Content for TS 23.009 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.3…
6…
6.2…
6.2.3
6.3…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.2.2…
8.2.4
8.3…
8.3.2…
9…
10…
11…
12…
12.8…
12.8.2
12.8.3
13…
14…
15…
8.2.2 Basic GSM to UMTS Handover procedure not requiring the establishment of a circuit connection between MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B
8.2.3 Procedure for subsequent GSM to UMTS handover requiring a circuit connection
...
...
8.2.2 Basic GSM to UMTS Handover procedure not requiring the establishment of a circuit connection between MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B p. 66
The basic GSM to UMTS handover procedures to be used when no circuit connection is required by MSC-A are similar to those described in subclause 8.2.1 for circuit switched calls. The main differences to the procedures described in subclause 8.2.1 relate to the establishment of circuits between the network entities and the Handover Number allocation.
In the case of basic GSM to UMTS handover, MSC-A shall specify to 3G_MSC-B that no Handover Number is required in the MAP-PREPARE-HANDOVER request (see TS 29.002). As for the basic GSM to UMTS handover using a circuit connection, the A-HO-REQUEST is transmitted at the same time. Any subsequent Handover Number allocation procedure will not be invoked until the completion of the basic GSM to UMTS handover procedure (see clause: Subsequent Channel Assignment using a circuit connection). 3G_MSC-B shall then perform the radio resources allocation as described in subclause 8.2.1. The MAP-PREPARE-HANDOVER response shall be returned to MSC-A including either the translated response of the radio resources allocation request received from RNS-B (A-HO-REQUEST-ACK/A-HO-FAILURE). The basic GSM to UMTS handover procedure will continue as described in clause 8.2.1 except that no circuit connection will be established towards 3G_MSC-B.
The relevant case for the basic GSM to UMTS handover without circuit connection is shown in Figure 25. As can be seen the major differences to the equivalent Figure 24 are the omission of any circuit establishment messaging and the omission of handover number allocation signalling.
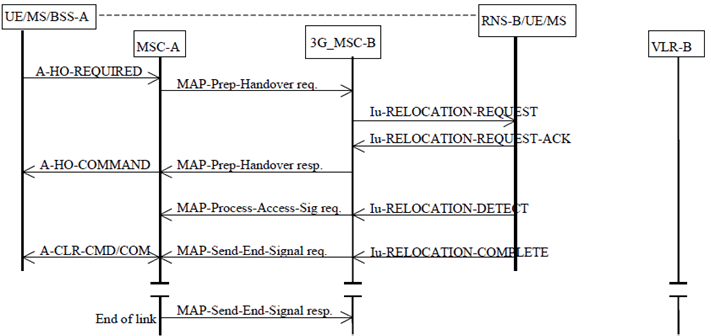
Figure 25: Basic GSM to UMTS Handover Procedure without circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
8.2.3 Procedure for subsequent GSM to UMTS handover requiring a circuit connection p. 66
After the call has been handed over to MSC-B, if the UE/MS leaves the GSM area of MSC-B during the same call and enters a UTRAN area, subsequent GSM to UMTS handover is necessary in order to continue the connection.
The following cases apply:
- the UE/MS moves back to the area of 3G_MSC-A;
- the UE/MS moves into the area of a third 3G_MSC (3G_MSC-B').
8.2.3.1 Description of subsequent GSM to UMTS handover procedure i): MSC-B to 3G_MSC-A p. 67
The procedure for successful GSM to UMTS handover from MSC-B back to 3G_MSC-A is shown in Figure 26.
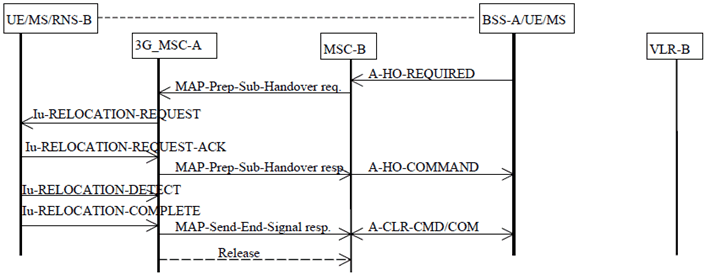
Figure 26: Subsequent GSM to UMTS handover procedure i): successful handover from MSC-B to 3G_MSC-A using a circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The procedure is as follows.
