Content for TS 23.161 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.4
6.3…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.3…
6.3.3.2…
6.4…
6.4.2.2…
6.5…
6.5.2…
6.5.3…
6.6…
6.6.1.3…
6.6.2…
6.7…
6.7.2…
6.8…
6.4 NBIFOM IP Flow Mapping
6.4.1 UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via 3GPP access
6.4.2 UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via Trusted WLAN access
6.4.2.1 Single-connection mode
...
...
6.4 NBIFOM IP Flow Mapping p. 37
6.4.1 UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via 3GPP access p. 37
This procedure is only used in Network-initiated NBIFOM mode when the UE wants to request the network to apply specific mappings of IP flows to 3GPP access. The network provides Routing Rules to the UE for this IP flow unless the request from the UE is not allowed by the subscription.
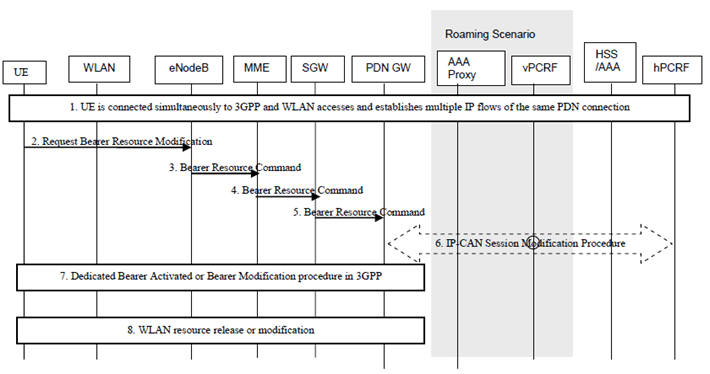
This procedure is similar to 6.3.3.1-1 with the following differences:
Step 2-5.
The PDN GW sends corresponding Routing rule(s) to the UE in Bearer Modification response.
The UE sends a Request Bearer Resource Modification message to the network, which includes the mapping information of an IP flow to 3GPP access.
Step 6.
When dynamic PCC is applied for the PDN connection, the PDN GW initiates an IP-CAN Modification procedure and provides the Routing Rule(s) for this IP flow according to the mapping information in a notification to the PCRF. The PCRF may reject the IP flow mapping request from UE. When the network rejects an IP flow mapping request, the network provides a certain cause value to the UE indicating why the request was rejected. This cause value may be used by the UE to determine when/if this IP flow mapping can be requested again.
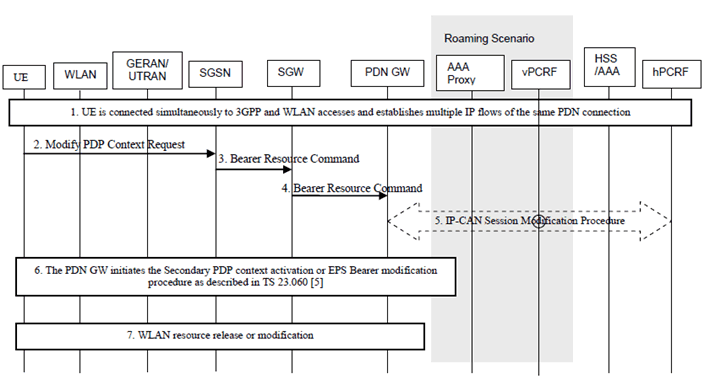
This procedure is similar to 6.3.3.1-2 with the following differences:
Step 2-5.
The PDN GW sends corresponding Routing rule(s) to the UE in Bearer Modification response.
The UE sends a Modify PDP Context Request message to the network, which includes the mapping information of an IP flow to 3GPP access.
Step 5.
When dynamic PCC is applied for the PDN connection, the PDN GW initiates an IP-CAN Modification procedure and provides the Routing Rule(s) for this IP flow according to the mapping information in a notification to the PCRF. The PCRF may reject the IP flow mapping request from UE. When the network rejects an IP flow mapping request, the network provides a certain cause value to the UE indicating why the request was rejected. This cause value may be used by the UE to determine when/if this IP flow mapping can be requested again.
Step 6.
The PDN GW initiates the Secondary PDP context activation or EPS Bearer modification procedure as described in TS 23.060, and including the Routing Rule(s).
When the SGSN receives Create Bearer Request or Update Bearer Request message from the SGW, the SGSN sends Request Secondary PDP Context Activation or Modify PDP Context Request to the UE as described in TS 23.060, including the Routing Rules received from the SGW. The SGSN also sends a Modify PDP Context Accept message to the UE in order to stop the timer which is set after Step 2.
The UE may accept or reject the Routing Rules. When the UE rejects the Routing Rules, the UE provides a cause value indicating why the request was rejected. The UE applies the accepted routing rules and acknowledges the applied rules in Activate Secondary PDP Context Request or Modify PDP Context Accept message.
6.4.2 UE Requested IP Flow Mapping via Trusted WLAN access p. 38
6.4.2.1 Single-connection mode p. 38
In single-connection mode, the UE sends the request for IP flow mapping over 3GPP access as described in clause 6.4.1.