Content for TS 23.278 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.4…
4.6…
4.6.1.1
4.6.1.2
4.6.1.3
4.6.1.4
4.6.1.5
4.6.1.6
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.7.3…
4.7.4…
4.7.5…
5…
6…
4.4 Description of CAMEL Subscriber Data
4.4.1 IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (IM-CSI)
4.4.1.1 Originating IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (O-IM-CSI)
4.4.1.2 Dialled Services IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (D-IM-CSI)
4.4.1.3 Terminating IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (VT-IM-CSI)
4.4.1.4 Other CAMEL Data
4.5 Description of CAMEL State Models
4.5.1 General Handling
4.5.2 Originating CAMEL Basic Call State Model (O-IM-BCSM)
4.5.3 Mapping of SIP Method/Response to O-IM-BCSM Detection Points
4.5.4 Terminating CAMEL Basic Call State Model (T-IM-BCSM)
4.5.5 Mapping of SIP Method/Response to T-IM-BCSM Detection Points
...
...
4.4 Description of CAMEL Subscriber Data p. 15
4.4.1 IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (IM-CSI) p. 15
This clause defines the contents of the IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information. IM-CSI data are provisioned in the HSS for subscribers having originating and/or terminating IP Multimedia CAMEL services. This information shall be sent by the HSS to the IM-SSF via the Si Interface. The IM-CSI data contains the O-IM-CSI, D-IM-CSI, and VT-IM-CSI.
4.4.1.1 Originating IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (O-IM-CSI) p. 15
4.4.1.1.1 gsmSCF Address p. 15
Address to be used to access the gsmSCF for a particular subscriber. The address shall be an E.164 number to be used for routeing.
4.4.1.1.2 Service Key p. 15
The Service Key identifies to the gsmSCF the service logic that shall apply.
4.4.1.1.3 Default Call Handling p. 15
The Default Call Handling indicates whether the IP Multimedia session shall be released or continued as requested in case of error in the IM-SSF to gsmSCF dialogue.
4.4.1.1.4 TDP List p. 15
The TDP List indicates on which detection point triggering shall take place. The following trigger detection points are possible: DP Collected_Info and DP Route_Select_Failure.
4.4.1.1.5 CAMEL Capability Handling p. 15
CAMEL Capability Handling indicates the phase of CAMEL which is asked by the gsmSCF for the service.
4.4.1.1.6 CSI Status p. 15
The CSI state indicates whether the O-IM-CSI is active or not.
4.4.1.1.7 Notification Flag p. 15
The notification flag indicates whether changes of the O-IM-CSI shall trigger the Notification on Change of Subscriber Data. In order to update the IM-SSF of IM CSI changes, this flag shall be set to yes.
4.4.1.1.8 DP Criteria p. 16
The DP criteria indicate whether the IM-SSF shall request the gsmSCF for instructions.
4.4.1.2 Dialled Services IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (D-IM-CSI) p. 16
4.4.1.2.1 gsmSCF Address p. 16
Address to be used to access the gsmSCF for a particular subscriber. The address shall be an E.164 number to be used for routeing.
4.4.1.2.2 Service Key p. 16
The Service Key identifies to the gsmSCF the service logic that shall apply.
4.4.1.2.3 Default Call Handling p. 16
The Default Call Handling indicates whether the IP Multimedia session shall be released or continued as requested in case of error in the IM-SSF to gsmSCF dialogue.
4.4.1.2.4 CAMEL Capability Handling p. 16
CAMEL Capability Handling indicates the phase of CAMEL which is asked by the gsmSCF for the service.
4.4.1.2.5 CSI Status p. 16
The CSI state indicates whether the D-IM-CSI is active or not.
4.4.1.2.6 Notification Flag p. 16
The notification flag indicates whether changes of the D-IM-CSI shall trigger the Notification on Change of Subscriber Data. In order to update the IM-SSF of IM CSI changes, this flag shall be set to yes.
4.4.1.2.7 DP Criteria p. 16
The DP criteria indicate whether the IM-SSF shall request the gsmSCF for instructions.
4.4.1.3 Terminating IP Multimedia CAMEL Subscription Information (VT-IM-CSI) p. 16
4.4.1.3.1 gsmSCF Address p. 16
Address to be used to access the gsmSCF for a particular subscriber. The address shall be an E.164 number to be used for routeing.
4.4.1.3.2 Service Key p. 16
The Service Key identifies to the gsmSCF the service logic that shall apply.
4.4.1.3.3 Default Call Handling p. 16
The Default Call Handling indicates whether the IP Multimedia session shall be released or continued as requested in case of error in the IM-SSF to gsmSCF dialogue.