If MSC-B supports inter-system handover to a CSG cell, 3G_MSC-A provided CSG subscription data during the basic inter-MSC handover, and BSS-A includes a CSG ID for the target cell in the A-HANDOVER-REQUIRED message, then MSC-B shall check the CSG membership of the UE for the target cell as described in subclause 4.2.1 before generating the MAP-PREPARE- SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request. If the UE fails the CSG membership check and the target cell is a CSG cell, MSC-B shall send an A-HANDOVER-REQUIRED-REJECT to BSS-A.
MSC-B sends the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request to 3G_MSC-A indicating the new MSC number (3G_MSC-A number), indicating also the identity of the target RNS where the call has to be handed over and including a complete A-HO-REQUEST message. (NOTE: MSC-B shall not send further MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER requests while a handover attempt is pending or before any timeouts). Since 3G_MSC-A is the call controlling MSC, this MSC needs no Handover Number for routing purposes; 3G_MSC-A can immediately initiate the search for free radio resources. 3G_MSC-A then inserts a transcoder between it's RNS and the connection to the other party.
When radio resources can be assigned, 3G_MSC-A shall return in the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response the complete A-HO-REQUEST-ACK message generated from the Iu-RELOCATION-REQUEST-ACK received from the RNS-B and possible extra BSSMAP information, amended by 3G_MSC-A due to the possible interworking between the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E-interface and the RANAP protocol used on the Iu-interface. If radio resources cannot be assigned or if a fault is detected on the target cell identity, or the target cell identity in the A-HO-REQUEST is not consistent with the target MSC number, the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response containing an A-HO-FAILURE message shall be given to MSC-B, in addition MSC-B shall maintain the connection with the UE/MS.
If the procedure in 3G_MSC-A is successful then MSC-B can request the UE/MS to retune to the new RNS-B on 3G_MSC-A. This is illustrated in Figure 26 by the A-HO-COMMAND message. The operation is successfully completed when 3G_MSC-A receives the Iu-RELOCATION-COMPLETE message.
After GSM to UMTS handover 3G_MSC-A shall release the circuit to MSC-B.
3G_MSC-A must also terminate the MAP procedure for the basic handover between 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B by sending an appropriate MAP message. MSC-B will clear the resources in BSS-A when the MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL response is received.
8.2.3.2 Description of subsequent GSM to UMTS handover procedure ii): MSC-B to 3G_MSC-B' p. 68
The procedure for successful GSM to UMTS handover from MSC-B to 3G_MSC-B' is shown in Figure 27.
The procedure consists of two parts:
- a subsequent handover from MSC-B back to MSC-A as described in subclause 7.3.1 (the same procedures apply if MSC-A is replaced by 3G_MSC-A); and
- a basic GSM to UMTS handover from MSC-A to 3G_MSC-B' as described in subclause 8.2.1.
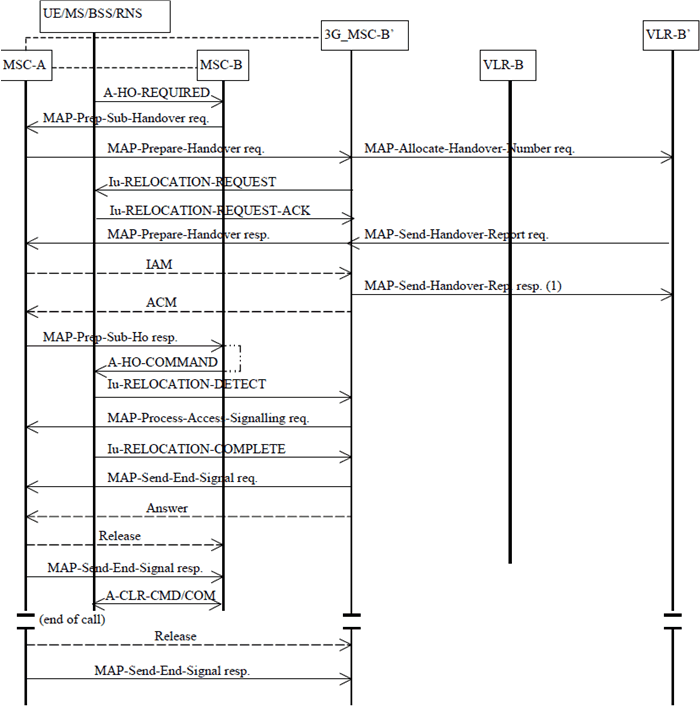
Figure 27: Subsequent GSM to UMTS handover procedure ii): Successful handover from MSC-B to 3G_MSC-B' requiring a circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)