Content for TS 23.246 Word version: 18.0.0
8.4 MBMS Registration Procedure p. 45
The MBMS Registration is the procedure by which a downstream node informs an upstream node that it would like to receive session attributes and data for a particular MBMS bearer service in order to distribute it further downstream. This procedure builds up a distribution tree for the delivery of MBMS session attributes and data from the BM-SC to the UEs interested in the service. This procedure results in the set-up of a corresponding MBMS Bearer Context in the nodes along the distribution tree, but it does not result in the establishment of bearer plane which will be established by the Session Start procedure.
The MBMS Registration procedure is initiated:
- When the first MBMS UE Context for a particular MBMS bearer service is created in the SGSN or GGSN (see clause "MBMS UE Context") and the corresponding MBMS Bearer Context is not already established in the node;
- When an MBMS Registration Request for a particular MBMS bearer service is received from a downstream node but the corresponding MBMS Bearer Context is not established in the node; or
- When a DRNC detects that it hosts UEs interested in the MBMS bearer service.
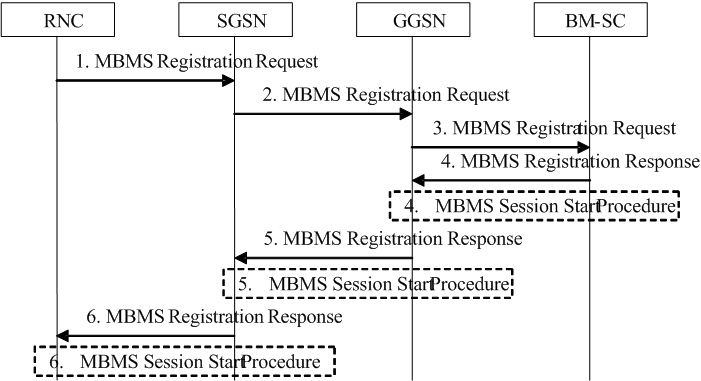
Step 1.
When the DRNC detects that it hosts UEs interested in the MBMS bearer service, the DRNC sends a MBMS Registration Request message to its parent SGSN if not already done. How the RNC determines its parent SGSN is a matter of implementation.
Step 2.
If the SGSN has no MBMS Bearer Context for an MBMS bearer service and the SGSN receives an MBMS Registration Request from an RNC for this MBMS bearer service, or if the first MBMS UE Context is created in the SGSN for an MBMS bearer service for which the SGSN has no corresponding MBMS Bearer Context, the SGSN creates an MBMS Bearer Context (in "Standby" state) and sends an MBMS Registration request (IP multicast address, APN) message to the GGSN. How the SGSN selects a GGSN is a matter of implementation; it may for instance be based on prior signalling related to a particular UE or via APN resolution.
Step 3.
If the GGSN has no MBMS Bearer Context for an MBMS bearer service and the GGSN receives an MBMS Registration from an SGSN for this MBMS bearer service, or when the first MBMS UE Context is created in the GGSN for an MBMS bearer service for which the GGSN has no MBMS Bearer Context, the GGSN creates an MBMS Bearer Context (in "Standby" state) and sends a Registration Request (IP multicast address, APN) message to the BM-SC. Proxy and Transport function The exact nature of the signalling between GGSN and BM-SC via Gmb interface is specified in TS 29.061.
Step 4.
Upon reception of an MBMS Registration Request from a GGSN, the BM-SC Proxy and Transport function adds the identifier of the GGSN to the "list of downstream nodes" parameter in its MBMS Bearer Context and responds with a MBMS Registration Response (TMGI, Required Bearer Capabilities) message. The exact nature of the signalling between GGSN and BM-SC via Gmb interface is specified in TS 29.061. If the MBMS Bearer Context is in the 'Active' state, the BM-SC initiates the Session Start procedure with the GGSN, as described in clause "MBMS Session Start Procedure".
Step 5.
If the GGSN receives a Registration Request from the SGSN in step 2, the GGSN:
Step 6.
- adds the identifier of the SGSN to the "list of downstream nodes" parameter in its MBMS Bearer Context,
- responds with an MBMS Registration Response (TMGI, Required Bearer Capabilities) message, and
- if the MBMS Bearer Context is in the 'Active' state, initiates the Session Start procedure with the SGSN, as described in clause "MBMS Session Start Procedure".
If the SGSN received MBMS Registration Request from the DRNC in step 1, the SGSN:
- adds the identifier of the RNC to the "list of downstream nodes" parameter in its MBMS Bearer Context,
- responds with an MBMS Registration Response message, and
- if the MBMS Bearer Context is in the 'Active' state, initiates the Session Start procedure with the DRNC, as described clause "MBMS Session Start Procedure".