Content for TS 23.283 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
10…
10.2…
10.3…
10.3.2
10.3.3…
10.3.4…
10.3.5…
10.3.6…
10.3.7…
10.3.8…
10.4…
10.5…
10.6…
10.6.2…
10.6.3…
10.7…
10.8…
10.11…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10.17…
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Introduction
5 Assumptions and architectural requirements
5.1 Key management
5.2 Packet format
6 Involved business relationships
7 Functional model
7.1 General
7.2 Functional model description
7.3 Functional entities description
7.4 Reference points
8 Identities
9 Application of functional model to deployments
...
...
1 Scope p. 11
The objective of this technical specification is to specify interworking between MC systems and LMR systems that satisfy the MCPTT requirements in TS 22.179, MCCoRe requirements in TS 22.280 and the MCData requirements (SDS only) in TS 22.282.
The present document refers to an InterWorking Function (IWF). The structure and functionality of the IWF is out of scope of the present document. The definition of reference points between the IWF and MC systems and the interactions between the IWF and MC systems are in scope of the present document.
2 References p. 11
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 22.280: "Mission Critical Services Common Requirements (MCCoRe); Stage 1".
[3]
TS 22.179: "Mission Critical Push to Talk (MCPTT); Stage 1".
[4]
TS 22.282: "Mission Critical Data services".
[5]
TS 23.280: "Common functional architecture to support mission critical services; Stage 2".
[6]
TS 23.282: "Functional architecture and information flows to support Mission Critical Data (MCData); Stage 2".
[7]
TS 23.379: "Functional architecture and information flows to support Mission Critical Push To Talk (MCPTT); Stage 2".
[8]
TS 33.180: "Security of the mission critical service"
[9]
TIA-603-D: "Land Mobile FM or PM Communications Equipment Measurement and Performance Standards".
[10]
ETSI TS 103 389: "Rail Telecommunications (RT); Global System for Mobile communications (GSM); Usage of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) on the Network Switching Subsystem (NSS) to Fixed Terminal Subsystem (FTS) interface for GSM Operation on Railways".
[11]
ETSI TS 102 610: "Railways Telecommunications (RT); Global System for Mobile communications (GSM); Usage of the User-to-User Information Element for GSM Operation on Railways".
[12]
ETSI TS 100 392-19-1: "Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA); Voice plus Data (V+D); Part 19: Interworking between TETRA and Broadband systems; Sub-part 1: Protocol specification for Interworking with 3GPP mission critical services"
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 12
3.1 Definitions p. 12
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
End-to-End Encryption:
encryption that is applied by an originating terminal or client and is decrypted only by chosen terminating terminals or clients.
User homed in the IWF:
is an MC service ID that represents an LMR user in the MC system.
Interworking:
a means of communication between mission critical systems and LMR systems whereby MC users obtaining service from a mission critical system can communicate with LMR users who are obtaining service from one or more LMR systems.
Interworking function:
adapts LMR Systems to mission critical systems via the IWF interface and supports interworking between LMR systems and mission critical systems.
Interworking group:
a group, which is composed of group members from the MC system and the LMR system and defined in the MC system or the LMR system.
LMR system:
the collection of applications, services, and enabling capabilities providing a land mobile radio service offering group and private communications.
LMR user:
a user of a device which allows participation in an LMR system.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 12
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
E2EE
End-to-End Encryption
IWF
InterWorking Function
KEK
Key Encryption Key (TETRA)
KMS
Key Management Service
MC
Mission Critical
MCPTT
Mission Critical Push To Talk
LMR
Land Mobile Radio
LMC
Location Management Client
LMS
Location Management Server
OTAK
Over-The-Air-Key Management (TETRA)
OTAR
Over-The-Air Rekeying (P25)
P25
Project 25
SDS
Short Data Service
TETRA
TErrestrial Trunked Radio
UE
User Equipment
UKEK
Unique Key Encryption Key (P25)
URI
Uniform Resource Identifier
UUI
User-to-User Information
4 Introduction p. 12
Mission critical users currently employ a wide range of LMR mission critical Push To Talk services, and associated data capabilities where available.
The present document describes the architecture to support the interworking between the MC system and the LMR system to satisfy interworking requirements specified in TS 22.179 and TS 22.282. Other LMR technologies may interwork as long as they conform to the present document.
The IWF, along with its LMR system, will appear as a peer interconnected MC system. This is meant as an approach for defining interactions on the IWF interface but is not intended to specify the functionality of the IWF nor meant to mandate a deployment model.
5 Assumptions and architectural requirements p. 13
5.1 Key management p. 13
Interworking requirements for key management for encrypted interworking include:
- a mechanism to securely (i.e. authenticity, integrity, confidentiality) share an LMR E2EE traffic key for a private call sessions between a party in an MCPTT system and a party in the LMR system;
- a mechanism to securely convey to group members, the LMR E2EE key or set of LMR E2EE keys associated with an MC service group or set of MC service groups, to be used for encryption of interworking group calls spanning the multiple systems;
- a mechanism to securely share with temporary group members in MC systems, the LMR E2EE key(s) associated with a temporary MC service group to be used in interworking group calls spanning the multiple systems;
- key management solutions shall not preclude the ability of an IWF to allow one or more individual Mission Critical Organizations from having sole control over and sole access to LMR E2EE traffic keys used for the entity's media traffic and users' key encryption keys (UKEKs or KEKs);
- key management solutions shall support the ability of the IWF to decrypt/reencrypt the media traffic for zero or more groups; and,
-
for deployments where Mission Critical Organizations wish to use LMR E2EE mechanisms when interworking with LMR users:
- a mechanism to securely provision an MC service client with the user's UKEK or KEK; and,
- a mechanism to convey LMR OTAR or OTAK message contents.
