TS 35.202
Specification of the
3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms
Document 2: Kasumi Specification
V18.0.0 (PDF)
2024/03 26 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 26 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 26 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 25 p.
V14.0.0
2017/03 26 p.
V13.0.0
2016/01 26 p.
V12.0.0
2014/09 26 p.
V11.0.0
2012/09 26 p.
V10.0.0
2011/04 26 p.
V9.0.0
2009/12 26 p.
V8.0.0
2008/12 26 p.
V7.0.0
2007/06 26 p.
V6.1.0
2005/10 26 p.
V5.0.0
2002/06 26 p.
V4.0.0
2001/08 26 p.
V3.1.2
2001/08 26 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Evans, Tim P.
VODAFONE Group Plc
Content for TS 35.202 Word version: 18.0.0
0f Foreword
0i Introduction
0 Scope
1 Outline of the normative part
2 Introductory information
3 KASUMI operation
4 Components of KASUMI
A Informative Section
A.1 Figures of the KASUMI Algorithm
A.2 Simulation Program Listing
$ Change history
0f Foreword p. 4
This Technical Specification has been produced by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms f8 & f9 have been developed through the collaborative efforts of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB), the Telecommunications Technology Association (TTA), the T1 Committee.
The f8 & f9 Algorithms Specifications may be used only for the development and operation of 3G Mobile Communications and services. Every Beneficiary must sign a Restricted Usage Undertaking with the Custodian and demonstrate that he fulfills the approval criteria specified in the Restricted Usage Undertaking.
Furthermore, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation holds essential patents on the Algorithms. The Beneficiary must get a separate IPR License Agreement from Mitsubishi Electronic Corporation Japan.
For details of licensing procedures, contact ETSI, ARIB, TTA or T1.
…
0i Introduction p. 4
This specification has been prepared by the 3GPP Task Force, and gives a detailed specification of the 3GPP Algorithm KASUMI. KASUMI is a block cipher that forms the heart of the 3GPP confidentiality algorithm f8, and the 3GPP integrity algorithm f9.
This document is the second of four, which between them form the entire specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms:
- 3GPP TS 35.201: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 1: f8 and f9 Specification".
- 3GPP TS 35.202: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 2: KASUMI Specification".
- 3GPP TS 35.203: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 3: Implementors' Test Data".
- 3GPP TS 35.204: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 4: Design Conformance Test Data".
0 Scope p. 6
This specification gives a detailed specification of the 3GPP Algorithm KASUMI. KASUMI is a block cipher that forms the heart of the 3GPP confidentiality algorithm f8, and the 3GPP integrity algorithm f9.
1 Outline of the normative part p. 8
Clause 2 introduces the algorithm and describes the notation used in the subsequent clauses.
Clause 3 defines the algorithm structure and its operation.
Clause 4 defines the basic components of the algorithm.
1.1 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 33.102: version 3.2.0: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Security Architecture".
[2]
TS 33.105: version 3.1.0: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Cryptographic Algorithm Requirements".
[3]
TS 35.201: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 1: f8 and f9 Specification".
[4]
TS 35.202: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 2: KASUMI Specification".
[5]
TS 35.203: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 3: Implementors' Test Data".
[6]
TS 35.204: "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; 3G Security; Specification of the 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity Algorithms; Document 4: Design Conformance Test Data".
[7]
ISO/IEC 9797-1:1999: "Information technology - Security techniques - Message Authentication Codes (MACs)".
2 Introductory information p. 8
2.1 Introduction p. 8
Within the security architecture of the 3GPP system there are two standardised algorithms: A confidentiality algorithm f8, and an integrity algorithm f9. These algorithms are fully specified in a companion document TS 35.201. Each of these algorithms is based on the KASUMI algorithm that is specified here.
KASUMI is a block cipher that produces a 64-bit output from a 64-bit input under the control of a 128-bit key.
2.2 Notation p. 9
2.2.1 Radix p. 9
We use the prefix 0x to indicate hexadecimal numbers.
2.2.2 Bit/Byte ordering p. 9
All data variables in this specification are presented with the most significant bit (or byte) on the left hand side and the least significant bit (or byte) on the right hand side. Where a variable is broken down into a number of sub-strings, the left most (most significant) sub-string consists of the most significant part of the original string and so on through to the least significant.
