Content for TS 23.283 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
10…
10.2…
10.3…
10.3.2
10.3.3…
10.3.4…
10.3.5…
10.3.6…
10.3.7…
10.3.8…
10.4…
10.5…
10.6…
10.6.2…
10.6.3…
10.7…
10.8…
10.11…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10.17…
10.15 First-to-answer call setup
10.15.1 Description
10.15.2 Information flows for first-to-answer call
10.15.3 Procedures
10.15.3.1 MCPTT user initiating a first-to-answer call
10.15.3.2 LMR user initiating a first-to-answer call
10.16 Enhanced status
10.16.1 General
10.16.2 Preset values for enhanced status
10.16.3 Enhanced status for on-network
10.16.3.1 Procedure (MCData to IWF)
10.16.3.2 Procedure (IWF to MCData)
10.15 First-to-answer call setup |R17| p. 177
10.15.1 Description p. 177
The present document specifies the interworking between LMR users and MCPTT clients for first-to-answer calls. It can be used based on MCPTT IDs, or based on functional alias for interworking with alternative addressing scheme used by the LMR system.
10.15.2 Information flows for first-to-answer call p. 177
10.15.2.1 IWF first-to-answer call request p. 177
Table 10.15.2.1-1 describes the information flow IWF first-to-answer call request from the MCPTT server to the IWF and from the IWF to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party |
| MCPTT ID
(see NOTE) | O | The MCPTT ID of the called party |
| Functional alias
(see NOTE) | O | The functional alias of the called party |
| Use floor control indication | M | This element indicates whether floor control will be used for the private call. |
| SDP offer | O | Media parameters of MCPTT client. |
| Implicit floor request | O | An indication that the user is also requesting the floor. |
| Location information | O | Location of the calling party |
|
NOTE:
One of these information elements must be present. If the information element MCPTT ID is present, it may consist of a set of MCPTT IDs. If the information element functional alias is present it must consist of a single functional alias.
|
||
10.15.2.2 IWF first-to-answer call response p. 178
Table 10.15.2.2-1 describes the information flow IWF first-to-answer call response from the MCPTT server to the IWF and from the IWF to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the calling party |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the called party |
| SDP answer | M | Media parameters selected |
10.15.2.3 IWF first-to-answer call cancel request p. 178
Table 10.15.2.3-1 describes the information flow IWF first-to-answer call cancel request from the MCPTT server to the IWF and from the IWF to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the calling party |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party |
10.15.2.4 IWF first-to-answer call cancel response p. 178
Table 10.15.2.4-1 describes the information flow IWF first-to-answer call cancel response from the MCPTT server to the IWF and from the IWF to the MCPTT server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the called party |
10.15.3 Procedures p. 179
10.15.3.1 MCPTT user initiating a first-to-answer call p. 179
In this procedure, an MCPTT user is initiating an MCPTT first-to-answer call for communicating with an LMR user via an IWF.
Pre-conditions:
- The calling MCPTT user has selected first-to-answer call.
- The MCPTT client is registered to the MCPTT service, as per procedure in subclause 10.2 in TS 23.379.
- The MCPTT server has subscribed to the MCPTT functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
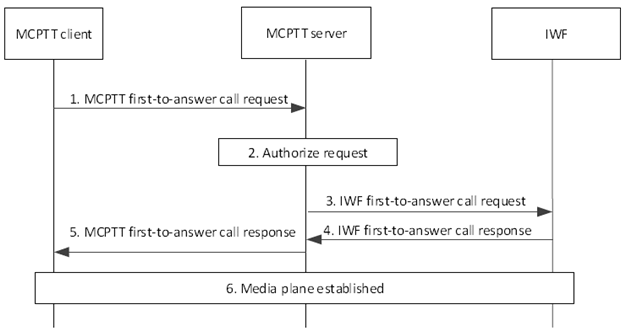
Step 1.
The MCPTT user at the MCPTT client initiates an MCPTT first-to-answer call. The MCPTT client sends an MCPTT first-to-answer call request towards the MCPTT server. The MCPTT first-to-answer call request contains the MCPTT ID corresponding to the calling MCPTT party and called LMR party, and an SDP offer containing one or more media types. The called LMR party can consist of a set of potential target recipients represented by their MCPTT IDs, or a functional alias. The following parameters are also included that describe the MCPTT client's choices:
Step 2.
- the encryption algorithm;
- the encryption mode (encrypted or not);
- an indication of whether the MCPTT client is requesting the floor, and if the MCPTT client is requesting the floor, and
- an indication of whether the call is to be full or half duplex (whether to establish floor control).
The MCPTT server checks whether the MCPTT user at the MCPTT client is authorized to initiate the first-to-answer call. The MCPTT server checks whether the provided functional alias of the calling user, if present, can be used and has been activated for the MCPTT user.
Step 3.
If authorized, the MCPTT server sends the IWF first-to-answer call request that may or may not include location of the requestor, depending on the outcome of the privacy check towards the IWF, including the original parameters and offering the same media types or a subset of the media types contained in the initial received request as per TS 23.379.
Step 4.