4.4.1.3.4 TDP List p. 16
The TDP List indicates on which detection point triggering shall take place. The following trigger detection points are allowed: DP Terminating_Attempt_Authorised, DP T_Busy, and DP T_No_Answer.
4.4.1.3.5 CAMEL Capability Handling p. 17
CAMEL Capability Handling indicates the phase of CAMEL which is asked by the gsmSCF for the service.
4.4.1.3.6 CSI Status p. 17
The CSI state indicates whether the VT-IM-CSI is active or not.
4.4.1.3.7 Notification Flag p. 17
The notification flag indicates whether changes of the VT-IM-CSI shall trigger the Notification on Change of Subscriber Data. In order to update the IM-SSF of IM CSI changes, this flag shall be set to yes.
4.4.1.3.8 DP Criteria p. 17
The DP criteria indicate whether the IM-SSF shall request the gsmSCF for instructions.
4.4.1.4 Other CAMEL Data p. 17
4.4.1.4.1 gsmSCF address list for CSI p. 17
The gsmSCF address list for CSI indicates a list of gsmSCF addresses to which Notification on Change of Subscriber Data is to be sent. In order to provide Notification on Change of Subscriber Data to the IM-SSF, the IM-SSF address shall be included in the gsmSCF address list.
The IM-SSF address is added to the address list for notification in the HSS as described in clause 4.6.1.2.
The IM-SSF shall handle the receipt of the Notification on Change of Subscriber Data using the same procedure as that of a gsmSCF.
4.5 Description of CAMEL State Models p. 17
In the IM Subsystem, calls are controlled by the Serving CSCF (S-CSCF) where a subscriber is registered. A state model describes the call control behaviour of an IM-SSF.
4.5.1 General Handling p. 17
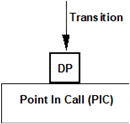
The Basic Call State Model (BCSM) is used to describe the handling of originating and terminating calls. It identifies the points in a call where gsmSCF based service applications is permitted to interact with the call control capabilities of an IM-SSF. Figure 4.3 illustrates how transitions between states, Detection Points and Points In Call components are shown in the BCSM diagrams.
4.5.2 Originating CAMEL Basic Call State Model (O-IM-BCSM) p. 18
4.5.2.1 Description of the O-IM-BCSM p. 18
The O-IM-BCSM is used to model the behaviour of an IM-SSF for an originating call. When an armed DP is encountered, O-IM-BCSM processing is suspended at the DP and the IM-SSF indicates this to the gsmSCF if appropriate.
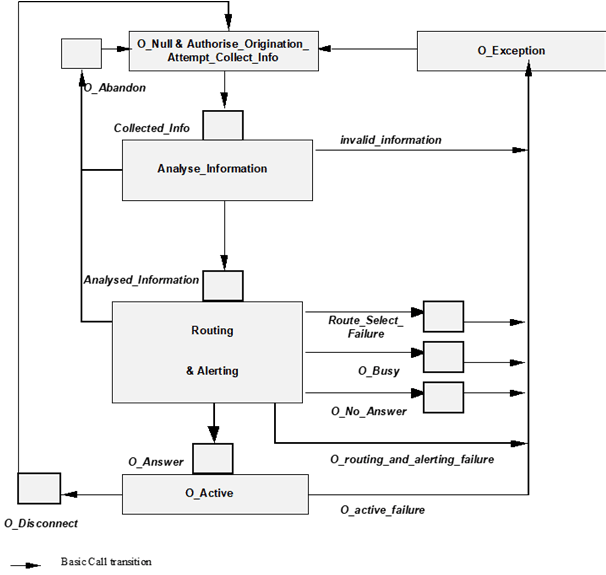
The following Table 4.1 defines the DPs that apply to originating calls.
| CAMEL Detection Point: | DP Type | Description: |
|---|---|---|
| DP Collected_Info | TDP-R | Indication that the O-IM-CSI is analysed |
| DP Analysed_Information | TDP-R | Availability of routeing address and nature of address. |
| DP Route_Select_Failure | TDP-R, EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that the session establishment failed. |
| DP O_Busy | EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that:
|
| DP O_No_Answer | EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that:
|
| DP O_Answer | EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that the session is accepted and answered by the terminating party. |
| DP O_Disconnect | EDP-N, EDP-R | A disconnect indication is received from the originating party or from the terminating party. |
| DP O_Abandon | EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that a disconnect indication is received from the originating party during the session establishment procedure. |
4.5.2.2 Description of Points In Call p. 19
This clause describes the Points In Call for originating calls. The entry events, actions and exit events are described for each Point in Call.
4.5.2.2.1 O_Null & Authorise_Origination_Attempt_Collect_Info p. 19
Entry events:
- Disconnection and clearing of a previous call (DP O_Disconnect) or default handling of exceptions by IM-SSF completed.
