS 23.205 when the MRFC takes the place of the MSC server and the MRFP takes the place of the MGW.
6.1.2 MRFP Unavailable p. 77
The MRFC recognises that the MRFP is unavailable in the following 4 cases:
1)
 2)
2)
The maintenance locking indication indicates that the MRFP is locked for new calls and that no new connections shall be established using this MRFP. The MRFP can choose between the "graceful" and the "forced" method. In the graceful method the connections are cleared when the corresponding calls are disconnected. In the forced method all connection are cleared immediately
In all of the above cases the MRFC shall prevent the usage of the MRFP until the MRFP has recovered or the communication with the MRFP is restored.
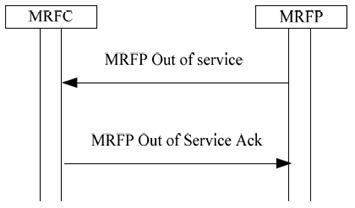
The signalling connection is unavailable

The MRFP indicates the failure condition to all connected MRFCs

The failure indication indicates that the MRFP will soon go out of service and that no new connections should be established using this MRFP. The MRFP can choose between the "graceful" and the "forced" method. In the graceful method the connections are cleared when the corresponding calls are disconnected. In the forced method all connection are cleared immediately.
3)
The MRFC recognises that the MRFP is not functioning correctly, e.g. because there is no reply on periodic sending of Audits. The periodic sending of Audits by MRFC should persist.
4)
The MRFP indicates the maintenance locking condition to all concerned MRFCs.
6.1.3 MRFP Available p. 77
The MRFC discovers that the MRFP is available when it receives an MRFP Communication Up message or an MRFP Restoration message. When the MRFC discovers that the MRFP is available the following shall occur:
1.
 2.
2.
 3.
3.
After this the MRFC can use the MRFP. If none of 1,2, or 3 happens the MRFC can initiate the MRFC Ordered Re-register procedure.
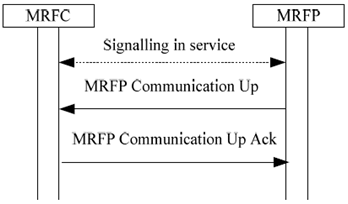
Signalling recovery
The MRFP indicates to all connected MRFCs that the signalling connection is restored.

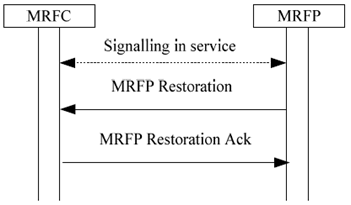
MRFP restoration/maintenance unlocking indication.
The MRFP indicates to all connected MRFCs that normal operation has resumed.

Figure 6.1.3.2: MRFP indicates recovery from a failure/or maintenance unlocking
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The MRFC recognises that the MRFP is now functioning correctly, e.g. because there is a reply on periodic sending of Audits.
6.1.4 MRFP Recovery p. 78
If the MRFP recovers from a failure, is maintenance unlocked, or it has been restarted, it registers to its known MRFCs using the MRFP Restoration procedure or the MRFP Registration procedure. The MRFP can indicate whether the Service has been restored or whether it has restarted with a cold or warm boot. The response sent to the MRFP indicates a signalling address to be used by the MRFP.
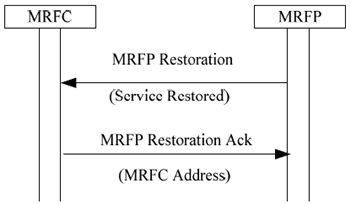
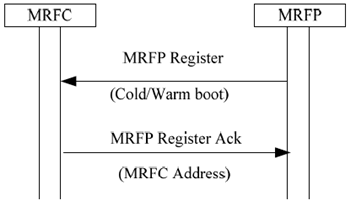
After the recovery the MRFC can use the MRFP.
6.1.5 MRFC Recovery p. 79
6.1.5.1 General p. 79
If an MRFP-unavailable condition is provoked by a failure/recovery action, the MRFC recovery sequence will, from an information flow point of view, look like MRFP unavailable and then MRFP available. If an MRFP-unavailable condition is not provoked, the MRFC recovery sequence will look like MRFP available.
After the information flow, the terminations affected by the recovery action are released.
6.1.5.2 MRFC Restoration p. 79
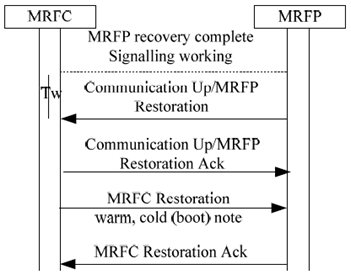
After the recovery action is complete and it is possible to signal to the MRFP the MRFC starts a timer Tw. If recovery indications are not received (MRFP Communication Up or MRFP Restoration) from the MRFP during Tw an Audit is sent. If the MRFC receives a recovery indication or MRFP communication up indication, it shall acknowledge the indication before the MRFC Restoration may be sent or the release procedure is initiated.
6.1.6 MRFP Re-register p. 79
When the MRFC requests an MRFP to perform a registration (see clause 6.1.7), the MRFP performs a re-registration to the MRFC which is defined in the MRFC address.
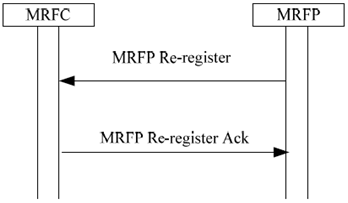
6.1.7 MRFP Re-registration Ordered by MRFC p. 80
If the MRFC knows that communication is possible, but the MRFP has not registered, the MRFC can order re-registration of the MRFP.
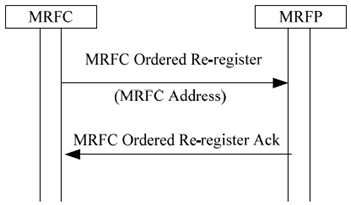
If the re-registration request is accepted the MRFP uses the MRFP Re-register procedure to register with the MRFC.