Content for TS 23.009 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.3…
6…
6.2…
6.2.3
6.3…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.2.2…
8.2.4
8.3…
8.3.2…
9…
10…
11…
12…
12.8…
12.8.2
12.8.3
13…
14…
15…
8.1.3 Procedure for subsequent UMTS to GSM handover requiring a circuit connection
8.1.4 Procedure for subsequent UMTS to GSM handover not requiring a circuit connection
...
...
8.1.3 Procedure for subsequent UMTS to GSM handover requiring a circuit connection p. 56
After the call has been handed over to 3G_MSC-B, if the UE/MS leaves the area of 3G_MSC-B during the same call and enters a GSM area, subsequent UMTS to GSM handover is necessary in order to continue the connection.
The following cases apply:
- the UE/MS moves back to the area of MSC-A;
- the UE/MS moves into the area of a third MSC (MSC-B').
8.1.3.1 Description of subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure i): 3G_MSC-B to MSC-A p. 57
The procedure for successful UMTS to GSM handover from MSC-B back to 3G_MSC-A is shown in Figure 20.
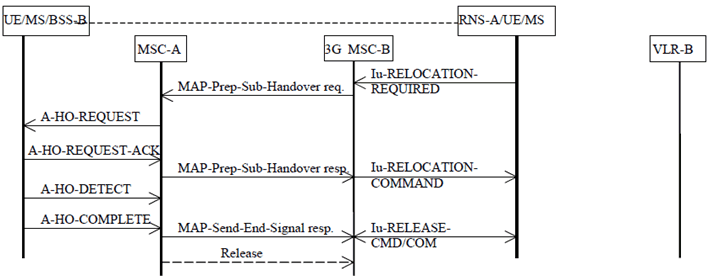
Figure 20: Subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure i): successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-A using a circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
8.1.3.1.1 With one circuit connection p. 57
The procedure is as follows.
3G_MSC-B sends the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request to MSC-A indicating the new MSC number (MSC-A number), indicating also the identity of the cell where the call has to be handed over and including a complete A-HO-REQUEST message. (NOTE: 3G_MSC-B shall not send further MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER requests while a handover attempt is pending or before any timeouts). Since MSC-A is the call controlling MSC, this MSC needs no Handover Number for routing purposes; MSC-A can immediately initiate the search for a free radio channel.
When a radio channel can be assigned, MSC-A shall return in the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response the complete A-HO-REQUEST-ACKNOWLEDGE message received from the BSS-B and possible extra BSSMAP information, amended by MSC-A due to the possible interworking between the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E-interface and the BSSMAP protocol used on the A-interface. If the traffic channel allocation is queued by BSS-B, the A-QUEUING-INDICATION may optionally be sent back to 3G_MSC-B. The further traffic channel allocation result (A-HO-REQUEST-ACK or A-HO-FAILURE) will be transferred to 3G_MSC-B using the MAP-FORWARD-ACCESS-SIGNALLING request. If a radio channel cannot be assigned or if a fault is detected on the target cell identity, or the target cell identity in the A-HO-REQUEST is not consistent with the target MSC number, the MAP PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response containing an A-HO-FAILURE message shall be given to 3G_MSC-B, in addition 3G_MSC-B shall maintain the connection with the UE/MS.
If the procedure in MSC-A is successful then 3G_MSC-B can request the UE/MS to retune to the new BSS-B on MSC-A. This is illustrated in Figure 20 by the Iu-RELOCATION-COMMAND message. The operation is successfully completed when MSC-A receives the A-HO-COMPLETE message.
After UMTS to GSM handover MSC-A shall release the circuit to 3G_MSC-B.
MSC-A must also terminate the MAP procedure for the basic UMTS to GSM handover between MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B by sending an appropriate MAP message. 3G_MSC-B will clear the resources in RNS-A when the MAP SEND-END-SIGNAL response is received.
8.1.3.1.2 With multiple circuit connections (Optional functionality) p. 57
If 3G_MSC-B supports the optional supplementary service Multicall (See TS 23.135), 3G_MSC-B shall have the following functionality additionally to the description in subclause 8.1.3.1.1.
Upon receipt of the IU-RELOCATION-REQUIRED from RNS-A which indicates the target is BSS, 3G_MSC-B shall select one bearer to be handed over if the UE is engaged with multiple bearers. After that, the 3G_MSC-B generates an A-HO-REQUEST message for the selected bearer and sends it to 3G_MSC-A over MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request with indication of RAB ID of the selected bearer.
When MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response including an A-HO-REQUEST-ACK is received from the 3G_MSC-A, 3G_MSC-B sends IU-RELOCATION-COMMAND, which indicates the bearers not to be handed over as bearers to be released, to RNS-A.
