Content for TS 23.161 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.4
6.3…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.3…
6.3.3.2…
6.4…
6.4.2.2…
6.5…
6.5.2…
6.5.3…
6.6…
6.6.1.3…
6.6.2…
6.7…
6.7.2…
6.8…
6.4.2.2 Multi-connection mode p. 38
This procedure is only used in NW-initiated NBIFOM mode when the UE wants to request the NW to apply a specific mapping of an IP flow to TWAN access. The NW provides Routing Rules to the UE for this IP flow.
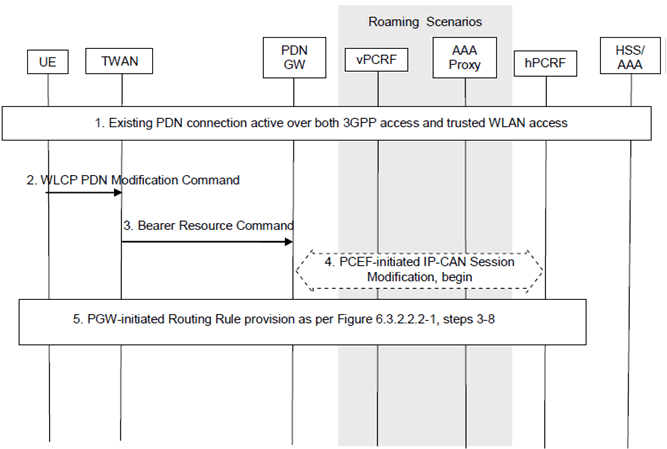
Figure 6.4.2.2-1: UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via Trusted WLAN access using GTP
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The PDN Connection is active simultaneously over 3GPP access and WLAN accesses.
Step 2.
The UE sends a WLCP PDN Modification Command message to the TWAN, which includes the IP Flow mapping information requested by the UE.
Step 3.
The TWAN sends a Bearer Resource Command message to the PDN GW. The message includes the requested IP Flow mapping information.
Step 4.
The PDN GW initiates the IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure with the PCRF. In this request, the PDN GW provides the requested IP Flow mapping information to the PCRF. The PCRF analyses the received Routing Rules, makes a policy decision and provides new or updated PCC rules to the PDN GW with corresponding access type information. The PCRF may reject the requests from UE. When the network rejects a request, the network provides a cause value to the UE indicating why the request was rejected. The UE should be able to determine, based on the cause value provided with the rejection, how to handle the flow mapping, e.g. whether or not the request may be retried at a later stage.
Step 5.
The PDN GW decides to update the Routing Rules based on the received PCC Rules. This step is the same as steps 3-8 in Figure 6.3.2.2.2-1.
6.4.3 UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via Untrusted WLAN access p. 39
This procedure is only used in network-initiated mode when the UE wants to request the network to apply a specific mapping of an IP flow to untrusted WLAN access. The network provides Routing Rules to the UE for this IP flow.
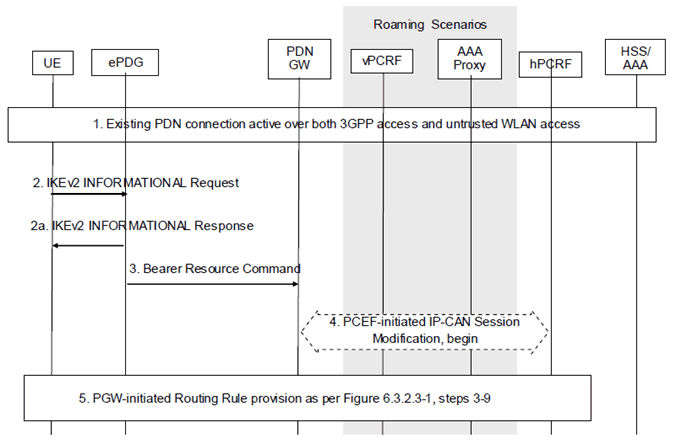
Figure 6.4.3-1: UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via untrusted WLAN access using GTP
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The PDN Connection is active simultaneously over 3GPP access and WLAN accesses.
Step 2.
The UE sends an IKEv2 INFORMATIONAL Request message to the ePDG, which includes the IP Flow mapping information requested by the UE.
Step 2a.
The ePDG sends an IKEv2 INFORMATIONAL Response message to the UE.
Step 3.
The ePDG sends a Bearer Resource Command message to the PDN GW. The message includes the requested IP Flow mapping information.
Step 4.
The PDN GW initiates the IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure with the PCRF. In this request, the PDN GW provides the requested IP Flow mapping information to the PCRF. The PCRF analyses the received Routing Rules, makes a policy decision and provides new or updated PCC rules to the PDN GW with corresponding access type information. The PCRF may reject the requests from UE. When the network rejects a request, the network provides a cause value to the UE indicating why the request was rejected. The UE should be able to determine, based on the cause value provided with the rejection, how to handle the flow mapping, e.g. whether or not the request may be retried at a later stage.
Step 5.
The PDN GW decides to update the Routing Rules based on the received PCC Rules. This step is the same as steps 3-9 in Figure 6.3.2.3-1.