TS 38.410
NG-RAN — NG interface –
General Aspects and Principles
V18.2.0 (PDF)
2024/06 22 p.
V17.1.0
2022/06 20 p.
V16.4.0
2021/09 19 p.
V15.2.0
2018/12 17 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Godin, Philippe
Nokia France
Content for TS 38.410 Word version: 18.2.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
4 General aspects
5 Functions of the NG interface
6 Signalling procedures of the NG interface
7 NG interface protocol structure
8 Other NG interface specifications
$ Change history
1 Scope p. 5
The present document is an introduction to the 3GPP TS 38.41x series of technical specifications that define the NG interface for the interconnection of an NG-RAN node to the 5GC (5G Core Network).
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 38.411: "NG-RAN; NG layer 1".
[3]
TS 38.412: "NG-RAN; NG signalling transport".
[4]
TS 38.413: "NG-RAN; NG Application Protocol (NGAP) ".
[5]
TS 38.414: "NG-RAN; NG data transport".
[6]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G system".
[7]
TS 38.300: "NR; Overall Description; Stage 2".
[8]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G system".
[9]
TS 38.415: "PDU Session User Plane Protocol".
[10]
TS 38.455: "NR Positioning Protocol A (NRPPa)".
[11]
TS 36.300: "E-UTRAN; Overall description; Stage 2".
[12]
TS 23.247: "Architectural enhancements for 5G multicast-broadcast services; Stage 2".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 6
3.1 Definitions p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply.
A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
gNB:
as defined in TS 38.300.
NB-IoT:
as defined in TS 36.300.
ng-eNB:
as defined in TS 38.300.
NG-RAN node:
as defined in TS 38.300.
UPF:
as defined in TS 23.501.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply.
A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
5GC
5G Core Network
AMF
Access and Mobility Management Function
CIoT
Cellular IoT
CN
Core Network
DRX
Discontinuous Reception
MBS
Multicast/Broadcast Service
MT
Mobile Terminated
NB-IoT
Narrow Band Internet of Things
NG-U
NG User plane interface
PTP
Point to Point
PTM
Point to Multipoint
QMC
QoE Measurement Collection
QoE
Quality of Experience
RIM
Remote Interference Management
SMF
Session Management Function
UP
User Plane
UPF
User Plane Function
4 General aspects p. 6
4.1 NG Architecture p. 6
The NG-RAN is layered into a Radio Network Layer (RNL) and a Transport Network Layer (TNL). The NG-RAN architecture, i.e. the NG-RAN logical nodes and interfaces between them, are defined as part of the RNL.
The NG-RAN architecture consists of a set of gNBs and ng-eNBs which are connected to the 5GC through the NG interface and is specified in TS 38.300.
The NG-RAN may have several NG access points towards the 5GC. As a minimum, each NG access point (in NG-RAN or 5GC) shall independently fulfil the requirements of the relevant NG specifications (3GPP 38.41x series - see clause 7).
NG is a logical interface.
There may be multiple NG-C logical interfaces towards the 5GC from any one NG-RAN node. The selection of the NG-C interface is then determined by the NAS Node Selection function as described in clause 5.
There may be multiple NG-U logical interfaces towards the 5GC from any one NG-RAN node. The selection of the NG-U interface is done within the 5GC and signalled to the NG-RAN node by the AMF.
4.2 NG interface general principles p. 7
The general principles for the specification of the NG interface are as follows:
- the NG interface is open;
- the NG interface supports the exchange of signalling information between the NG-RAN and 5GC;
- from a logical standpoint, the NG is a point-to-point interface between an NG-RAN node and a 5GC node. A point-to-point logical interface is feasible even in the absence of a physical direct connection between the NG-RAN and 5GC;
- the NG interface supports control plane and user plane separation;
- the NG interface separates Radio Network Layer and Transport Network Layer;
- the NG interface is future proof to fulfil different new requirements and support of new services and new functions;
- the NG interface is decoupled with the possible NG-RAN deployment variants;
-
the NG Application Protocol supports modular procedures design and uses a syntax allowing optimized encoding/
decoding efficiency.
4.3 NG interface specification objectives p. 7
The NG interface specification facilitates the following:
- inter-connection of NG-RAN nodes with AMFs supplied by different manufacturers;
- separation of NG interface Radio Network functionality and Transport Network functionality to facilitate introduction of future technology.