After 3G_MSC-A receives A-HO-COMPLETE message from BSS-B, 3G_MSC-A shall release calls via BSS-B, which has been carried by the bearers not to be handed over, and then 3G_MSC-A sends MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL response to 3G_MSC-B.
8.1.3.2 Description of subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure ii): 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' p. 58
The procedure for successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' is shown in Figure 21.
The procedure consists of two parts:
- a subsequent UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B back to 3G_MSC-A as described in subclause 8.1.3.1 (the same procedures apply if 3G_MSC-A is replaced by MSC-A); and
- a basic handover from 3G_MSC-A to MSC-B' as described in subclause 7.1.
8.1.3.2.1 With one circuit connection p. 58
3G_MSC-B sends the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request to 3G_MSC-A indicating a new MSC number (which is the identity of MSC-B'), indicating also the target cell identity and including a complete A HO REQUEST, 3G_MSC-A then starts a basic handover procedure towards MSC-B'.
If 3G_MSC-A supports A interface over IP, then for speech calls 3G_MSC-A may include the AoIP-Supported Codecs List (Anchor) in the MAP-PREPARE-HANDOVER request towards MSC-B'. For a detailed description of the handling of this codec list by 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B' see TS 23.153.
When 3G_MSC-A receives the ACM from MSC-B', 3G_MSC-A informs 3G_MSC-B that MSC-B' has successfully allocated the radio resources on BSS-B' side by sending the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response containing the complete A-HO-REQUEST-ACKNOWLEDGE received from BSS-B' and possible extra BSSMAP information, amended by 3G_MSC-A due to the possible interworking between the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E interface between 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B' and the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E-interface between 3G_MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B. Now 3G_MSC-B can start the procedure on the radio path.
For 3G_MSC-A the UMTS to GSM handover is completed when it has received the MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL REQUEST from MSC-B' containing the A-HO-COMPLETE received from the BSS-B'. The circuit between 3G_MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B is released. 3G_MSC-A also sends the MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL response to 3G_MSC-B in order to terminate the original MAP dialogue between 3G_MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B. 3G_MSC-B releases the radio resources when it receives this message.
If the traffic channel allocation is queued by the BSS-B', the A-QUEUING-INDICATION may optionally be sent back to 3G_MSC-B. If no radio channel can be allocated by MSC-B' or no circuit between 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B' can be established or a fault is detected on the target cell identity or the target cell identity in the A-HO-REQUEST is not consistent with the target MSC number, 3G_MSC-A informs 3G_MSC-B by using the A-HO-FAILURE message included in the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response. 3G_MSC-B shall maintain the existing connection with the UE/MS.
When the subsequent UMTS to GSM handover is completed, MSC-B' is considered as MSC-B. Any further inter-MSC handover is handled as described earlier for a subsequent handover.
8.1.3.2.2 With multiple circuit connections (Optional functionality) p. 58
If 3G_MSC-B supports the optional supplementary service Multicall (See TS 23.135), 3G_MSC-B shall have the following functionality additionally to the description in subclause 8.1.3.2.1.
Upon receipt of the IU-RELOCATION-REQUIRED from RNS-B 3G_MSC-B shall select one bearer to be handed over if the UE is engaged with multiple bearers. After that, the 3G_MSC-B generates an A-HO-REQUEST message for the selected bearer and sends it to 3G_MSC-A over MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request with indication of RAB ID of the selected bearer.
Upon receipt of the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER request from 3G_MSC-B, 3G_MSC-A starts a basic handover procedure towards MSC-B'.
When 3G_MSC-A receives the ACM from MSC-B', 3G_MSC-A informs 3G_MSC-B that MSC-B' has successfully allocated the radio resources on BSS-B' side by sending the MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response containing the complete A-HO-REQUEST-ACK received from BSS-B' and possible extra BSSAP information, amended by 3G_MSC-A due to the possible interworking between the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E-interface between 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B' and the BSSMAP protocol carried on the E-interface between 3G_MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B.
When MAP-PREPARE-SUBSEQUENT-HANDOVER response including an A-HO-REQUEST-ACK is received from 3G_MSC-A, 3G_MSC-B sends IU-RELOCATION-COMMAND, which indicates the bearers not to be handed over as bearers to be released, to RNS-A.
After 3G_MSC-A receives MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL request from MSC-B', 3G_MSC-A shall release calls via MSC-B', which has been carried by the bearers not to be handed over, and then 3G_MSC-A sends MAP-SEND-END-SIGNAL response to 3G_MSC-B.
