Content for TS 33.128 Word version: 19.1.0
4 General
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Basic principles for internal interfaces
4.3 Basic principles for external handover interfaces
4.4 Service scoping
4.5 LI product filtering
...
...
4 General p. 27
4.1 Introduction p. 27
The present document provides details of the internal and external interfaces required for a network operator, access provider and/or service provider to provide the necessary information to a Law Enforcement Agency (LEA) required to meet LI requirements. LI requirements for 3GPP networks and services are given in TS 33.126.
The high-level architecture that defines the necessary interfaces is specified in TS 33.127. The generic high-level interception architecture is as follows:
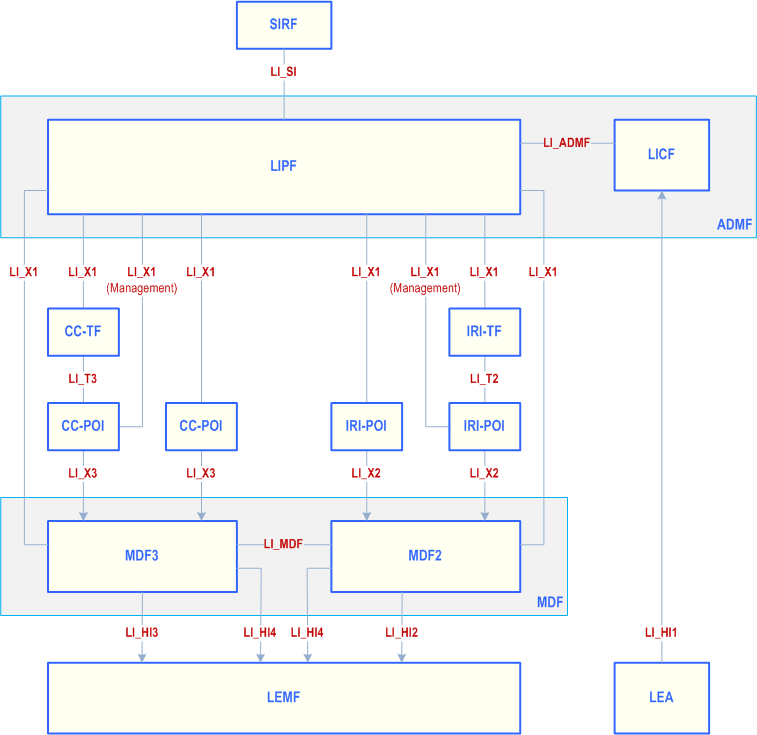
The generic high-level acquisition architecture is as follows:
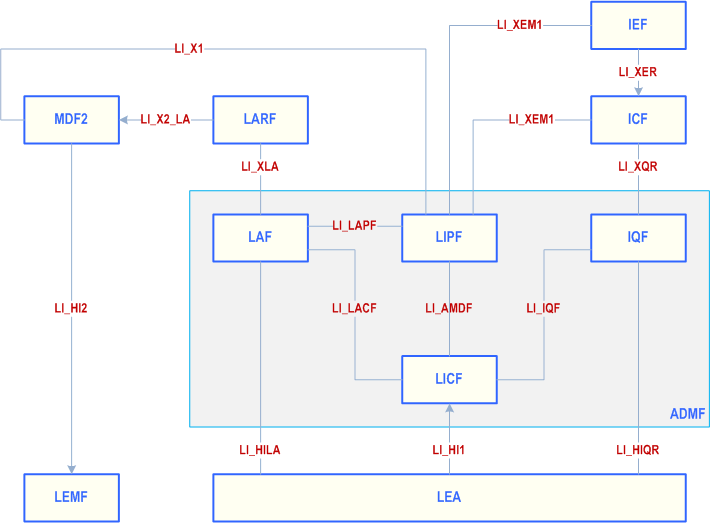
The specification of the interfaces is split into two parts:
- Internal interfaces used between an operator's network functions are described in clause 4.2.
- External interfaces used in communicating with a LEA are described in clause 4.3.
4.2 Basic principles for internal interfaces p. 29
This clause lists the internal interfaces shown in clause 4.1, indicates the protocol used to realise each interface, and gives a reference to the relevant clauses of the present document that specify how the protocol is to be used for the given interface.
