Content for TS 23.259 Word version: 18.0.0
7.4 PN access control procedure in the CS domain
7.4.1 General
7.4.2 PN access control procedure (When the caller is not in the PN access control list)
7.4.3 PN access control procedure in CS domain (When the caller is in the PN access control list)
$ Change history
7.4 PN access control procedure in the CS domain p. 38
7.4.1 General p. 38
PN access control deals with a user having access control over his Personal Network, wherein he may restrict access to his UEs. These UEs of the PN, over which access control has been enabled, are configured as controllee UE. To initiate sessions with these controllee UEs, the originating UEs need to be configured by the PN-user in a PN access control list. For information regarding the originating UEs that are configured in the PN access control list, which is the case in majority of the scenarios, the user nominates a controller UE to handle the access control. In this case, the network queries the user whether the call to the controllee UE may be allowed to go through. If the user allows it, the network allows the call to go through.
7.4.2 PN access control procedure (When the caller is not in the PN access control list) p. 38
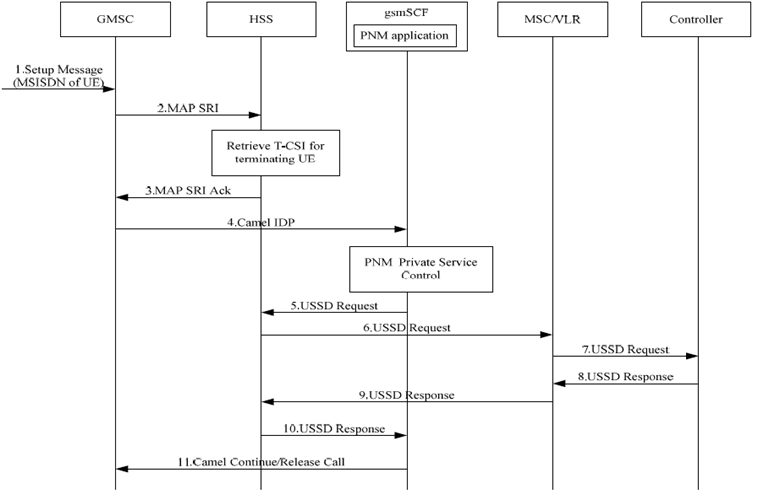
If the caller is not in the PN access control list the gsmSCF interacts with the controller UE in order to route the call to the Controllee UE. Figure 7.4.2-1 shows the implementation of access control procedure in CS domain when the caller is not in PN access control list.
Step 1.
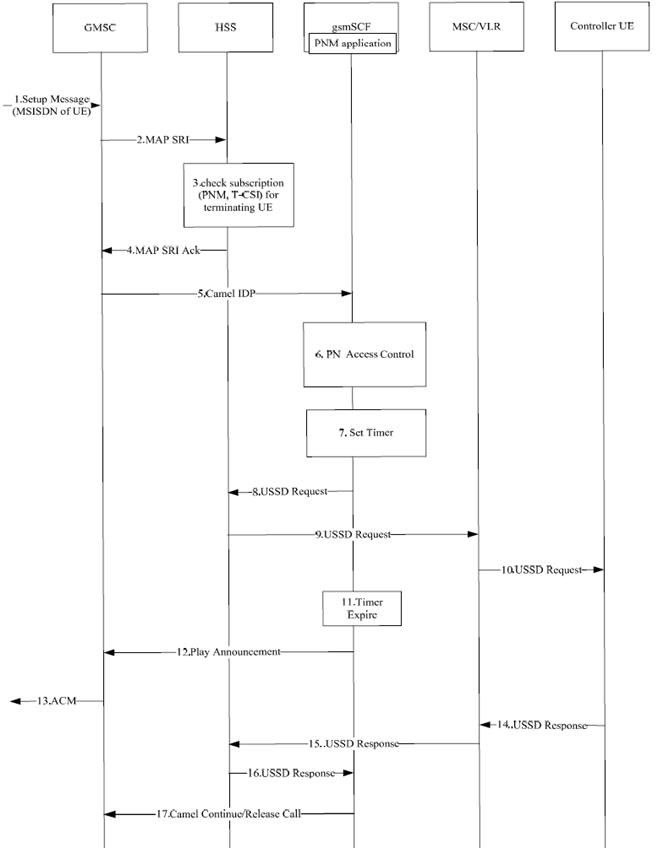
Figure 7.4.2-2 provides a solution for the time delay problem which can occur during interaction between the network and the controller UE.
A call request to the UE located in PN containing the MSISDN of the UE arrives at the GMSC.
Step 2.
GMSC queries the HSS for routing Information by sending MAP SRI.
Step 3.
HSS checks the subscription information for the called party. Further the HSS provides the information for the PNM subscriber including the T-CSI. The HSS returns the T-CSI to the GMSC in the response (MAP-SRI-ACK)
Step 4.