The IWF sends an IWF first-to-answer call response to the MCPTT server, indicating that the IWF does support one of the requested media types. The response indicates success or failure. If the indication is failure, the response may include one or more alternatives to the parameter values contained in step 3.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server forwards the MCPTT first-to-answer call response to the MCPTT client. If the result parameter indicates success, then the MCPTT client proceeds to step 6. Otherwise, if the parameters returned in the MCPTT first-to-answer call response are acceptable to the MCPTT client, then the MCPTT client can send a new MCPTT first-to-answer call request with the new parameters and behaves according to those parameters. The calling MCPTT user may be notified of the change in parameters, for example, that the call is to be without floor control. The MCPTT user can choose to end the call rather than continue with the new parameters. If the parameters returned are not acceptable to the MCPTT client, then the call fails.
Step 6.
The MCPTT client has successfully established media plane for communication to the IWF and either end can transmit media. The MCPTT system initiating the call is responsible of granting the floor, solving competing floor requests and issuing floor revoked indications.
10.15.3.2 LMR user initiating a first-to-answer call p. 180
In this procedure, an MCPTT user is initiating an MCPTT first-to-answer call for communicating with an LMR user via an IWF.
Pre-conditions:
- The calling LMR user has selected first-to-answer call
- The MCPTT client is registered to the MCPTT service, as per procedure in subclause 10.2 in TS 23.379.
- The MCPTT server has subscribed to the MCPTT functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
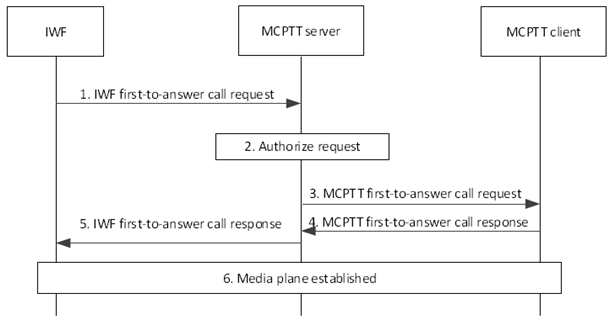
Step 1.
The IWF sends an IWF first-to-answer call request towards the MCPTT server. The IWF first-to-answer call request contains the MCPTT ID corresponding to the calling LMR party and called MCPTT party, and an SDP offer containing one or more media types. The called MCPTT party can consist of a set of potential target recipients represented by their MCPTT IDs, or a functional alias. The following parameters are also included that describe the LMR party's choices:
Step 2.
- the encryption algorithm;
- the encryption mode (encrypted or not);
- an indication of whether the LMR user is requesting the floor, and if the LMR user is requesting the floor, and
- an indication of whether the call is to be full or half duplex (whether to establish floor control).
The MCPTT server checks whether the MCPTT user at the MCPTT client is authorized to receive the first-to-answer call. The MCPTT server checks whether the provided functional alias of the calling user, if present, can be used and has been activated for the LMR user.
Step 3.
If authorized, the MCPTT server sends the MCPTT first-to-answer call request towards the MCPTT client, including the original parameters and offering the same media types or a subset of the media types contained in the initial received request as per TS 23.379.
Step 4.
The MCPTT client sends an MCPTT first-to-answer call response to the MCPTT server, indicating that the MCPTT client does support one of the requested media types. The response indicates success or failure. If the indication is failure, the response may include one or more alternatives to the parameter values contained in step 3.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server sends the IWF first-to-answer call response to the IWF offering the same media type as that sent in step 4. If the parameters returned are not acceptable to the IWF, then the call fails. If the parameters returned in the IWF private call response are different but acceptable to the IWF, then the IWF can send a new IWF private call request with the new parameters starting with step 1, which is to essentially restart the call. If there is no change of parameter, then the call proceeds to step 6.
Step 6.
The MCPTT client has successfully established media plane for communication to the IWF and either end can transmit media. The MCPTT system initiating the call is responsible of granting the floor, solving competing floor requests and issuing floor revoked indications.
10.16 Enhanced status |R17| p. 181
10.16.1 General p. 181
Clause 7.9 of TS 23.282 describes a high-level procedure to provide enhanced status information to all the receiving MCData users.
10.16.2 Preset values for enhanced status p. 181
The configuration of preset values into the group configuration data is described in clause 7.9.2 of TS 23.282.
10.16.3 Enhanced status for on-network p. 181
10.16.3.1 Procedure (MCData to IWF) p. 181
The procedure for an MCData user requesting to share enhanced status to an MCData group is as specified in clause 7.9.3 of TS 23.282 for the enhanced status for on-network use; one or more users using MCData clients 2-n may be LMR users behind an IWF that has affiliated to the MCData group (see clause 10.1.2 of the present document). The IWF behaves as a peer MCData server.
10.16.3.2 Procedure (IWF to MCData) p. 182
The procedure for an IWF requesting, on behalf of an LMR user, to share enhanced status to an MCData group is as specified in subclause 7.9.3 of TS 23.282 for the enhanced status for on-network use, with the exception that MCData client 1 is located behind an IWF and one or more of the MCData clients 2 to n can be behind IWFs that have affiliated to the MCData group (see clause 10.1.2 of the present document). The IWF behaves as a peer MCData server to other MCData servers.