Content for TS 23.221 Word version: 18.0.0
6.4 Relationship between MM and SM states for an UE
6.5 Requirement in case of temporarily loss of coverage of packet UE
6.6 MM functionality in different UE service states
6.7 The RRC state machine
6.8 Relationship between CS and PS service states and RRC state for an UE
6.9 Service registration and location update
6.10 Paging initiated by CN
...
...
6.4 Relationship between MM and SM states for an UE p. 26
When a UE is attached to PS service, it may have, but need not have, some EPS Bearer/PDP context established with GERAN or UTRAN Access. With E-UTRAN access a PS attached UE has at least one EPS Bearer context established.
If the UE has no EPS Bearer/PDP context established (SM-Inactive), no radio access bearer are established for PS service. The UE is in RRC connected mode, only if the state is CS-CONNECTED state or PS-CONNECTED state (i.e. only a PS signalling connection is established).
If the UE has at least one EPS Bearer/PDP context established (SM-Active), the UE can be in PS-CONNECTED state or in PS-IDLE state.
6.5 Requirement in case of temporarily loss of coverage of packet UE p. 26
A packet attached UE using non-real time bearer shall not lose its EPS Bearer/PDP context in case of temporarily loss of coverage. Within the network, it shall be possible to use timers to detect when a UE has been out of coverage for a long period of time and, dependent upon operator policy, to then remove unused EPS Bearer/PDP context(s).
6.6 MM functionality in different UE service states p. 26
CS service states and related MM functionality:
The state transition from CS-IDLE to CS-CONNECTED is performed when a signalling connection is established between UE and CN for CS services. In GSM this state transition is triggered by the message CM_SERVICE_REQUEST or PAGE_RESPONSE.
Moving from CS-CONNECTED to CS-IDLE:
The state transition from CS-CONNECTED to CS-IDLE is performed when the signalling connection for CS services is released, e.g. at call release and no other CS service is ongoing. A radio link failure can also trigger this state transition.
Moving from CS-IDLE to CS-DETACHED:
The transition from CS-IDLE to CS-DETACHED can be triggered by some action from the user of the UE but an expiring timer in the network could also trigger it. The UE is marked as CS_DETACHED in the CN and then as a consequence no CS service establishment is possible.
Moving from PS-IDLE to PS-CONNECTED:
The state transition from PS-IDLE to PS-CONNECTED is performed when a signalling connection is established between UE and CN for PS services.
Moving from PS-CONNECTED to PS-IDLE:
The state transition from PS-CONNECTED to PS-IDLE is performed when the signalling connection for PS services is released, e.g. at release of a PS service, no other PS service is ongoing and at release of the RRC connection in case of very low level of activity. A radio link failure can also trigger this state transition.
Moving from PS-IDLE to PS-DETACHED:
The transition from PS-IDLE to PS-DETACHED can be triggered by some action from the user of the UE but an expiring timer in the network could also trigger it. The UE is marked as PS_DETACHED in the CN and then as a consequence no PS service establishment is possible.
- CS-DETACHED: The UE is not reachable by the network for CS services. The UE does not initiate LA updates at LA changes and no periodic CS service updates;
- CS-IDLE: The UE is reachable by paging for CS services. The UE initiates LA updates at LA changes. The UE may initiate periodic CS service updates and this depends on the CS periodic update state of the present LA;
- CS-CONNECTED: The UE has a signalling connection for CS services established between the UE and the CN. The UE does not initiate LA update (even not when the present LA changes) and no periodic CS service updates.
- PS-DETACHED: The UE is not reachable by the network for PS services. The UE does not initiate TA/RA updates at TA/RA changes and no periodic PS service updates;
- PS-IDLE: The UE is reachable by paging for PS services. The UE initiates TA/RA updates at TA/RA changes. The UE may initiate periodic PS service updates and this depends on the PS periodic update state of the present TA/RA;
- PS-CONNECTED: The UE has a signalling connection for PS services established between the UE and the CN. The UE initiates TA/RA update when RAI in MM system information changes. No periodic PS service updates.
6.7 The RRC state machine p. 27
The UTRAN RRC state machine is a description model of how the UE and the RAN co-operate regarding RRC functionality. The RRC state describes the state of the UE in the RAN. Here follows a brief description of the UTRAN RRC state machine, for more information see TS 25.301 and TS 25.303. The E-UTRAN RRC state machine is described in TS 36.331.
The RRC state machine exists as peer entities, one in the UE and one in RAN. Apart from transient situations and error cases they are synchronised. Figure 6.4 illustrates the main modes/states of the RRC state machine.
