Content for TS 23.433 Word version: 19.0.0
0…
4…
7…
8…
9.2…
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.4…
9.3…
9.3.2.2…
9.3.3…
9.3.4…
9.4…
9.5…
9.5.3…
9.5.4…
9.6…
9.7…
9.7.3…
9.7.4…
9.8…
9.9…
9.10…
A…
C…
7 Architecture
7.1 General
7.2 Architecture
7.3 Functional entities
7.3.1 General
7.3.2 SEAL Data Delivery server
7.3.3 SEAL Data Delivery client
7.4 Reference points
7.4.1 General
7.4.2 SEALDD-UU
7.4.3 SEALDD-C
7.4.4 SEALDD-S
7.4.5 SEALDD-E
7.4.6 N6
7.4.7 N33/N5
7.5 Cardinality rules
7.5.1 General
7.5.2 Functional Entity Cardinality
7.5.2.1 VAL client
7.5.2.2 SEALDD client
7.5.2.3 SEALDD server
7.5.2.4 VAL server
7.5.3 Reference Point Cardinality
7.5.3.1 SEALDD-C (Between VAL client and SEALDD client)
7.5.3.2 SEALDD-S (Between VAL layer and SEALDD server)
7.5.3.3 SEALDD-UU (Between SEALDD client and SEALDD server)
7.5.3.4 SEALDD-E (Between SEALDD server and SEALDD server)
...
...
7 Architecture p. 16
7.1 General p. 16
The architecture for the SEAL data delivery enabler is based on the generic functional model specified in clause 6.2 of TS 23.434.
This clause provides the overall architecture description:
- Clause 7.2 describes the functional architecture;
- Clause 7.3 describes the functional entities;
- Clause 7.4 describes the reference points; and
- Clause 7.5 describes the cardinality of functional entities and reference points.
7.2 Architecture p. 16
This clause describes the architecture for enabling SEAL Data Delivery applications in the following representations:
- A service-based representation as specified in TS 23.434, where the SEAL Data Delivery Enabler Layer functions (e.g. SEALDD server) enable other authorized Vertical Application Layer functions (e.g. VAL server) to access their services.
- A service-based representation as specified in TS 23.501, where the Network Functions (e.g. NEF) enable authorized SEAL Data Delivery Layer functions (e.g. SEALDD server) i.e. Application Functions, to access their services;
- A service-based representation, where the Core Network Northbound APIs as specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502, are utilized by authorized SEAL Data Delivery Enabler Layer functions via CAPIF core function specified in TS 23.222; and
- A reference point representation, where existing interactions between any two functions (e.g. SEALDD client and SEALDD server) is shown by an appropriate point-to-point reference point (e.g. SEALDD-UU).
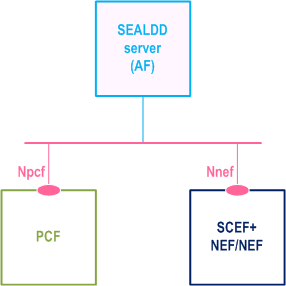
The SEALDD server acts as AF for consuming network services from the 3GPP 5G Core Network entities over the Service Based Architecture specified in TS 23.501.
Figure 7.2-2 illustrates the service-based representation for utilization of the Core Network (5GC, EPC) northbound APIs via CAPIF.
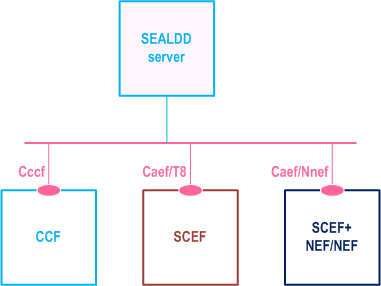
The SEALDD server acts as authorized API invoker to consume services from the Core Network (5GC, EPC) northbound API entities like SCEF, NEF, SCEF+NEF which act as API Exposing Function as specified in TS 23.222.
The mechanism for northbound APIs discovery using the service-based interfaces depicted in Figure 7.2-3 is as specified in TS 23.222.
Figure 7.2-3 illustrates the architecture for SEAL Data Delivery enabler service.
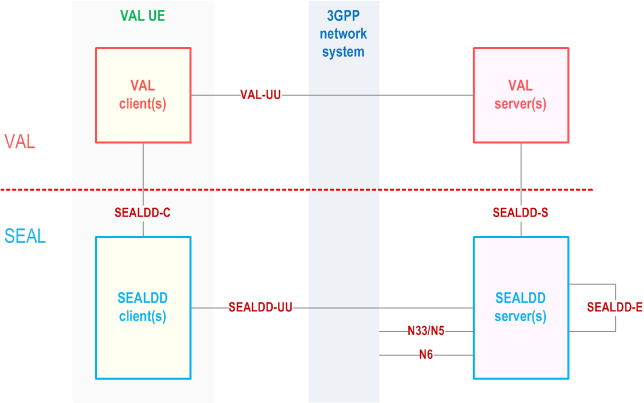
The SEALDD server can communicate with the control plane of 3GPP core network via N33/N5 interface with the SEALDD control plane functionality.
For uplink traffic, VAL client sends application data traffic to SEALDD client for SEALDD service over SEALDD-C. After data plane packet processing by SEALDD client, the application data traffic is converted to SEALDD data traffic and transferred to SEALDD server over SEALDD-UU. The SEALDD server restores the application data traffic and sends it to VAL server over SEALDD-S. For downlink traffic, VAL server sends application data traffic to SEALDD server for SEALDD service over SEALDD-S. After data plane packet processing by SEALDD server, the application data traffic is converted to SEALDD data traffic and transferred to SEALDD client over SEALDD-UU. The SEALDD client restores the application data traffic and sends it to VAL client over SEALDD-C. Optionally, VAL deployments may choose to route application signalling traffic and application data traffic for some or all functions it offers using SEALDD service and Figure 7.2-4 illustrates the architecture for achieving this. In this case the VAL client and VAL server may choose not to maintain application connection by themselves and transfer all the application traffic over SEALDD connections for those functions. The data storage functionality may be provided by SEALDD server or provided by other storage functions in VAL server, or other cloud platform.