5.2 Packet format p. 13
Each LMR technology defines its own packet format for voice media transmission. For interworking sessions, there might be cases where LMR formatted media is required to be transferred between the IWF and LMR aware MCPTT clients. An example of such a case is where E2EE is used and thus the IWF is not able to decrypt the media. In such cases, media that is sent over the IWF-1 interface needs to be routed within MCPTT systems to/from LMR aware MCPTT clients using methods described in TS 23.379.
Requirements for media transmission across the IWF-1 interface include:
- media transmission to carry the LMR formatted media between the IWF and LMR aware MCPTT clients; and
- the MCPTT system, along with the IWF, may choose to encrypt the LMR formatted media using 3GPP mechanisms.
6 Involved business relationships p. 14
No business relationships have been identified.
7 Functional model p. 14
7.1 General p. 14
7.2 Functional model description p. 14
Figure 7.2-1 shows the functional model for the application plane for interworking between MC systems and LMR systems. Functional entities and interfaces depicted on the right-hand side of the IWF-x interfaces are defined in TS 23.280, TS 23.379, and TS 23.282.
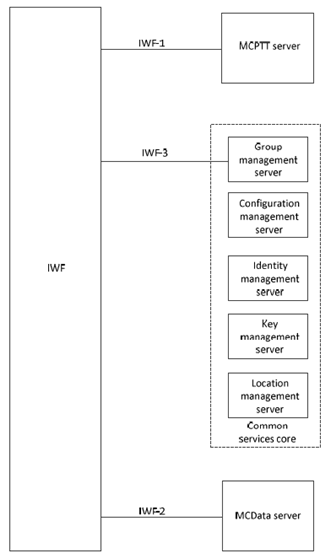
7.3 Functional entities description p. 15
7.3.1 IWF p. 15
The IWF supports most of the functionality of peer MCPTT and MCData systems, with some differences, as specified in the present document. The IWF supports any necessary protocol translation and identity mapping between the MC systems and the IWF. The internal function of the IWF is out of scope of the present document.
7.4 Reference points p. 15
7.4.1 Reference point IWF-1 (between the IWF and the MCPTT server) p. 15
The IWF-1 reference point, which exists between the IWF and the MCPTT server, provides peer to peer interconnection between an LMR system and the MCPTT system. IWF-1 supports a subset of MCPTT-3 as defined in TS 23.379, with some differences, as specified in the present document. The IWF-1 interface is supported by the same signalling plane protocol(s) as defined for MCPTT-3 except as specified in the present document.
7.4.2 Reference point IWF-2 (between the IWF and the MCData server) p. 15
The IWF-2 reference point, which exists between the IWF and the MCData server, provides SDS interconnection between an LMR system and the MCData system. IWF-2 supports a subset of the functionality of MCData-SDS-1 and MCData-SDS-2, as defined in TS 23.282 with some differences, as specified in the present document. The IWF-2 interface is supported by the same signalling plane protocol(s) as defined for MCData-3 except as specified in the present document.
7.4.3 Reference point IWF-3 (between the IWF and the group management server) p. 15
The IWF-3 reference point, which exists between the IWF and the group management server, provides group management interconnection between an LMR system and the MC system. IWF-3 is based upon CSC-16, as defined in TS 23.280 with some differences, as specified in the present document.
7.4.4 Reference point IWF-4 (between the IWF and the LMS) |R18| p. 15
The IWF-4 reference point, which exists between the IWF and the LMS, provides location information exchange between an LMR system and the MC system. Support of the IWF-4 reference point is optional, since there is no guarantee that the interworked LMR system can support location information.
8 Identities p. 15
8.1 Identity mapping p. 15
The IWF provides centralised support for interworking between an MCPTT or MCData system and an LMR system. In MCPTT systems, the identity of an LMR user is provided as an MCPTT ID, and the identity of an LMR group is provided as an MCPTT group ID, which can be used by the IWF to derive the corresponding identities used in an LMR system. Similarly, in MCData systems, the identity of an LMR user is provided as an MCData ID, and the identity of an LMR group is provided as an MCData group ID, which can be used by the IWF to derive the corresponding identities used in an LMR system.
Identities provided on IWF-x reference points are described in clause 8 of TS 23.280.
The IWF can perform the identity mapping between an MCPTT system or MCData system and an LMR system during exchange of signalling and media messages.
The assignment of a functional alias that belongs to the MC system to a user homed in the IWF enables the mapping to corresponding role-based addressing schemes applicable in the LMR system.
9 Application of functional model to deployments p. 16
No applications of functional model to deployments have been identified.