The GMSC triggers a CAMEL activity which results in sending a CAMEL IDP to gsmSCF.
Step 5-7.
The gsmSCF executes the PN access control logic and will check with the controller UE about the acceptability of call request by sending USSD request message to the controller UE via HSS and MSC/VLR.
Step 8.
The controller UE displays the text provided and awaits user input. The user decides whether the call request is allowed or not and accordingly the controller UE will send the USSD response message to MSC/VLR.
Step 9-10.
The MSC/VLR will forward this USSD response message to gsmSCF via HSS.
Step 11.
The gsmSCF will continue the call or release the call by sending the CAMEL continue message/release call message to the GMSC according to the controller UE's response Based on the decision by the controller UE the call will established or released.
Step 1.
A call request to a UE containing the MSISDN of the UE arrives at the GMSC.
Step 2.
The GMSC queries the HSS for routing Information by sending MAP SRI.
Step 3-4.
The HSS checks the subscription information for the called party. Further the HSS provides the information for the PNM subscriber including the T-CSI. The HSS returns the T-CSI to the GMSC in the response.
Step 5.
The GMSC triggers a CAMEL activity which results in sending a CAMEL IDP to gsmSCF.
Step 6. & 8-10.
The gsmSCF executes the PN access control logic and will check with the controller UE about the acceptability of the call request by sending USSD request message to the controller UE via HSS and MSC/VLR.
Step 7.
The gmsSCF will start the Timer.
Step 11.
Supervision of the started timer by the gsmSCF.
Step 12-13.
If the time out occurs because no response from the controller UE, the gsmSCF will send the Play Announcement message to the GMSC and the GMSC will send an early ACM to the originating UE.
Step 14.
The controller UE displays the text provided and awaits user input. The user decides whether the call request is allowed or not and accordingly the controller UE will send the USSD response message to MSC/VLR.
Step 15-16.
The MSC/VLR will forward this USSD response message to the gsmSCF via the HSS.
Step 17.
The gsmSCF will send a message to GMSC to stop playing the announcement if it is generated. The gsmSCF will continue the call or release the call by sending the CAMEL continue message/release call message to the GMSC according to the controller UE's response.
7.4.3 PN access control procedure in CS domain (When the caller is in the PN access control list) p. 41
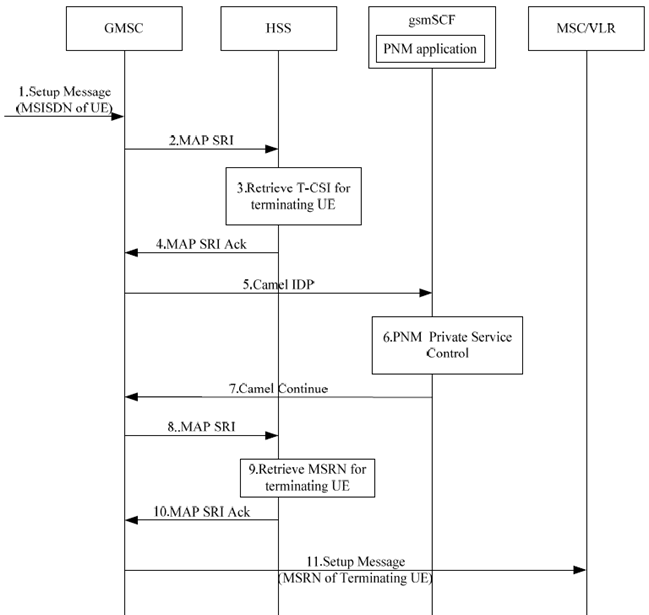
Figure 7.4.3-1 shows the PN access control procedure when the caller is in PN access control list.
Step 1.
A call request to the PN UE containing the MSISDN of the UE arrives at the GMSC.
Step 2.
The GMSC queries the HSS for routing Information by sending MAP SRI.
Step 3-4.
The HSS checks the subscription information for the called party. Further the HSS provides the information for the PNM subscriber including the T-CSI. The HSS returns the T-CSI to the GMSC in the response.
Step 5.
The GMSC triggers a CAMEL activity which results in sending a CAMEL IDP to gsmSCF.
Step 6.
The gsmSCF executes the PN access control logic for access control procedure. The calling party is part of the access control list for this PN.
Step 7.
Based on the positive result, the gsmSCF send the CAMEL CONTINUE message to GMSC to continue the call.
Step 8.
The GMSC queries the HSS for routing Information by sending MAP SRI with 'Suppress T CSI' set.
Step 9.
The HSS returns the retrieved MSRN to the GMSC in response by sending MAP SRI_ACK.
Step 10.
The GMSC generates a call request message containing MSRN and sends it to MSC/VLR.