For example if a 64-bit value X is subdivided into four 16-bit substrings P, Q, R, S we have:
X = 0x0123456789ABCDEF
we have:
P = 0x0123, Q = 0x4567, R = 0x89AB, S = 0xCDEF.
In binary this would be:
X = 0000000100100011010001010110011110001001101010111100110111101111
with
P = 0000000100100011
Q = 0100010101100111
R = 1000100110101011
S = 1100110111101111
2.2.3 Conventions p. 9
We use the assignment operator '=', as used in several programming languages. When we write
<variable> = <expression>
we mean that <variable> assumes the value that <expression> had before the assignment took place. For instance,
x = x + y + 3
means
(new value of x) becomes (old value of x) + (old value of y) + 3.
2.2.4 Subfunctions p. 9
KASUMI decomposes into a number of subfunctions (FL, FO, FI) which are used in conjunction with associated sub-keys (KL, KO, KI) in a Feistel structure comprising a number of rounds (and rounds within rounds for some subfunctions). Specific instances of the function and/or keys are represented by XXi,j where i is the outer round number of KASUMI and j is the inner round number.
For example the function FO comprises three rounds of the function FI, so we designate the third round of FI in the fifth round of KASUMI as FI5,3.
2.2.5 List of Symbols p. 10
=
The assignment operator.
⊕
The bitwise exclusive-OR operation.
||
The concatenation of the two operands.
<<<n
The left circular rotation of the operand by n bits.
ROL( )
The left circular rotation of the operand by one bit.
∩
The bitwise AND operation.
∪
The bitwise OR operation.
2.3 List of Functions and Variables p. 10
fi( )
The round function for the ith round of KASUMI
FI()
A subfunction within KASUMI that translates a 16-bit input to a 16-bit output using a 16-bit subkey.
FL()
A subfunction within KASUMI that translates a 32-bit input to a 32-bit output using a 32-bit subkey.
FO()
A subfunction within KASUMI that translates a 32-bit input to a 32-bit output using two 48-bit subkeys.
K
A 128-bit key.
KLi,KOi,KIi
subkeys used within the ith round of KASUMI.
S7[]
An S-Box translating a 7-bit input to a 7-bit output.
S9[]
An S-Box translating a 9-bit input to a 9-bit output.
3 KASUMI operation p. 10
3.1 Introduction p. 10
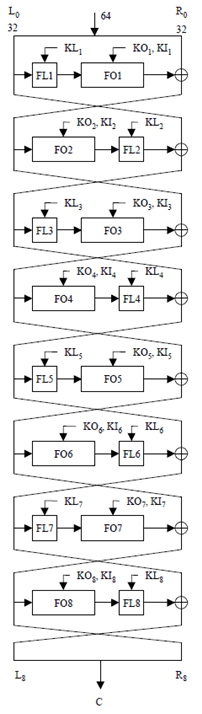
(See Figure 1 in Annex A.1)
KASUMI is a Feistel cipher with eight rounds. It operates on a 64-bit data block and uses a 128-bit key. In this clause we define the basic eight-round operation. In clause 4 we define in detail the make-up of the round function fi( ).
3.2 Encryption p. 11
KASUMI operates on a 64-bit input I using a 128-bit key K to produce a 64-bit output OUTPUT, as follows:
The input I is divided into two 32-bit strings L0 and R0, where
The result OUTPUT is equal to the 64-bit string (L8 || R8) offered at the end of the eighth round. See Figure 1 of Annex A.1.
In the specifications for the f8 and f9 functions we represent this transformation by the term:
I = L0 || R0
Then for each integer i with 1 ≤ i ≤ 8 we define:
Ri = Li-1, Li = Ri-1 ⊕ fi(Li-1, RKi )
This constitutes the ith round function of KASUMI, where fi denotes the round function with Li-1 and round key RKi as inputs (see clause 4 below).
OUTPUT = KASUMI[ I ]K
4 Components of KASUMI p. 11
4.1 Function fi p. 11
(See Figure 1 in Annex A.1)
The function fi( ) takes a 32-bit input I and returns a 32-bit output O under the control of a round key RKi, where the round key comprises the subkey triplet of (KLi, KOi, KIi). The function itself is constructed from two subfunctions; FL and FO with associated subkeys KLi (used with FL) and subkeys KOi and KIi (used with FO).
The fi( ) function has two different forms depending on whether it is an even round or an odd round.
