Content for TS 33.535 Word version: 18.4.0
4 Architecture for AKMA
4.1 Reference model
4.2 Network elements
4.2.1 AAnF
4.2.2 AF
4.2.3 NEF
4.2.4 AUSF
4.2.5 UDM
4.3 AKMA Service Based Interfaces(SBIs)
4.3.0 General
4.4 Security requirements and principles for AKMA
4.4.0 General
4.4.1 Requirements on Ua* reference point
4.4.2 Requirements on AKMA Key Identifier (A-KID)
4.4.3 Requirements on the UE
4.5 AKMA reference points
...
...
4 Architecture for AKMA p. 8
4.1 Reference model p. 8
Figure 4.1-1 shows a fundamental network model of AKMA, as well as the interfaces between them.
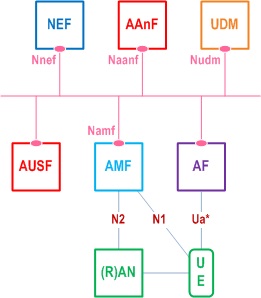
Figure 4.1-2 shows the AKMA architecture using the reference point representation.
The AKMA service requires a new logical entity, called the AKMA Anchor Function (AAnF).
The AKMA Architecture in Figure 4.1-2 is applicable to both roaming scenario and non-roaming scenario:
- non-roaming: UE is in HPLMN and accessing an AF;
- roaming scenario#1: UE is in VPLMN and accessing an internal HPLMN AF;
- roaming scenario#2: UE is in VPLMN and accessing an internal VPLMN AF;
- roaming scenario#3: UE is in VPLMN and accessing an external AF in the Data Network.
4.2 Network elements p. 9
4.2.1 AAnF p. 9
The AAnF is the anchor function in the HPLMN. The AAnF stores the AKMA Anchor Key (KAKMA) and SUPI/GPSI for AKMA service, which is received from the AUSF/UDM after the UE completes a successful 5G primary authentication. The AAnF also generates the key material to be used between the UE and the Application Function (AF) and maintains UE AKMA contexts. The AAnF sends SUPI/GPSI of the UE to AF located inside the operator's network according to the AF request or sends SUPI to NEF. If GPSI is required, the AAnF retrieves the GPSI from UDM based on available SUPI. The AAnF has the capability to trigger a primary authentication for KAKMA refreshing purpose.
4.2.2 AF p. 9
The AF is defined in TS 23.501 with additional functions:
- AF with the AKMA service enabling requests for AKMA Application Key, called KAF, from the AAnF using A-KID.
- AF shall be authenticated and authorized by the operator network before providing the KAF to the AF.
- The AF located inside the operator's network performs the AAnF selection.
4.2.3 NEF p. 9
The NEF is defined in TS 23.501 with additional functions:
- The NEF enables and authorizes the external AF assessing AKMA service and forwards the request towards the AAnF.
- The NEF performs the AAnF selection.
4.2.4 AUSF p. 10
The AUSF is defined in TS 23.501 with additional functions:
- AUSF provides the SUPI and AKMA key material (A-KID,KAKMA) of the UE to the AAnF.
- AUSF performs the AAnF selection.
4.2.5 UDM p. 10
The UDM is defined in TS 23.501 with the additional functions:
- UDM stores AKMA subscription data of the subscriber and provides AKMA indication and RID to AUSF.
- UDM triggers primary authentication to refresh KAKMA.
4.3 AKMA Service Based Interfaces(SBIs) p. 10
4.3.0 General p. 10
The following interfaces are involved in AKMA network architecture:
- Nnef: Service-based interface exhibited by NEF.
- Nudm: Service-based interface exhibited by UDM.
- Naanf: Service-based interface exhibited by AAnF.
4.3.1 Void
4.4 Security requirements and principles for AKMA p. 10
4.4.0 General p. 10
The following security requirements are applicable to AKMA:
- AKMA shall reuse the same UE subscription and the same credentials used for 5G access.
- AKMA shall reuse the 5G primary authentication procedure and methods specified in TS 33.501 for the sake of implicit authentication for AKMA services.
- The SBA interface between the AAnF and the AUSF shall be confidentiality, integrity and replay protected.
- The SBA interface between AAnF and AF/NEF shall be confidentiality, integrity and replay protected.
- The SBA interface between AAnF and UDM shall be confidentiality, integrity and replay protected.
- The AKMA Application Key (KAF) shall be provided with a maximum lifetime based on the operator's local authentication policy.
4.4.1 Requirements on Ua* reference point p. 11
The Ua* reference point is application specific. The generic requirements for Ua* are:
- Ua* protocol shall be able to carry AKMA Key Identifier (A-KID).
- The UE and the AKMA AF shall be able to secure the reference point Ua* using the AKMA Application Key derived from the AKMA Anchor Key.
- The Ua* protocol shall be able to handle the expiration of KAF.
4.4.2 Requirements on AKMA Key Identifier (A-KID) p. 11
Requirements for AKMA Key Identifier (A-KID) are:
- A-KID shall be globally unique.
- A-KID shall be usable as a key identifier in protocols used in the reference point Ua*.
- AKMA AF shall be able to identify the AAnF serving the UE from the A-KID.
4.4.3 Requirements on the UE |R17| p. 11
The requirements on the UE are:
- Applications on the UE shall not be able to get access to KAKMA.
- An application on the UE shall only get the KAF keys related to specific AF Identifiers (AF_IDs) that the application is authorized to get.
- An application on the UE shall not be able to get access to the KAF keys that belong to other applications.
4.5 AKMA reference points p. 11
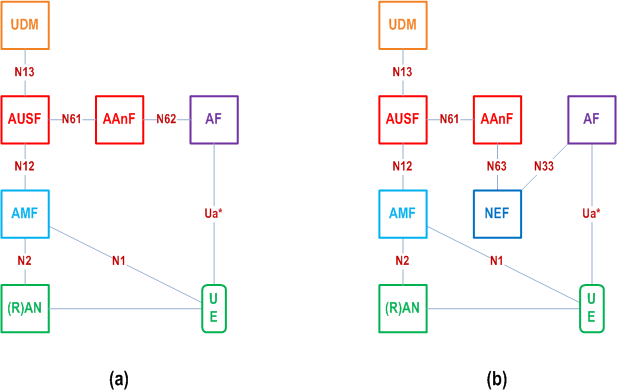
The AKMA architecture reuses the following reference point from the 5GC for the execution of the primary authentication procedure:
N1:
The AKMA architecture defines the following reference points:
Reference point between the UE and the AMF.
N2:
Reference point between the (R)AN and the AMF.
N12:
Reference point between AMF and AUSF.
N13:
Reference point between the UDM and the AUSF.
N33:
Reference point between NEF and an external AF.
N61:
Reference point between the AAnF and the AUSF.
N62:
Reference point between the AAnF and an internal AF.
N63:
Reference point between the AAnF and NEF.
Ua*:
Reference point between the UE and an AF.