4.4 NG interface capabilities p. 7
The NG interface supports:
- procedures to establish, maintain and release NG-RAN part of PDU sessions;
- procedures to perform intra-RAT handover and inter-RAT handover;
- the separation of each UE on the protocol level for user specific signalling management;
- the transfer of NAS signalling messages between UE and AMF;
- mechanisms for resource reservation for packet data streams;
- procedures to establish, maintain and release NG-RAN part of MBS sessions.
5 Functions of the NG interface p. 8
5.1 General p. 8
The following clauses describe the functions supported over the NG interface.
5.2 Paging function p. 8
The paging function supports the sending of paging requests to the NG-RAN nodes involved in the paging area e.g. the NG-RAN nodes of the TA(s) the UE is registered.
The function also supports CN controlled subgrouping paging for UE Power Saving.
5.3 UE Context Management function p. 8
The UE Context management function allows the AMF to establish, modify or release a UE Context in the AMF and the NG-RAN node e.g. to support user individual signalling on NG.
The function also enables the AMF to manage RRC state notifications of a CM-CONNECTED UE.
5.4 Mobility Management function p. 8
The mobility function for UEs in CM-CONNECTED includes the intra-system handover function to support mobility within NG-RAN and inter-system handover function to support mobility from/to EPS system. It comprises the preparation, execution and completion of handover via the NG interface.
5.5 PDU Session Management function p. 8
The PDU Session function is responsible for establishing, modifying and releasing the involved PDU sessions NG-RAN resources for user data transport once a UE context is available in the NG-RAN node.
NGAP supports transparent relaying of PDU Session related information by the AMF as described in TS 23.502.
5.6 NAS Transport function p. 8
The NAS Signalling Transport function provides means to transport or reroute a NAS message (e.g. for NAS mobility management), or report the non-delivery of a NAS message for a specific UE over the NG interface.
5.7 NAS Node Selection function p. 8
The interconnection of NG-RAN nodes to multiple AMFs is supported in the 5GS architecture.
Therefore, a NAS node selection function is located in the NG-RAN node to determine the AMF association of the UE, based on the UE's temporary identifier, which was assigned to the UE by the AMF. When the UE's temporary identifier has not been yet assigned or is no longer valid the NG-RAN node may instead take into account other information (e.g. slicing information, onboarding indication) to determine the AMF. When the NG-RAN node is configured to ensure that the selected AMF serves the country where the UE is located, as described in TS 23.501, the NG-RAN node takes into account UE location information, if available, when determining the AMF.
This functionality is located in the NG-RAN node and enables proper routing via the NG interface. On NG, no specific procedure corresponds to the NAS Node Selection Function.
5.8 NG Interface Management function p. 9
The NG-interface management functions provide:
- means to ensure a defined start of NG-interface operation (reset);
- means to handle different versions of application part implementations and protocol errors (error indication).
5.9 Warning Message Transmission function p. 9
The warning message transmission function provides means to transfer warning messages via NG interface or cancel ongoing broadcast of warning messages. It also provides the capability for the NG-RAN to inform the AMF that ongoing PWS operation has failed for one or more areas, or that one or more areas may be reloaded by the CBC.
5.10 Configuration Transfer function p. 9
The Configuration Transfer function is a generic mechanism that allows the request and transfer of RAN configuration information (e.g. SON information) between two RAN nodes via the core network.
5.11 Trace function p. 9
The Trace function provides means to control trace sessions in the NG-RAN node.
5.12 AMF Management function p. 9
The AMF management function supports AMF planned removal and AMF auto-recovery as specified in TS 23.501.
5.13 Multiple TNL Associations Support Function p. 9
When there are multiple TNL associations between a NG-RAN node and an AMF, the NG-RAN node selects the TNL association for NGAP signalling based on the usage and the weight factor of each TNL association received from the AMF, and uses the TNL association as specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502. If an AMF releases a TNL association or a TNL association has failed, the NG-RAN node selects a new one as specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502.
5.14 AMF Load Balancing function p. 9
The NG interface supports the indication by the AMF of its relative capacity to the NG-RAN node in order to achieve load-balanced AMFs within the pool area.
5.15 Location Reporting function p. 9
This function enables the AMF to request the NG-RAN node to report the UE's current location, or the UE's last known location with timestamp, or the UE's presence in a configured area of interest.