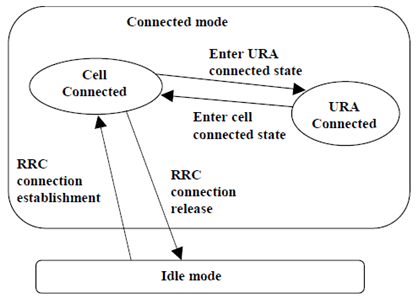
Figure 6.4: RRC modes, main RRC states and main mode/state transitions
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
RRC-Idle_mode:
In the Idle mode there is no connection established between UE and RAN. There is no signalling between RAN and the UE except for system information that is sent from RAN down link on a Broadcast channel to the UE. The UE can also receive paging messages with a CN identity on the PCH. There is no information on the UE stored in RAN in this state.
RRC-Connected_mode:
In the Connected mode the main states are Cell Connected state and URA connected state. In this mode there is one RNC that is acting as Serving RNC (SRNC), and an RRC connection is established between the UE and this SRNC.
- When the UE position is known on cell level, the UE is in the cell connected state. When in cell connected state, the RRC connection mobility is handled by handover procedures.
- When the UE position is known on URA level, the UE is in the URA connected state. The URA contains a set of cells. URA updating procedures provides the mobility functionality in this state. In URA connected state no dedicated radio resources are used.
6.8 Relationship between CS and PS service states and RRC state for an UE p. 28
This clause describes the relationship for the UTRAN. In E-UTRAN the RRC operates for PS services only despite some extensions for supporting the provision of CS services via GERAN/UTRAN.
During non-transient conditions the following relations are valid between service states and RRC modes for an UE:
- when in either CS-CONNECTED state or PS-CONNECTED state, or in both CS-CONNECTED state and PS-CONNECTED state, then the UE is in RRC connected mode;
- when in neither CS-CONNECTED state nor PS-CONNECTED state, then the UE is in RRC idle mode.
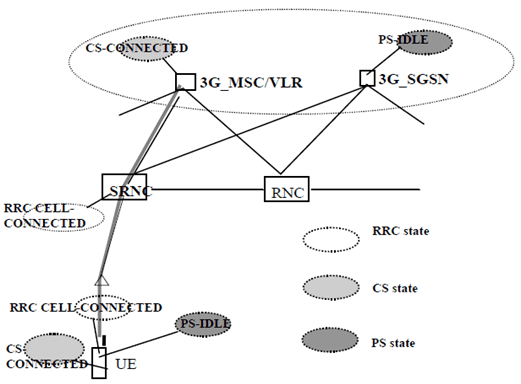
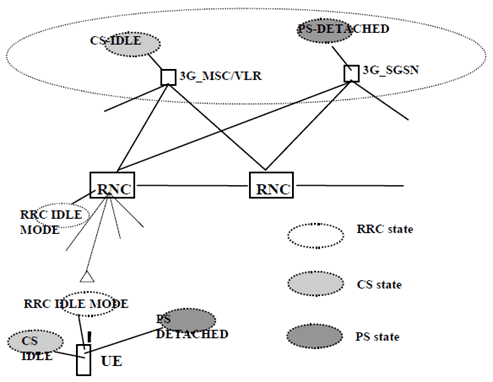
6.9 Service registration and location update p. 29
6.9.1 Introduction p. 29
Service registration (attach) in the respective CN domain is done initially (after UE being detached due to e.g. power off). When a registration area is changed a location update is performed. In addition, periodic registration can be performed. Here follows descriptions of when the respective CN registration area is changed.
6.9.2 Location area update p. 30
LA update is initiated by the UE to inform the CS domain of the CN that the UE has entered a new LA. In case the new LA is in an area served by another CN node, the LA update also triggers the registration of the subscriber in the new CN node and a location update for CS services towards the HLR/HSS.
LA update is only initiated by the UE when the UE is in state CS-IDLE, and this independently of the PS state. If the UE is CS-IDLE but RRC connected, which means that the UE is in PS-CONNECTED state, LA update is initiated by the UE when it receives information indicating a new LA.
6.9.3 Tracking and Routing area update p. 30
TA/RA update is initiated by the UE to inform the PS domain of the CN that the UE has entered a new TA/RA. In case the new TA/RA is in an area served by another CN node, the TA/RA update also triggers the registration of the subscriber in the new CN node and a location update for PS services towards the HSS.
TA/RA update is initiated by the UE when the UE is in state PS-IDLE, and this independently of the CS state. If the UE is PS-IDLE but UTRAN RRC connected, which means that the UE is in CS-CONNECTED state, RA update is initiated by the UE when it receives information indicating a new RA.
When the UE is in PS-CONNECTED state the UE initiates TA/RA update when TAI/RAI in MM system information changes.
6.9.4 Combined updates p. 30
The GSM radio interface combined procedures and their support via the Gs interface is the starting point for the support of combined updates. With E-UTRAN access combined update procedures may be used by MME and MSC.
6.10 Paging initiated by CN p. 30
A CN node requests paging only for UE in CS-IDLE state or PS IDLE state. Paging from a CN node is done independent of the service state of the UE in the other CN domain type.
CS and PS paging is co-ordinated within the UTRAN. Details on how the co-ordination is achieved and the parameters to be provided by the CN are specified in TS 25.413. The procedures required between the UTRAN and UE are in TS 25.331.