Content for TS 23.246 Word version: 18.0.0
8.11 Inter SGSN Serving RNS Relocation Procedure
8.12 MBMS Broadcast Service Activation
8.13 MBMS Broadcast service de-activation
8.15 MBMS UE Linking/De-linking mechanism
...
...
8.11 Inter SGSN Serving RNS Relocation Procedure p. 60
This procedure is performed when the SGSN changes due to SRNS relocation. It bases on the SRNS Relocation procedure specified in TS 23.060. The procedure is performed regardless whether MBMS sessions are ongoing or not. The handling of any PDP contexts established by the UE is not changed compared to the procedure without MBMS. The procedure described below does not show all details of the SRNS relocation procedure. Only for the MBMS specific additions the steps are described.
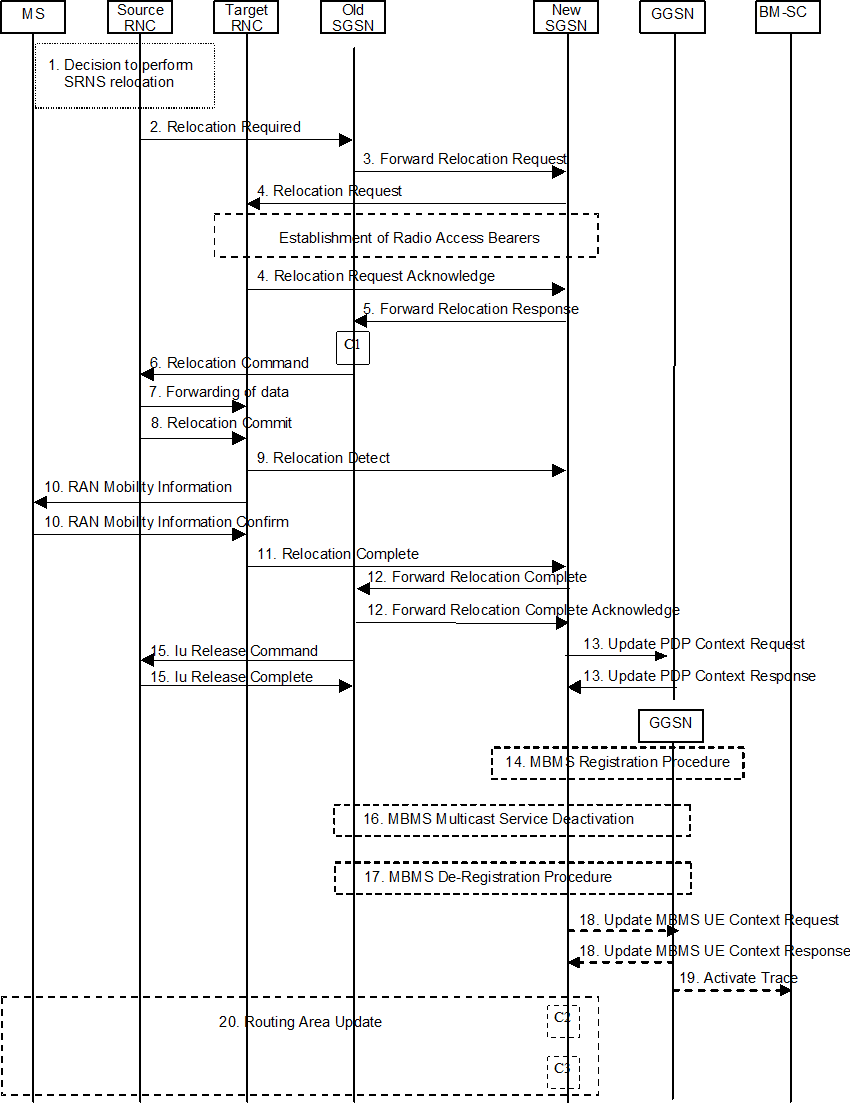
Step 3.
The old SGSN transfers the MBMS UE Context(s). in the Forward Relocation Request message to the new SGSN
Step 5.
An MBMS supporting SGSN indicates its MBMS support in the Forward Relocation Response message.
Step 14.
In case the new SGSN supports MBMS it verifies for each MBMS UE Context received whether it has a corresponding MBMS Bearer Context. For each MBMS Bearer Context not yet existing in the SGSN the SGSN creates an MBMS Bearer Context (in "Standby" state) and initiates the MBMS Registration Procedure. See clause "MBMS Registration Procedure".
Step 16.
In case the new SGSN indicated no MBMS support in step 3) the old SGSN deactivates all MBMS UE contexts of the UE in SGSN, GGSN and BMSC by initiating deactivation procedure(s) as described in clause "8.7 MBMS Multicast Service Deactivation".
Step 17.
If the old SGSN does not have any more MBMS UE Contexts for this MBMS bearer service and the "list of downstream nodes" in the corresponding MBMS Bearer Context is empty, the SGSN initiates the MBMS De-Registration Procedure. See clause "MBMS De-Registration Procedure".
Step 18.
If the new SGSN supports the MBMS and for the MBMS UE context(s) received in step 5) the new SGSN sends Update MBMS UE Context Request (Serving network identity, MS Time Zone, CGI/SAI, RAT Type, Additional MBMS Trace Info) to the GGSNs concerned. The GGSNs update their MBMS UE Context fields and return Update MBMS UE Context Response. The GGSN sends updated Serving network identity to the BM-SC. The inclusion of CGI/SAI shall be according rules detailed in clause 15.1.1a in TS 23.060.
Step 19.
If the GGSN receives new or updated Additional MBMS Trace Info from the new SGSN, the GGSN sends an Activate Trace (Additional MBMS Trace Info) message to the BM-SC.
Step 20.
An SGSN without MBMS support does not indicate MBMS feature support in the Routing Area Update Accept message. On the other hand if the SGSN supports MBMS, the Routing Area Update Accept indicates to the UE that the network supports MBMS.
8.12 MBMS Broadcast Service Activation p. 62
MBMS Broadcast service activation is the procedure by which a UE locally activates a broadcast MBMS bearer service:
- The MBMS broadcast service activation procedure does not register the user in the network. There is no MBMS bearer service specific signalling exchanged between the UE and the Network.
- The broadcast service activation procedure does not establish MBMS UE contexts in UE, SGSN and GGSN.
8.13 MBMS Broadcast service de-activation p. 62
The MBMS Broadcast service de-activation by the UE is local to the UE, i.e. without interaction with the Network.
8.14 Void
8.15 MBMS UE Linking/De-linking mechanism p. 62
MBMS UE Linking is the process by which UE MBMS context(s) is (are) provided to an Iu-mode RAN.
MBMS UE linking procedure is performed when the UE is PMM-CONNECTED at least in the following cases.
- When a UE which has a MBMS UE context is moved to the PMM CONNECTED state and a PS RAB is established. This may happen at any point in time e.g. before, during and between Sessions.
- When a UE joins the MBMS bearer service and is in the PMM CONNECTED state due to an existing PS RAB. This may happen at any point in time e.g. before, during and between Sessions.
- When a UE is moved to the PMM CONNECTED state via the MBMS Service Request procedure. This may happen at any point in time during a MBMS session.