- Abandon event is reported from Analyse_Information or Routing and Alerting PIC.
- Exception event is reported.
- Interface is idled.
- Originating call: SIP INVITE request message containing the dialled number is received from MS.
- Information being analysed e.g., O-IM-CSI is analysed.
- Originating CSI is analysed.
- An exception condition is encountered. For this PIC, if the call encounters one of these exceptions during the PIC processing, the exception event is not visible because there is no corresponding DP. Example exception condition: Calling party abandons call.
4.5.2.2.2 Analyse_Information p. 20
Entry events:
- Originating CSI is analysed. (DP Collected Info).
- New routeing information is received when Busy event (DP O_Busy), Route Select Failure event (DP Route_Select_Failure), Not Reachable event (DP O_Busy) or No Answer event (DP O_No_Answer) is reported from Routing and Alerting PIC.
- New routeing information is received when Disconnect event is reported from O_Active PIC.
- Compare the called party number with the dialled services information.
- Availability of routeing address and nature of address. (DP Analysed_Information).
- An exception condition is encountered (e.g. wrong number)- this leads to the O_Exception PIC.
- Calling party abandons the call- this leads to the O_Abandon DP.
4.5.2.2.3 Routing and Alerting p. 20
Entry events:
- Availability of routeing address and nature of address. (DP Analysed_Information).
- Information is being analysed and/or translated according to dialling plan to determine routeing address.
- Routeing address being interpreted.
- Call is being processed by the terminating half BCSM. Continued processing of SIP call session setup (e.g., ringing) is taking place. Waiting for indication from terminating half BCSM that the call has been answered by terminating party.
- Indication from the terminating half BCSM that the call is accepted and answered by terminating party (DP O_Answer).
- An exception condition is encountered - this leads to the O_Exception PIC.
- Calling party abandons the call- this leads to the O_Abandon DP.
- A busy indication is received from the terminating party - this leads to the O_Busy DP.
- A not reachable indication is received from the terminating party - this leads to the O_Busy DP.
- Attempt to select the route for the call fails - this leads to the Route_Select_Failure DP.
4.5.2.2.4 O_Active p. 20
Entry events:
- Indication from the terminating half BCSM that the call is accepted and answered by the terminating party (DP O_Answer).
- SIP session established between originating party and terminating party.
- Call release is awaited.
- A disconnection indication is received from the originating party, or received from the terminating party via the terminating half BCSM. (DP - O_Disconnect).
- An exception condition is encountered.
4.5.2.2.5 O_Exception p. 21
Entry events:
- An exception condition is encountered. In addition to specific examples listed above, exception events include any type of failure, which means that the normal exit events for a PIC can not be met.
- Default handling of the exception condition is being provided. This includes general actions necessary to ensure that no resources remain inappropriately allocated such as:
- If any relationship exists between the IM-SSF and the gsmSCF, the IM-SSF shall send an error information flow closing the relationships and indicating that any outstanding call handling instructions will not run to completion.
- Resources made available for setting up the SIP call session are released.
- Default handling of the exception condition by IM-SSF completed.
4.5.3 Mapping of SIP Method/Response to O-IM-BCSM Detection Points p. 21
This clause describes mapping of SIP methods and responses to CAMEL Detection Points.
| CAMEL O-IM-BCSM DP: | SIP Method/Response |
|---|---|
| DP Collected_Info | INVITE |
| DP Analysed_Information | N/A |
| DP Route_Select_Failure | 4XX (except 401, 407, 408, 480, 486), 5xx, and 6xx (except 600, 603) |
| DP O_Busy | 486 Busy Here 600 Busy Everywhere |
| DP O_No_Answer | 603 Decline 408 Request Timeout 480 Temp Unavailable |
| DP O_Answer | 200 OK |
| DP O_Disconnect | BYE |
| DP O_Abandon | CANCEL |
4.5.4 Terminating CAMEL Basic Call State Model (T-IM-BCSM) p. 22
4.5.4.1 Description of the T-IM-BCSM p. 22
The T-IM-BCSM is used to model the behaviour of an IM-SSF for a terminating call. When a DP is encountered, T-IM-BCSM processing is suspended at the DP and IM-SSF indicates this to the gsmSCF if appropriate.