For rounds 1,3,5 and 7 we define:
fi(I, RKi) = FO( FL( I, KLi), KOi, KIi )
and for rounds 2,4,6 and 8 we define:
fi(I, RKi) = FL( FO( I, KOi, KIi ), KLi )
i.e. For odd rounds the round data is passed through FL( ) and then FO( ), whilst for even rounds it is passed through FO( ) and then FL( ).
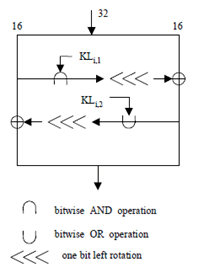
4.2 Function FL p. 11
(See Figure 4 in Annex A.1)
The input to the function FL comprises a 32-bit data input I and a 32-bit subkey KLi. The subkey is split into two 16-bit subkeys, KLi,1 and KLi,2 where
KLi = KLi,1 || KLi,2.
The input data I is split into two 16-bit halves, L and R where I = L || R.
We define:
R' = R ⊕ ROL( L ∩ KLi,1 )
L' = L ⊕ ROL( R' ∪ KLi,2 )
The 32-bit output value is (L' || R').
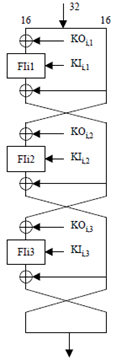
4.3 Function FO p. 12
(See Figure 2 in Annex A.1)
The input to the function FO comprises a 32-bit data input I and two sets of subkeys, a 48-bit subkey KOi and 48-bit subkey KIi.
The 32-bit data input is split into two halves, L0 and R0 where I = L0 || R0.
The 48-bit subkeys are subdivided into three 16-bit subkeys where
KOi = KOi,1 || KOi,2 || KOi,3 and KIi = KIi,1 || KIi,2 || KIi,3.
Then for each integer j with 1 ≤ j ≤ 3 we define:
Rj = FI(Lj-1 ⊕ KOi,j , KIi,j ) ⊕ Rj-1
Lj = Rj-1
Finally we return the 32-bit value (L3 || R3).
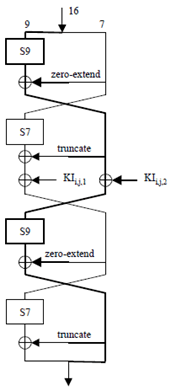
4.4 Function FI p. 12
(See Figure 3 in Annex A.1. The thick and thin lines in this diagram are used to emphasise the difference between the 9 bit and 7 bit data paths respectively).
The function FI takes a 16-bit data input I and 16-bit subkey KIi,j. The input I is split into two unequal components, a 9-bit left half L0 and a 7-bit right half R0 where I = L0 || R0.
Similarly the key KIi,j is split into a 7-bit component KIi,j,1 and a 9-bit component KIi,j,2 where KIi,j = KIi,j,1 || KIi,j,2.
The function uses two S-boxes, S7 which maps a 7-bit input to a 7-bit output, and S9 which maps a 9-bit input to a 9-bit output. These are fully defined in clause 4.5. It also uses two additional functions which we designate ZE( ) and TR( ). We define these as:
ZE( x )
takes the 7-bit value x and converts it to a 9-bit value by adding two zero bits to the most-significant end.
TR( x )
takes the 9-bit value x and converts it to a 7-bit value by discarding the two most-significant bits.
We define the following series of operations:
L1 = R0
R1 = S9[L0] ⊕ ZE(R0)
L2 = R1 ⊕ KIi,j,2
R2 = S7[L1] ⊕ TR(R1) ⊕ KIi,j,1
L3 = R2
R3 = S9[L2] ⊕ ZE(R2)
L4 = S7[L3] ⊕ TR(R3)
R4 = R3
The function returns the 16-bit value (L4 || R4).
4.5 S-boxes p. 13
The two S-boxes have been designed so that they may be easily implemented in combinational logic as well as by a look-up table. Both forms are given for each table.
The input x comprises either seven or nine bits with a corresponding number of bits in the output y. We therefore have:
x = x8 || x7 || x6 || x5 || x4 || x3 || x2 || x1 || x0
and
y = y8 || y7 || y6 || y5 || y4 || y3 || y2 || y1 || y0
where the x8, y8 and x7,y7 bits only apply to S9, and the x0 and y0 bits are the least significant bits.