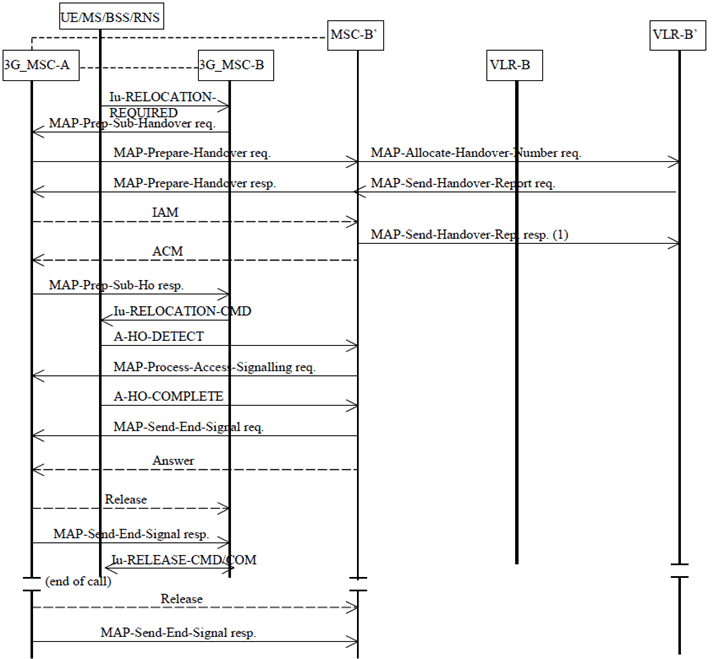
Figure 21: Subsequent handover procedure ii): Successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' requiring a circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
8.1.4 Procedure for subsequent UMTS to GSM handover not requiring a circuit connection p. 60
As for the subsequent UMTS to GSM handover with a circuit connection, the same two cases of subsequent handover apply:
- the UE/MS moves back to the area of MSC-A;
- the UE/MS moves into the area of a third MSC (MSC-B').
8.1.4.1 Description of subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure i): 3G_MSC-B to MSC-A p. 61
The procedure for successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B back to MSC-A without circuit connection is shown in Figure 22. The only difference with the Figure 20, is that no circuit release is needed between MSC-A and 3G_MSC-B.
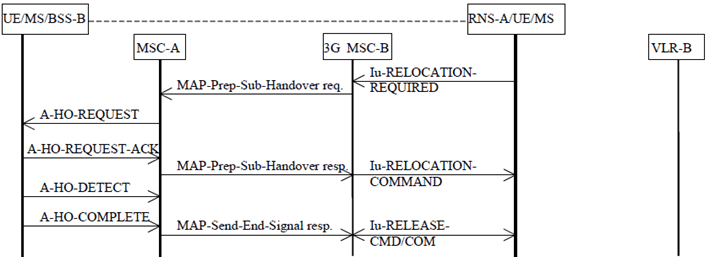
Figure 22: Subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure i): Successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-A not requiring a circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
8.1.4.2 Description of the subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure without circuit connection ii): 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' p. 61
The procedure for successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' is shown in Figure 23.
The procedure consists of two parts:
- a subsequent UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B back to 3G_MSC-A as described in subclause 8.1.4.1 (the same procedures apply if 3G_MSC-A is replaced by MSC-A); and
- a basic handover from 3G_MSC-A to MSC-B' as described in subclause 7.2.
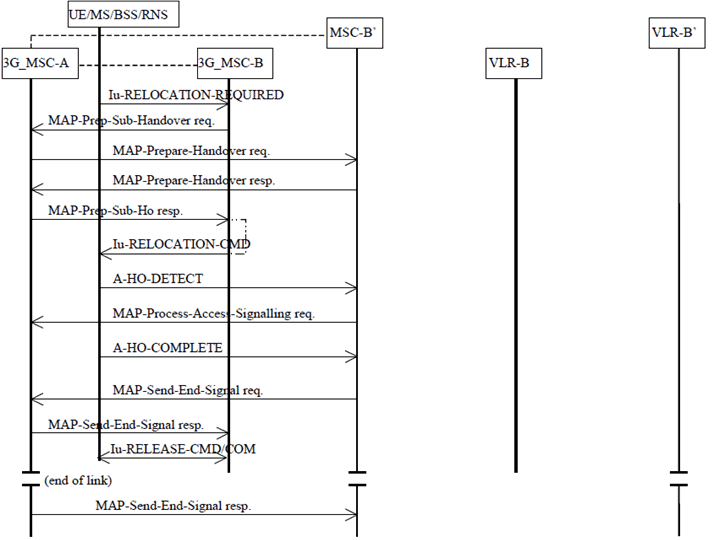
Figure 23: Subsequent UMTS to GSM handover procedure ii): Successful UMTS to GSM handover from 3G_MSC-B to MSC-B' without circuit connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)