TS 36.414
E-UTRAN – S1 Interface
Data Transport
V18.0.0 (PDF)
2024/03 10 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 10 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 10 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 10 p.
V14.1.0
2017/06 10 p.
V13.0.0
2015/12 10 p.
V12.1.0
2014/12 10 p.
V11.0.0
2012/09 10 p.
V10.1.0
2011/06 10 p.
V9.0.1
2011/04 10 p.
V8.4.0
2009/03 10 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Dr. Reininger, Philippe
Huawei Tech.(UK) Co. Ltd
Content for TS 36.414 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
4 Data Link Layer
5 S1 Interface user plane protocol
$ Change History
1 Scope p. 5
The present document specifies the standards for user data transport protocols and related signalling protocols to establish user plane transport bearers over the S1 interface.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 29.281: "General Packet Radio System (GPRS) Tunnelling Protocol User Plane (GTPv1-U)".
[3]
RFC 768 (1980-08): "User Datagram Protocol".
[4]
RFC 2474 (1998-12): "Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the Ipv4 and Ipv6 Headers".
[5]
RFC 2460 (1998-12): "Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification".
[6]
RFC 791 (1981-09): "Internet Protocol".
[7]
TS 36.401: "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN); Architecture description".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 5
3.1 Definitions p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions below apply. Terms and definitions not defined below can be found in TR 21.905.
S1:
interface between an eNB and an EPC, providing an interconnection point between the EUTRAN and the EPC. It is also considered as a reference point.
E-RAB:
as defined in TS 36.401.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
eNB
E-UTRAN Node B
EPC
Evolved Packet Core
E-RAB
E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer
E-UTRAN
Evolved UTRAN
GTP
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
IP
Internet Protocol
TEID
Tunnel Endpoint Identifier
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
4 Data Link Layer p. 6
Any data link protocol that fulfils the requirements toward the upper layer may be used.
5 S1 Interface user plane protocol p. 6
5.1 General p. 6
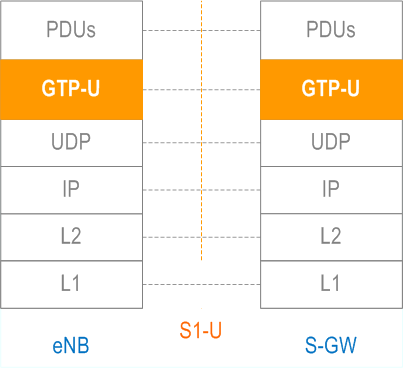
The transport layer for data streams over S1 is an IP based Transport. The following Figure shows the transport protocol stacks over S1.
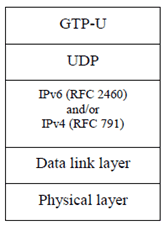
The GTP-U (TS 29.281) protocol over UDP over IP shall be supported as the transport for data streams on the S1 interface. The data link layer is as specified in clause 4.
The transport bearer is identified by the GTP-U TEID (TS 29.281) and the IP address (source TEID, destination TEID, source IP address, destination IP address).
5.2 GTP-U p. 6
The GTP-U (TS 29.281) protocol shall be used over the S1 interface toward the EPC.
5.3 UDP/IP p. 6
The path protocol used shall be UDP (RFC 768).
The UDP port number for GTP-U shall be as defined in TS 29.281.
The eNB and the EPC shall support fragmentation and assembly of GTP packets at the IP layer.
The eNB and the EPC shall support IPv6 (RFC 2460) and/or IPv4 (RFC 791).
There may be one or several IP addresses in the eNB and in the EPC. The packet processing function in the EPC shall send downstream packets of a given E-RAB to the eNB IP address (received in S1-AP) associated to that particular E-RAB. The packet processing function in the eNB shall send upstream packets of a given E-RAB to the EPC IP address (received in S1-AP) associated to that particular E-RAB.
The Transport Layer Address signalled in S1-AP messages is a bit string of
5.4 Diffserv code point marking p. 7
IP Differentiated Services code point marking (RFC 2474) shall be supported. The mapping between traffic categories and Diffserv code points shall be configurable by O&M based on QoS Class Identifier (QCI) Characteristics and other E-UTRAN traffic parameters (e.g. ARP). Traffic categories are implementation-specific and may be determined from the application parameters.