In the logic equations:
x0x1x2 implies x0 ∩ x1 ∩ x2 where ∩ is the AND operator.
⊕ is the exclusive-OR operator.
Following the presentation of the logic equations and the equivalent look-up table an example is given of the use of each.
4.5.1 S7 p. 13
Gate Logic:
If we have an input value = 38, then using the decimal table S7[38] = 58.
For the combinational logic we have:
y0 =x1x3⊕x4⊕x0x1x4⊕x5⊕x2x5⊕x3x4x5⊕x6⊕x0x6⊕x1x6⊕x3x6⊕x2x4x6⊕x1x5x6
⊕x4x5x6
y1 =x0x1⊕x0x4⊕x2x4⊕x5⊕x1x2x5⊕x0x3x5⊕x6⊕x0x2x6⊕x3x6⊕x4x5x6⊕1
y2 =x0⊕x0x3⊕x2x3⊕x1x2x4⊕x0x3x4⊕x1x5⊕x0x2x5⊕x0x6⊕x0x1x6⊕x2x6⊕x4x6⊕1
y3 =x1⊕x0x1x2⊕x1x4⊕x3x4⊕x0x5⊕x0x1x5⊕x2x3x5⊕x1x4x5⊕x2x6⊕x1x3x6
y4 =x0x2⊕x3⊕x1x3⊕x1x4⊕x0x1x4⊕x2x3x4⊕x0x5⊕x1x3x5⊕x0x4x5⊕x1x6⊕x3x6
⊕x0x3x6⊕x5x6⊕1
y5 =x2⊕x0x2⊕x0x3⊕x1x2x3⊕x0x2x4⊕x0x5⊕x2x5⊕x4x5⊕x1x6⊕x1x2x6⊕x0x3x6
⊕x3x4x6⊕x2x5x6⊕1
y6 =x1x2⊕x0x1x3⊕x0x4⊕x1x5⊕x3x5⊕x6⊕x0x1x6⊕x2x3x6⊕x1x4x6⊕x0x5x6
Decimal Table:
54, 50, 62, 56, 22, 34, 94, 96, 38, 6, 63, 93, 2, 18,123, 33, 55,113, 39,114, 21, 67, 65, 12, 47, 73, 46, 27, 25,111,124, 81, 53, 9,121, 79, 52, 60, 58, 48,101,127, 40,120,104, 70, 71, 43, 20,122, 72, 61, 23,109, 13,100, 77, 1, 16, 7, 82, 10,105, 98, 117,116, 76, 11, 89,106, 0,125,118, 99, 86, 69, 30, 57,126, 87, 112, 51, 17, 5, 95, 14, 90, 84, 91, 8, 35,103, 32, 97, 28, 66, 102, 31, 26, 45, 75, 4, 85, 92, 37, 74, 80, 49, 68, 29,115, 44, 64,107,108, 24,110, 83, 36, 78, 42, 19, 15, 41, 88,119, 59, 3Example:
38 = 01001102 ⇒ x6 = 0, x5=1, x4=0, x3=0, x2=1, x1=1, x0=0
which gives us:
y0 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 0
y1 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 1
y2 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 0
y3 = 1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 1
y4 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 1
y5 = 1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 1
y6 = 1⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 0
Thus y = 01110102 = 58
4.5.2 S9 p. 14
Gate Logic:
If we have an input value = 138, then using the decimal table S9[138] = 339.