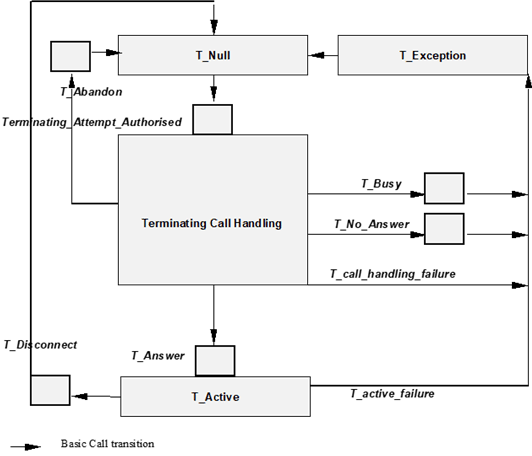
The following Table 4.3 defines the DPs that apply to terminating calls.
| CAMEL DP: | DP Type | Description: |
|---|---|---|
| DP Terminating_
Attempt_Authorised | TDP-R | Indication that the VT-IM-CSI is analysed. |
| DP T_Busy | TDP-R, EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that:
|
| DP T_No_Answer | TDP-R, EDP-N, EDP-R | Indication that an application timer associated with the T_No_Answer DP expires. |
| DP T_Answer | EDP-N, EDP-R | Session is accepted and answered by terminating party. |
| DP T_Disconnect | EDP-N, EDP-R | A disconnect indication is received from the terminating party or from the originating party. |
| DP T_Abandon | EDP-N, EDP-R | A disconnect indication is received from the originating party during the session establishment procedure. |
4.5.4.2 Description of Points In Call p. 23
This clause describes the Points In Call for terminating calls. The entry events, actions and exit events are described for each Point in Call.
4.5.4.2.1 T_Null p. 23
Entry events:
- Disconnection and clearing of a previous call (DP T_Disconnect) or default handling of exceptions by IM-SSF completed.
- Abandon event is reported from Terminating Call Handling PIC.
- Exception event is reported.
- Interface is idled.
- SIP INVITE message for terminating call request is received, the appropriate information is analysed.
- VT-IM-CSI is analysed.
- Terminating CSI is analysed.
-
An exception condition is encountered. For this PIC, if the call encounters one of these exceptions during the PIC processing, the exception event is not visible because there is no corresponding DP.
Example exception condition is:
- Calling party abandons call.
4.5.4.2.2 Terminating Call Handling p. 23
Entry events:
- Terminating CSI (if available) is analysed. (DP Terminating_Attempt_Authorised).
- New routeing information is received when Busy event (DP T_Busy) or No Answer event (DP T_No_Answer) is reported from Terminating Call Handling PIC.
- New routeing information is received when Disconnect event is reported from T_Active PIC.
- New routeing information is received when the terminating party not reachable is reported from Terminating Call Handling PIC.
- Routeing address and call type being interpreted. The next route or terminating access is being selected.
- The terminating party is being alerted. Waiting for the call to be answered by terminating party.
- Call is accepted and answered by terminating party.
- An exception condition is encountered - this leads to the T_Exception PIC. Example exception conditions: the SIP call session request was not successful.
- Calling party abandons the call - this leads to the T_Abandon DP.
- A busy indication is received from the terminating party's P-CSCF - this leads to the T_Busy DP.
- Not reachable event detected from the terminating party's P-CSCF - this leads to the T_Busy DP.
- If no reply timer expires and DP T_No_Answer is armed - this leads to the T_No_Answer DP.
4.5.4.2.3 T_Active p. 24
Entry events:
- Indication that the call is accepted and answered by the terminating party. (DP T_Answer).
- SIP session established between originating party and terminating party.
- Call release is awaited.
- A disconnection indication is received from the terminating party, or received from the originating party via the originating half BCSM. (DP T_Disconnect).
- An exception condition is encountered. In addition to specific examples listed above, exception events include any type of failure that means that the normal exit events for a PIC can not be met.
4.5.4.2.4 T_Exception p. 24
Entry events:
- An exception condition is encountered. In addition to specific examples listed above, exception events include any type of failure, which means that the normal exit events for PIC cannot be met.
- Default handling of the exception condition is being provided. This includes general actions necessary to ensure that no resources remain inappropriately allocated such as:
- If any relationship exists between the IM-SSF and the gsmSCF, the IM-SSF shall send an error information flow closing the relationships and indicating that any outstanding call handling instructions will not run to completion.
- Resources made available for setting up the SIP call session are released.
- Default handling of the exception condition by IM-SSF completed.
4.5.5 Mapping of SIP Method/Response to T-IM-BCSM Detection Points p. 25
This clause describes mapping of SIP methods and responses to CAMEL Detection Points.
| CAMEL T-IM-BCSM DP: | SIP Method/Response |
|---|---|
| DP Terminating_Attempt_
_Authorised | INVITE |
| DP T_Busy | 4XX (except 401, 407, 408, 480), 5xx, and 6xx (except 603) |
| DP T_No_Answer | 603 Decline 408 Request Timeout 480 Temp Unavailable |
| DP T_Answer | 200 OK |
| DP T_Disconnect | BYE |
| DP T_Abandon | CANCEL |