5.16 AMF Re-allocation function p. 9
This function allows to redirect an initial connection request issued by an NG-RAN node from an initial AMF towards a target AMF selected by 5GC. In this case the NG-RAN node initiates an Initial UE Message procedure over one NG interface instance and receives the first downlink message to close the UE-associated logical connection over a different NG interface instance.
5.17 UE Radio Capability Management function p. 10
The UE Radio Capability Management function is related to the UE radio capability handling.
5.18 NRPPa Signaling Transport function p. 10
The NRPPa (NR Positioning Protocol A) Signalling Transport function provides means to transport an NRPPa (TS 38.455) message transparently over the NG interface.
5.19 Overload Control function p. 10
The overload function provides means to enable AMF controls the load that the NG-RAN node(s) are generating.
5.20 Report of Secondary RAT data volumes Function p. 10
The Report of Secondary RAT data volumes Function enables the NG-RAN node to report Secondary RAT usage data information in case of MR-DC, either with a dedicated procedure or by including Secondary RAT usage data information in other messages.
5.21 RIM Information Transfer function |R16| p. 10
The RIM Information Transfer function is a generic mechanism that allows the transfer of Remote Interference Management (RIM) information between two RAN nodes via the core network.
5.22 Retrieve UE Information function |R16| p. 10
The Retrieve UE Information function enables the NG-RAN node to request UE information (e.g. QoS differentiation information) from the AMF before the setup of the NG connection for NB-IoT UE(s) using Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimization.
5.23 RAN CP Relocation Indication function |R16| p. 10
The RAN CP Relocation Indication function enables the initiation of the UE-associated logical NG-connection for a NB-IoT UE using Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation following a re-establishment request. It allows to have the re-estabblishment request authenticated by the AMF.
5.24 Suspend-Resume function |R16| p. 10
This function enables to suspend the UE-associated logical NG-connection and release the NG-U tunnel while storing the UE context in the NG-RAN for a faster subsequent resume as specified for User Plane CIoT 5GS optimizations in TS 23.501. In this version of the specification, this function only applies for long eDRX cycles.
5.25 Connection Establishment Indication Function |R16| p. 10
The connection establishment indication function enables the AMF to complete the establishment of the UE-associated logical NG-connection.
5.26 AMF CP Relocation Indication Function |R16| p. 10
The AMF CP relocation indication function enables the AMF to inform the previously serving NG-RAN node that the UE's connection is to be relocated to a new NG-RAN node.
5.27 NR MBS Session Management function |R17| p. 11
The MBS Session Management function is responsible for establishing, modifying and releasing the involved NR MBS sessions NG-RAN resources for user data transport once an MBS context is available in the NG-RAN node.
NGAP supports transparent relaying of MBS Session related information by the AMF as described in TS 23.247.
5.28 Multicast Group Paging Function |R17| p. 11
The Multicast group paging function supports the sending of multicast group paging requests to the NG-RAN nodes in order to group-page UEs that have joined the Multicast MBS Session.
5.29 QMC support function |R17| p. 11
The QMC function provides means to manage the QMC sessions and support the mobility of QMC sessions over the NG interface.
5.30 MT Communication Handling function |R18| p. 11
The function enables to support MT data and signalling handling within the 5GC for UEs in RRC_INACTIVE state with extended DRX beyond 10.24s as specified in TS 23.501.
5.31 Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting function |R18| p. 11
The Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting function enables the AMF to request the NG-RAN node to report the RAN timing synchronisation status information, and for the NG-RAN node to provide the RAN timing synchronisation status information to the AMF.
6 Signalling procedures of the NG interface p. 11
6.1 PDU Session Management Procedures p. 11
The following PDU Session management procedures are used to establish, release or modify PDU sessions.
- PDU Session Resource Setup;
- PDU Session Resource Release;
- PDU Session Resource Modify;
- PDU Session Resource Notify;
- PDU Session Resource Modify Indication.
6.2 UE Context Management Procedures p. 11
The following UE Context management procedures are used to establish, release or modify the UE context. They may also be used to report RRC state transition from NG-RAN to 5GC.
- Initial Context Setup;
- UE Context Release Request;
- UE Context Release;
- UE Context Modification;
- RRC Inactive Transition Report.