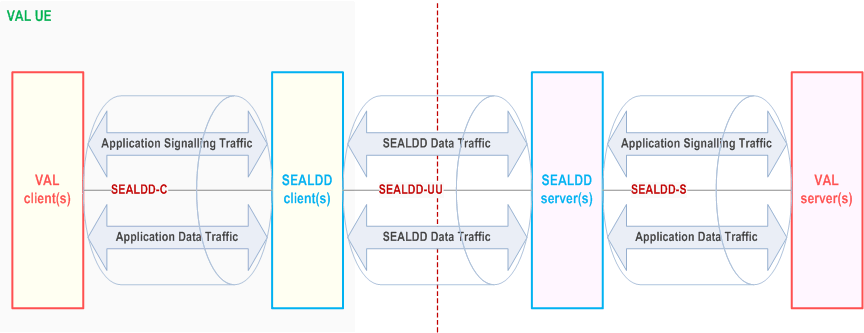
The SEAL Data Delivery client interacts with the SEAL data delivery server to establish application layer data transport path.
Through this path, the SEALDD server and client provides data transport service capabilities such as data plane packet processing (e.g. packet duplication, elimination or transport coordination), data forwarding, data caching, background data transfer, etc. to support the VAL server and VAL client. Annex C describes a typical lifecycle of SEALDD to establish the SEALDD connection for the VAL client and VAL server.
7.3 Functional entities p. 19
7.3.1 General p. 19
The functional entities for SEALDD service are described in the following clauses.
7.3.2 SEAL Data Delivery server p. 19
The SEAL data delivery server functional entity acts as the application server for the data delivery enablement. The SEALDD server supports the following capabilities:
- Supporting the transmission for application signalling data and application media/data, by using 3GPP network.
- Providing the application data/media handling capabilities (e.g. storage, management, transmission).
- Interacting with 5GC via N33/N5 (i.e. send control plane requirements or receive control plane notification) with usage of capability exposed by 3GPP network.
7.3.3 SEAL Data Delivery client p. 19
The SEAL data delivery client functional entity acts as the application client for the data delivery enablement. The SEALDD client supports the following capabilities:
- Supporting the transmission for application signalling data and application media/data, by using 3GPP network.
7.4 Reference points p. 19
7.4.1 General p. 19
The reference points for the functional model for SEALDD are described in the following clauses.
7.4.2 SEALDD-UU p. 20
Reference point between SEALDD client and SEALDD server used to transfer data content and exchange information for SEALDD service provisioning, control, reporting etc.
7.4.3 SEALDD-C p. 20
Reference point between SEALDD client and VAL client to enable northbound client side API exposed by SEALDD client to VAL client for data delivery and SEALDD service provisioning, control, reporting etc.
7.4.4 SEALDD-S p. 20
Reference point between SEALDD server and VAL server to enable northbound server side API exposed by SEALDD server to VAL server for data delivery and SEALDD service provisioning, control, reporting etc.
7.4.5 SEALDD-E p. 20
Reference point enables interactions between two SEALDD servers to transfer data content and exchange information for SEALDD service provisioning, control, reporting etc.
7.4.6 N6 p. 20
Reference point enables interactions between SEALDD server and 5GC to transfer SEALDD traffic packets.
7.4.7 N33/N5 p. 20
Reference point enables interactions between SEALDD server and 5GC to send control plane requirements or receive control plane notification for optimized data transmission.
7.5 Cardinality rules p. 20
7.5.1 General p. 20
The cardinality rules for the SEALDD entities and SEALDD reference points are described in the following clauses.
7.5.2 Functional Entity Cardinality p. 20
7.5.2.1 VAL client p. 20
The following cardinality rules apply for VAL clients:
- One or more VAL client(s) may be located in a VAL UE.
7.5.2.2 SEALDD client p. 20
The following cardinality rules apply for SEALDD clients:
- One or more SEALDD client(s) may be located in a VAL UE.
7.5.2.3 SEALDD server p. 20
The following cardinality rules apply for SEALDD server:
- One or more SEALDD server(s) may be located in network.
7.5.2.4 VAL server p. 21
The following cardinality rules apply for VAL server:
- One or more VAL server(s) may be located in network.
7.5.3 Reference Point Cardinality p. 21
7.5.3.1 SEALDD-C (Between VAL client and SEALDD client) p. 21
The following cardinality rules apply for the reference of SEALDD-C:
- One VAL client may communicate with only one SEALDD client; and
- One SEALDD client may communicate with one or more VAL client(s) concurrently.
7.5.3.2 SEALDD-S (Between VAL layer and SEALDD server) p. 21
The following cardinality rules apply for the reference of SEALDD-S:
- One VAL server may communicate with one or more SEALDD server; and
- One SEALDD server may communicate with one or more VAL server(s) concurrently.
7.5.3.3 SEALDD-UU (Between SEALDD client and SEALDD server) p. 21
The following cardinality rules apply for the reference of SEALDD-UU:
- One SEALDD client may communicate with one or more SEALDD servers.
- One SEALDD server may communicate with one or more SEALDD client(s) concurrently.
7.5.3.4 SEALDD-E (Between SEALDD server and SEALDD server) p. 21
The following cardinality rules apply for the reference of SEALDD-E:
- One SEALDD server may communicate with one or more SEALDD server(s) concurrently.