For the combinational logic we have:
138 = 0100010102 ⇒
y0 = x0x2⊕x3⊕x2x5⊕x5x6⊕x0x7⊕x1x7⊕x2x7⊕x4x8⊕x5x8⊕x7x8⊕1 y1 = x1⊕x0x1⊕x2x3⊕x0x4⊕x1x4⊕x0x5⊕x3x5⊕x6⊕x1x7⊕x2x7⊕x5x8⊕1 y2 = x1⊕x0x3⊕x3x4⊕x0x5⊕x2x6⊕x3x6⊕x5x6⊕x4x7⊕x5x7⊕x6x7⊕x8⊕x0x8⊕1 y3 = x0⊕x1x2⊕x0x3⊕x2x4⊕x5⊕x0x6⊕x1x6⊕x4x7⊕x0x8⊕x1x8⊕x7x8 y4 = x0x1⊕x1x3⊕x4⊕x0x5⊕x3x6⊕x0x7⊕x6x7⊕x1x8⊕x2x8⊕x3x8 y5 = x2⊕x1x4⊕x4x5⊕x0x6⊕x1x6⊕x3x7⊕x4x7⊕x6x7⊕x5x8⊕x6x8⊕x7x8⊕1 y6 = x0⊕x2x3⊕x1x5⊕x2x5⊕x4x5⊕x3x6⊕x4x6⊕x5x6⊕x7⊕x1x8⊕x3x8⊕x5x8⊕x7x8 y7 = x0x1⊕x0x2⊕x1x2⊕x3⊕x0x3⊕x2x3⊕x4x5⊕x2x6⊕x3x6⊕x2x7⊕x5x7⊕x8⊕1 y8 = x0x1⊕x2⊕x1x2⊕x3x4⊕x1x5⊕x2x5⊕x1x6⊕x4x6⊕x7⊕x2x8⊕x3x8Decimal Table:
167,239,161,379,391,334, 9,338, 38,226, 48,358,452,385, 90,397, 183,253,147,331,415,340, 51,362,306,500,262, 82,216,159,356,177, 175,241,489, 37,206, 17, 0,333, 44,254,378, 58,143,220, 81,400, 95, 3,315,245, 54,235,218,405,472,264,172,494,371,290,399, 76, 165,197,395,121,257,480,423,212,240, 28,462,176,406,507,288,223, 501,407,249,265, 89,186,221,428,164, 74,440,196,458,421,350,163, 232,158,134,354, 13,250,491,142,191, 69,193,425,152,227,366,135, 344,300,276,242,437,320,113,278, 11,243, 87,317, 36, 93,496, 27, 487,446,482, 41, 68,156,457,131,326,403,339, 20, 39,115,442,124, 475,384,508, 53,112,170,479,151,126,169, 73,268,279,321,168,364, 363,292, 46,499,393,327,324, 24,456,267,157,460,488,426,309,229, 439,506,208,271,349,401,434,236, 16,209,359, 52, 56,120,199,277, 465,416,252,287,246, 6, 83,305,420,345,153,502, 65, 61,244,282, 173,222,418, 67,386,368,261,101,476,291,195,430, 49, 79,166,330, 280,383,373,128,382,408,155,495,367,388,274,107,459,417, 62,454, 132,225,203,316,234, 14,301, 91,503,286,424,211,347,307,140,374, 35,103,125,427, 19,214,453,146,498,314,444,230,256,329,198,285, 50,116, 78,410, 10,205,510,171,231, 45,139,467, 29, 86,505, 32, 72, 26,342,150,313,490,431,238,411,325,149,473, 40,119,174,355, 185,233,389, 71,448,273,372, 55,110,178,322, 12,469,392,369,190, 1,109,375,137,181, 88, 75,308,260,484, 98,272,370,275,412,111, 336,318, 4,504,492,259,304, 77,337,435, 21,357,303,332,483, 18, 47, 85, 25,497,474,289,100,269,296,478,270,106, 31,104,433, 84, 414,486,394, 96, 99,154,511,148,413,361,409,255,162,215,302,201, 266,351,343,144,441,365,108,298,251, 34,182,509,138,210,335,133, 311,352,328,141,396,346,123,319,450,281,429,228,443,481, 92,404, 485,422,248,297, 23,213,130,466, 22,217,283, 70,294,360,419,127, 312,377, 7,468,194, 2,117,295,463,258,224,447,247,187, 80,398, 284,353,105,390,299,471,470,184, 57,200,348, 63,204,188, 33,451, 97, 30,310,219, 94,160,129,493, 64,179,263,102,189,207,114,402, 438,477,387,122,192, 42,381, 5,145,118,180,449,293,323,136,380, 43, 66, 60,455,341,445,202,432, 8,237, 15,376,436,464, 59,461Example:
x8 = 0, x7 = 1, x6 = 0, x5=0, x4=0, x3=1, x2=0, x1=1, x0=0
which gives us:
y0 = 0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 1 y1 = 1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 1 y2 = 1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 0 y3 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 0 y4 = 0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 1 y5 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 0 y6 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0 = 1 y7 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1 = 0 y8 = 0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕0⊕1⊕0⊕0 = 1Thus y = 1010100112 = 339
4.6 Key Schedule p. 15
KASUMI has a 128-bit key K. Each round of KASUMI uses 128 bits of key that are derived from K. Before the round keys can be calculated two 16-bit arrays Kj and Kj' (j=1 to 8) are derived in the following manner:
The 128-bit key K is subdivided into eight 16-bit values K1…K8 where
K = K1 || K2 || K3 ||…|| K8.