6.3 NAS transport procedures p. 12
The NAS transport procedures enable transparent transfer of NAS signalling data between the AMF and the UE. The procedures providing this functionality are:
- Initial UE Message (NG-RAN node initiated);
- Uplink NAS transport (NG-RAN node initiated);
- Downlink NAS transport (AMF initiated);
- NAS non delivery indication (NG-RAN node initiated);
- Reroute NAS Request (AMF initiated).
6.4 UE Mobility Management Procedures p. 12
The following UE Mobility management procedures are used to prepare, execute or cancel handovers:
- Handover Preparation;
- Handover Resource Allocation;
- Handover Notification;
- Path Switch Request;
- Uplink RAN Status Transfer;
- Downlink RAN Status Transfer;
- Handover Cancellation ;
- Handover Success;
- Uplink RAN Early Status Transfer;
- Downlink RAN Early Status Transfer.
6.5 Paging procedure p. 12
The following paging procedure is used to send paging requests to the NG-RAN nodes involved in the paging area:
- Paging.
6.6 AMF Management procedures p. 12
The following AMF management procedures are used by the AMF to inform the NG-RAN nodes about an AMF's status, and to release the UE TNLA binding for specific UE(s):
- AMF Status Indication;
- UE TNLA binding release.
6.7 NG Interface Management procedures p. 12
The following procedures are used to manage the NG interface:
- NG Setup;
- RAN Configuration Update;
- AMF Configuration Update;
- NG Reset;
- Error Indication.
6.8 Warning message transmission procedures p. 13
The following procedures are used to manage the broadcasting of warning messages:
- Write-Replace Warning;
- PWS Cancel;
- PWS Restart Indication;
- PWS Failure Indication.
6.9 Location Reporting procedures p. 13
The following procedures are used to report the location of the UE:
- Location Reporting Control;
- Location Report;
- Location Reporting Failure Indication.
6.10 UE Radio Capability Management procedures p. 13
The following procedures are related to the UE radio capability handling:
- UE Radio Capability Check;
- UE Radio Capability Info Indication;
- UE Radio Capability ID Mapping.
6.11 UE Tracing procedures p. 13
The following procedures are used to trace the UE:
- Trace Start;
- Trace Failure Indication;
- Deactivate Trace;
- Cell Traffic Trace.
6.12 NR Positioning Protocol A (NRPPa) procedures p. 13
The following procedures are used for NRPPa signalling:
- Downlink UE Associated NRPPa Transport;
- Uplink UE Associated NRPPa Transport;
- Downlink non-UE Associated NRPPa Transport;
- Uplink non-UE Associated NRPPa Transport.
6.13 Overload Control procedures p. 14
The following procedures are used by the AMF to start or stop overload control:
- Overload Start procedure;
- Overload Stop procedure.
6.14 Configuration Transfer procedures p. 14
The following procedures are used by the AMF to transfer the RAN configuration information:
- Downlink RAN Configuration Transfer procedure;
- Uplink RAN Configuration Transfer procedure.
6.15 Secondary RAT Data Usage Report procedure p. 14
The following procedure is used to provide information on the used resources of the secondary RAT:
- Secondary RAT Data Usage Report procedure.
6.16 RIM Information Transfer procedures |R16| p. 14
The following procedures are used by the AMF to transfer the Remote Interference Management (RIM) information:
- Downlink RIM Information Transfer procedure;
- Uplink RIM Information Transfer procedure.
6.17 Retrieve UE Information procedures |R16| p. 14
The following procedures are used by the NG-RAN node to retrieve UE information from the AMF:
- Retrieve UE Information Request procedure;
- UE Information Transfer procedure.
6.18 RAN CP Relocation Indication procedures |R16| p. 14
The following procedure is used by the NG-RAN node to initiate the UE-associated logical NG-connection for the RAN CP Relocation function:
- RAN CP Relocation Indication procedure.
6.19 UE Context Suspend procedure |R16| p. 14
The following procedure is to suspend the UE-associated logical NG-connection and release the NG-U tunnel with the 5GC while keeping the UE context in NG-RAN. In this version of the specification, this procedure applies only if the NG-RAN node is an ng-eNB.
- UE Context Suspend procedure.
6.20 Connection Establishment Indication procedure |R16| p. 15
The following procedure is used to enable the AMF to provide information to the NG-RAN node to complete the establishment of the UE-associated logical NG-connection, for UEs using CIoT 5GS Optimization:
- Connection Establishment Indication.