| Interface | Description | Protocol used to realise interface | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| LI_ADMF | Used to pass intercept provisioning information form the LICF to the LIPF. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_IQF | Used to pass information related to IEFs and ICF to IQF. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_LAFC | Used to pass information from LICF to LAF. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_LAFP | Used to pass information from LIPF to LAF. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_MDF | Used by MDF2 and MDF3 in interactions necessary to correctly generate CC and IRI from xCC and xIRI. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_SI | Used to provide system information to the LIPF from the SIRF. | Out of scope of the present document. | |
| LI_ST | Used to transfer LI state information to and from the LISSF. | TS 29.598. | See clauses 5.10 and 6.2.3.10 |
| LI_T2 | Used to pass triggering information from the IRI-TF to a Triggered IRI-POI. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.2.4 |
| LI_T3 | Used to pass triggering information from a CC-TF to a Triggered CC-POI. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.2.4 |
| LI_X1 | Used to configure and audit Directly-provisioned POIs, TFs and MDFs. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.2.2 |
| LI_X1 (Management) | Used to audit Triggered POIs. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.2.3 |
| LI_X2 | Used to pass xIRI from IRI-POIs to the MDF2. | ETSI TS 103 221-2 [8]. | See clause 5.3.2 |
| LI_X2_LA | Used to pass xIRI from LARF to the MDF2 | ETSI TS 103 221-2 [8]. | See clause 5.3.5 |
| LI_X3 | Used to pass xCC from CC-POIs to the MDF3. | ETSI TS 103 221-2 [8]. | See clause 5.3.3 |
| LI_XEM1 | Used by the LICF/LIPF to manage IEFs and ICF. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.2.7 |
| LI_XER | Used to pass identifier association event records from IEFs to ICF. | See clause 5.9. | See clause 5.9 |
| LI_XLA | Used to send the location acquisition requests from LAF to LARF and used by the LARF to send the location acquisition responses to the LAF. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.12 |
| LI_XQR | Used to pass queries from IQF to ICF and responses from ICF to IQF. | ETSI TS 103 221-1 [7]. | See clause 5.8 |
4.3 Basic principles for external handover interfaces p. 30
This clause lists the external handover interfaces shown in clause 4.1, indicates the protocol used to realise each interface, and gives a reference to the relevant clauses of the present document that specify how the protocol is to be used for the given interface.
| Interface | Description | Protocol used to realise interface | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| LI_HI1 | Used to send warrant and other interception request information from LEA to operator. | ETSI TS 103 120 [6] shall be supported. Other methods (e.g. manual exchange) may be used depending on national regulatory requirements. | See clause 5.4 |
| LI_HI2 | Used to send IRI from the MDF2 to the LEMF. | ETSI TS 102 232-1 [9] and ETSI TS 102 232-7 [10] shall be supported. | See clause 5.5 |
| LI_HI3 | Used to send CC from the MDF3 to the LEMF. | ETSI TS 102 232-1 [9] and ETSI TS 102 232-7 [10] shall be supported. | See clause 5.5 |
| LI_HI4 | Used to send LI notification information from MDF2/MDF3 to LEMF. | ETSI TS 102 232-1 [9] and ETSI TS 102 232-7 [10] shall be supported. | See clause 5.6 |
| LI_HILA | Used to send the location acquisition requests from LEA to CSP and used by the CSP to send the location acquisition responses to the LEA. | ETSI TS 103 120 [6] shall be supported. | See clause 5.11 |
| LI_HIQR | Used to send warrant and other identifier association query information from LEA to CSP and used by the CSP to send query responses to the LEA. | ETSI TS 103 120 [6] shall be supported. | See clause 5.7 |
4.4 Service scoping p. 31
4.4.1 General p. 31
The interception product shall be delivered to the LEMF over LI_HI2 and LI_HI3, observing the service scoping described in the following clauses.
4.4.2 CSP service type p. 31
The LIPF shall be able to provision the POIs, TFs and MDF2/MDF3 according to the requirements of the warrant with the following CSP service type(s):
- Voice.
- Data.
- Messaging.
- Push-to-Talk (including MCPTT).
- LALS (the Target Positioning service, per clause 7.3.3.2 of TS 33.127).
- RCS (including all associated services).
4.4.3 Delivery type p. 31
- IRI.
- CC.
- IRI and CC.
4.4.4 Location Reporting p. 32
The LIPF shall be able to provision the POIs and MDF2 according to the requirements of the warrant with the following location reporting types:
- Report location only at the beginning and end of a session.
- Do not report location.
4.4.5 LALS Triggering p. 32
- This option is used to activate the LALS triggered location service (clause 7.3.3.3 of TS 33.127) for the target.
4.4.6 Roaming Interception p. 32
- Stop interception when the target is roaming outbound internationally.
4.5 LI product filtering p. 32
4.5.1 General p. 32
As described in TS 33.127 Annex B, the ADMF is responsible for providing administration and local management of the warrant including filtering criteria. Some of the reasons these criteria may be applied include LEA initiated suspend/resume (TS 33.127 Annex C), as a part of location dependent interception management, or bandwidth optimization.
This document currently defines the following methods for providing and provisioning the criteria for filtering LI product:
- Traffic Policies (see clause 4.5.2).
4.5.2 Traffic policies p. 32
ETSI TS 103 120 [6] clause 7.5 defines a traffic policy object which represents a policy from an LEA that is to be applied to authorized intercept product.
The use of Traffic Policies over LI_X1 can be found in clause 5.2.8.
The use of Traffic Policies over LI_HI1 can be found in clause 5.4.4.