A second array of subkeys, Kj' is derived from Kj by applying:
For each integer j with 1 ≤ j ≤ 8
The round subkeys are then derived from Kj and Kj' in the manner defined in Table 1.
Kj' = Kj ⊕ Cj
Where Cj is the constant value defined in Table 2.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KLi,1 | K1<<<1 | K2<<<1 | K3<<<1 | K4<<<1 | K5<<<1 | K6<<<1 | K7<<<1 | K8<<<1 |
| KLi,2 | K3' | K4' | K5' | K6' | K7' | K8' | K1' | K2' |
| KOi,1 | K2<<<5 | K3<<<5 | K4<<<5 | K5<<<5 | K6<<<5 | K7<<<5 | K8<<<5 | K1<<<5 |
| KOi,2 | K6<<<8 | K7<<<8 | K8<<<8 | K1<<<8 | K2<<<8 | K3<<<8 | K4<<<8 | K5<<<8 |
| KOi,3 | K7<<<13 | K8<<<13 | K1<<<13 | K2<<<13 | K3<<<13 | K4<<<13 | K5<<<13 | K6<<<13 |
| KIi,1 | K5' | K6' | K7' | K8' | K1' | K2' | K3' | K4 |
| KIi,2 | K4' | K5' | K6' | K7' | K8' | K1' | K2' | K3' |
| KIi,3 | K8' | K1' | K2' | K3' | K4' | K5' | K6' | K7' |
| C1 | 0x0123 |
| C2 | 0x4567 |
| C3 | 0x89AB |
| C4 | 0xCDEF |
| C5 | 0xFEDC |
| C6 | 0xBA98 |
| C7 | 0x7654 |
| C8 | 0x3210 |
A Informative Section p. 17
This part of the document is purely informative and does not form part of the normative specification of KASUMI.
A.1 Figures of the KASUMI Algorithm p. 17
KASUMI has a number of characteristics that may be exploited in a hardware implementation and these are highlighted here.
- The simple key schedule is easy to implement in hardware.
- The S-Boxes have been designed so that they may be implemented by a small amount of combinational logic rather than by large look-up tables.
- The S7-Box and S9-Box operations in the FI function may be carried out in parallel (see alternative presentation in Figure 5).
- The FIi,1 and FIi,2 operations may be carried out in parallel (see alternative presentation in Figure 6).
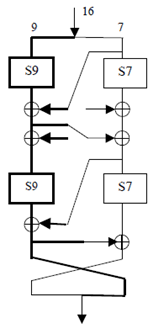
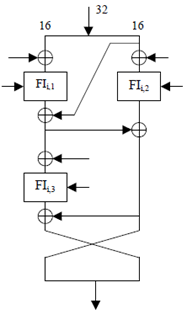
A.2 Simulation Program Listing p. 18
Header file
/*---------------------------------------------------------
* Kasumi.h
*---------------------------------------------------------*/
typedef unsigned char u8;
typedef unsigned short u16;
typedef unsigned long u32;
void KeySchedule( u8 *key );
void Kasumi( u8 *data );
C Code
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Kasumi.c
*-----------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* A sample implementation of KASUMI, the core algorithm for the
* 3GPP Confidentiality and Integrity algorithms.
*
* This has been coded for clarity, not necessarily for efficiency.
*
* This will compile and run correctly on both Intel (little endian)
* and Sparc (big endian) machines. (Compilers used supported 32-bit ints).
*
* Version 1.1 08 May 2000
*
*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "Kasumi.h"
/*--------- 16 bit rotate left ------------------------------------------*/
#define ROL16(a,b) (u16)((a<<b)|(a>>(16-b)))
/*------- unions: used to remove "endian" issues ------------------------*/
typedef union {
u32 b32;
u16 b16[2];
u8 b8[4];
} DWORD;
typedef union {
u16 b16;
u8 b8[2];
} WORD;
/*-------- globals: The subkey arrays -----------------------------------*/
static u16 KLi1[8], KLi2[8];
static u16 KOi1[8], KOi2[8], KOi3[8];
static u16 KIi1[8], KIi2[8], KIi3[8];
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* FI()
* The FI function (fig 3). It includes the S7 and S9 tables.