6.21 AMF CP Relocation Indication procedure |R16| p. 15
The following procedure is used to inform the previously serving NG-RAN node that the UE's connection is to be relocated to a new NG-RAN node, for UEs using Control Plane CIoT 5GS optimizations:
- AMF CP Relocation Indication.
6.22 UE Context Resume procedure |R16| p. 15
The following procedure is used to resume the UE context, resume the suspended logical NG-connection and re-establish the related NG-U tunnel in the 5GC for the involved UE. In this version of the specification, this procedure applies only if the NG-RAN node is an ng-eNB.
- UE Context Resume procedure.
6.23 NR MBS Session Management Procedures |R17| p. 15
The following list of MBS Session management procedures are used to establish, release, or modify NG-RAN resources for a NR MBS session:
- Broadcast Session Resource Setup;
- Broadcast Session Modification;
- Broadcast Session Resource Release;
- Broadcast Session Resource Release Required;
- Broadcast Session Transport;
- Multicast Session Activation;
- Multicast Session Deactivation;
- Multicast Session Update;
- Distribution Setup;
- Distribution Release;
6.24 Multicast Group Paging Procedures |R17| p. 15
The following Multicast Group Paging procedure is used to send multicast group paging requests to the NG-RAN nodes:
- Multicast Group Paging.
6.25 The procedures for supporting QMC |R17| p. 16
The following procedures are used to control the QMC sessions in the UE and to transfer QMC session information to the target NG-RAN node during the intra-system intra-RAT or intra-system inter-RAT mobility of a UE:
- Initial Context Setup;
- UE Context Modification;
- Handover Preparation;
- Handover Resource Allocation.
6.26 MT Communication Handling procedures |R18| p. 16
The following procedures are used by the NG-RAN node to request the AMF to activate or deactivate the CN based MT communication handling for UEs in RRC_INACTIVE state with long extended DRX beyond 10.24 seconds, and by the 5GC to indicate availability of downlink data or downlink signalling to the NG-RAN node.
- MT Communication Handling procedure;
- RAN Paging Request procedure;
- Path Switch Request procedure.
6.27 Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting procedures |R18| p. 16
The following procedures are used to report the RAN timing synchronisation status information:
- Timing Synchronization Status;
- Timing Synchronization Status Report.
7 NG interface protocol structure p. 16
7.1 NG Control Plane p. 16
The control plane protocol stack of the NG interface is shown on Figure 7.1-1. The transport network layer is built on IP transport. For the reliable transport of signalling messages, SCTP is added on top of IP. The application layer signalling protocol is referred to as NGAP (NG Application Protocol).
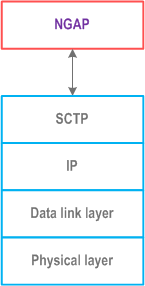
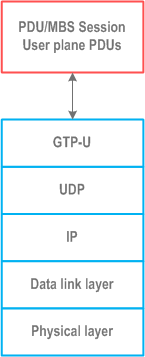
7.2 NG User Plane p. 17
The NG user plane (NG-U) interface is defined between a NG-RAN node and a UPF. The NG-U interface provides non guaranteed delivery of PDU Session/MBS session user plane PDUs between the NG-RAN node and the UPF.
The protocol stack for NG-U is shown in Figure 7.2-1.
8 Other NG interface specifications p. 17
8.1 NG-RAN NG interface: NG layer 1 (TS 38.411) p. 17
TS 38.411 specifies the physical layer technologies that may be used to support the NG interface.
8.2 NG-RAN NG interface: NG signalling transport (TS 38.412) p. 17
TS 38.412 specifies how the NGAP signalling messages are transported over NG.
8.3 NG-RAN NG interface: NG application protocol (NGAP) (TS 38.413) p. 17
TS 38.413 specifies the radio network layer signalling procedures of the control plane between the NG-RAN node and the AMF.
8.4 NG-RAN NG interface: NG data transport (TS 38.414) p. 17
TS 38.414 specifies the standards for user data transport protocols over the NG interface.
8.5 NG-RAN NG interface: NG PDU Session user plane protocol (TS 38.415) p. 17
TS 38.415 specifies the PDU Session User Plane protocol procedures, and the PDU Set Information User Plane protocol procedures over the NG interface.