* Transforms a 16-bit value.
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static u16 FI( u16 in, u16 subkey )
{
u16 nine, seven;
static u16 S7[] = {
54, 50, 62, 56, 22, 34, 94, 96, 38, 6, 63, 93, 2, 18,123, 33,
55,113, 39,114, 21, 67, 65, 12, 47, 73, 46, 27, 25,111,124, 81,
53, 9,121, 79, 52, 60, 58, 48,101,127, 40,120,104, 70, 71, 43,
20,122, 72, 61, 23,109, 13,100, 77, 1, 16, 7, 82, 10,105, 98,
117,116, 76, 11, 89,106, 0,125,118, 99, 86, 69, 30, 57,126, 87,
112, 51, 17, 5, 95, 14, 90, 84, 91, 8, 35,103, 32, 97, 28, 66,
102, 31, 26, 45, 75, 4, 85, 92, 37, 74, 80, 49, 68, 29,115, 44,
64,107,108, 24,110, 83, 36, 78, 42, 19, 15, 41, 88,119, 59, 3};
static u16 S9[] = {
167,239,161,379,391,334, 9,338, 38,226, 48,358,452,385, 90,397,
183,253,147,331,415,340, 51,362,306,500,262, 82,216,159,356,177,
175,241,489, 37,206, 17, 0,333, 44,254,378, 58,143,220, 81,400,
95, 3,315,245, 54,235,218,405,472,264,172,494,371,290,399, 76,
165,197,395,121,257,480,423,212,240, 28,462,176,406,507,288,223,
501,407,249,265, 89,186,221,428,164, 74,440,196,458,421,350,163,
232,158,134,354, 13,250,491,142,191, 69,193,425,152,227,366,135,
344,300,276,242,437,320,113,278, 11,243, 87,317, 36, 93,496, 27,
487,446,482, 41, 68,156,457,131,326,403,339, 20, 39,115,442,124,
475,384,508, 53,112,170,479,151,126,169, 73,268,279,321,168,364,
363,292, 46,499,393,327,324, 24,456,267,157,460,488,426,309,229,
439,506,208,271,349,401,434,236, 16,209,359, 52, 56,120,199,277,
465,416,252,287,246, 6, 83,305,420,345,153,502, 65, 61,244,282,
173,222,418, 67,386,368,261,101,476,291,195,430, 49, 79,166,330,
280,383,373,128,382,408,155,495,367,388,274,107,459,417, 62,454,
132,225,203,316,234, 14,301, 91,503,286,424,211,347,307,140,374,
35,103,125,427, 19,214,453,146,498,314,444,230,256,329,198,285,
50,116, 78,410, 10,205,510,171,231, 45,139,467, 29, 86,505, 32,
72, 26,342,150,313,490,431,238,411,325,149,473, 40,119,174,355,
185,233,389, 71,448,273,372, 55,110,178,322, 12,469,392,369,190,
1,109,375,137,181, 88, 75,308,260,484, 98,272,370,275,412,111,
336,318, 4,504,492,259,304, 77,337,435, 21,357,303,332,483, 18,
47, 85, 25,497,474,289,100,269,296,478,270,106, 31,104,433, 84,
414,486,394, 96, 99,154,511,148,413,361,409,255,162,215,302,201,
266,351,343,144,441,365,108,298,251, 34,182,509,138,210,335,133,
311,352,328,141,396,346,123,319,450,281,429,228,443,481, 92,404,
485,422,248,297, 23,213,130,466, 22,217,283, 70,294,360,419,127,
312,377, 7,468,194, 2,117,295,463,258,224,447,247,187, 80,398,
284,353,105,390,299,471,470,184, 57,200,348, 63,204,188, 33,451,
97, 30,310,219, 94,160,129,493, 64,179,263,102,189,207,114,402,
438,477,387,122,192, 42,381, 5,145,118,180,449,293,323,136,380,
43, 66, 60,455,341,445,202,432, 8,237, 15,376,436,464, 59,461};
/* The sixteen bit input is split into two unequal halves, *
* nine bits and seven bits - as is the subkey */
nine = (u16)(in>>7);
seven = (u16)(in&0x7F);
/* Now run the various operations */
nine = (u16)(S9[nine] ^ seven);
seven = (u16)(S7[seven] ^ (nine & 0x7F));
seven ^= (subkey>>9);
nine ^= (subkey&0x1FF);
nine = (u16)(S9[nine] ^ seven);
seven = (u16)(S7[seven] ^ (nine & 0x7F));
in = (u16)((seven<<9) + nine);
return( in );
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* FO()
* The FO() function.
* Transforms a 32-bit value. Uses <index> to identify the
* appropriate subkeys to use.
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static u32 FO( u32 in, int index )
{
u16 left, right;
/* Split the input into two 16-bit words */
left = (u16)(in>>16);
right = (u16) in;
/* Now apply the same basic transformation three times */
left ^= KOi1[index];
left = FI( left, KIi1[index] );
left ^= right;
right ^= KOi2[index];
right = FI( right, KIi2[index] );
right ^= left;
left ^= KOi3[index];
left = FI( left, KIi3[index] );
left ^= right;
in = (((u32)right)<<16)+left;
return( in );
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* FL()
* The FL() function.
* Transforms a 32-bit value. Uses <index> to identify the
* appropriate subkeys to use.
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static u32 FL( u32 in, int index )
{
u16 l, r, a, b;
/* split out the left and right halves */
l = (u16)(in>>16);
r = (u16)(in);
/* do the FL() operations */
a = (u16) (l & KLi1[index]);
r ^= ROL16(a,1);
b = (u16)(r | KLi2[index]);
l ^= ROL16(b,1);
/* put the two halves back together */
in = (((u32)l)<<16) + r;
return( in );
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Kasumi()
* the Main algorithm (fig 1). Apply the same pair of operations
* four times. Transforms the 64-bit input.
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void Kasumi( u8 *data )
{
u32 left, right, temp;
DWORD *d;
int n;
/* Start by getting the data into two 32-bit words (endian corect) */
d = (DWORD*)data;
left = (((u32)d[0].b8[0])<<24)+(((u32)d[0].b8[1])<<16)
+(d[0].b8[2]<<8)+(d[0].b8[3]);
right = (((u32)d[1].b8[0])<<24)+(((u32)d[1].b8[1])<<16)
+(d[1].b8[2]<<8)+(d[1].b8[3]);
n = 0;
do{ temp = FL( left, n );
temp = FO( temp, n++ );
right ^= temp;
temp = FO( right, n );
temp = FL( temp, n++ );
left ^= temp;
}while( n<=7 );
/* return the correct endian result */
d[0].b8[0] = (u8)(left>>24); d[1].b8[0] = (u8)(right>>24);
d[0].b8[1] = (u8)(left>>16); d[1].b8[1] = (u8)(right>>16);
d[0].b8[2] = (u8)(left>>8); d[1].b8[2] = (u8)(right>>8);
d[0].b8[3] = (u8)(left); d[1].b8[3] = (u8)(right);
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* KeySchedule()
* Build the key schedule. Most "key" operations use 16-bit
* subkeys so we build u16-sized arrays that are "endian" correct.
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void KeySchedule( u8 *k )
{
static u16 C[] = {
0x0123,0x4567,0x89AB,0xCDEF, 0xFEDC,0xBA98,0x7654,0x3210 };
u16 key[8], Kprime[8];
WORD *k16;
int n;
/* Start by ensuring the subkeys are endian correct on a 16-bit basis */
k16 = (WORD *)k;
for( n=0; n<8; ++n )
key[n] = (u16)((k16[n].b8[0]<<8) + (k16[n].b8[1]));
/* Now build the K'[] keys */
for( n=0; n<8; ++n )
Kprime[n] = (u16)(key[n] ^ C[n]);
/* Finally construct the various sub keys */
for( n=0; n<8; ++n )
{
KLi1[n] = ROL16(key[n],1);
KLi2[n] = Kprime[(n+2)&0x7];
KOi1[n] = ROL16(key[(n+1)&0x7],5);
KOi2[n] = ROL16(key[(n+5)&0x7],8);
KOi3[n] = ROL16(key[(n+6)&0x7],13);
KIi1[n] = Kprime[(n+4)&0x7];
KIi2[n] = Kprime[(n+3)&0x7];
KIi3[n] = Kprime[(n+7)&0x7];
}
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------
* e n d o f k a s u m i . c
*---------------------------------------------------------------------*/