Content for TS 29.561 Word version: 18.4.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Network Characteristics
4.1 Key characteristics of PLMN
4.2 Key characteristics of IP Networks
4.3 Key characteristics of Ethernet
5 Interworking Classifications
5.1 Service Interworking
5.2 Network Interworking
6 Reference Architecture
7 Interface to 5G Network services (User Plane)
...
...
1 Scope p. 7
The present specification defines the stage 3 interworking procedures for 5G Network interworking between PLMN and external DN or Network Slice Specific AAA.
The stage 2 requirements and procedures are contained in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502.
For interworking between 5G PLMN and external DNs, the present document is valid for both 3GPP accesses and non-3GPP accesses.
2 References p. 7
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[3]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[4]
TS 29.281: "General Packet Radio System (GPRS) Tunnelling Protocol User Plane (GTPv1-U)".
[5]
TS 29.061: "Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) supporting packet based services and Packet Data Networks (PDN)".
[6]
RFC 3748: "Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)".
[7]
RFC 3579: "RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) Support For Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)".
[8]
RFC 2865: "Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)".
[9]
RFC 3162: "RADIUS and IPv6".
[10]
RFC 4818: "RADIUS Delegated-IPv6-Prefix Attribute".
[11]
RFC 5216: "The EAP-TLS Authentication Protocol".
[12]
TS 23.228: "IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2".
[13]
TS 24.229: "IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on SIP and SDP; Stage 3".
[14]
RFC 2132: "DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions".
[15]
RFC 3361: "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP-for-IPv4) Option for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers".
[16]
RFC 3646: "DNS Configuration options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)".
[17]
RFC 3319: "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv6) Options for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers".
[18]
RFC 2131: "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol".
[19]
RFC 1542: "Clarification and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol".
[20]
RFC 4039: "Rapid Commit Option for the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4)".
[21]
RFC 3315: "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)".
[22]
RFC 3736: "Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for IPv6".
[23]
RFC 7155: "Diameter Network Access Server Application".
[24]
RFC 6733: "Diameter Base Protocol".
[25]
RFC 4072: "Diameter Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Application".
[26]
RFC 2866: "RADIUS Accounting".
[27]
RFC 5176: "Dynamic Authorization Extensions to Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)".
[28]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, addressing and identification".
[29]
RFC 1825: "Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol".
[30]
RFC 1826: "IP Authentication Header".
[31]
RFC 1827: "IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)".
[32]
RFC 4291: "IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture".
[33]
RFC 4861: "Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (IPv6)".
[34]
RFC 4862: "IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration".
[35]
RFC 1027: "Using ARP to Implement Transparent Subnet Gateways".
[36]
IEEE 802.3-2015: IEEE Standard for Ethernet.
[37]
RFC 5281: "Extensible Authentication Protocol Tunneled Transport Layer Security Authenticated Protocol Version 0 (EAP-TTLSv0)".
[38]
TS 23.380: "IMS Restoration Procedures".
[39]
TS 29.571: "5G System; Common Data Types for Service Based Interfaces; Stage 3".
[40]
TS 29.502: "5G System; Session Management Services; Stage 3".
[41]
TS 29.229: "Cx and Dx interfaces based on Diameter protocol; Protocol details".
[42]
TS 24.501: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3".
[43]
TS 23.316: "Wireless and wireline convergence access support for the 5G System (5GS)".
[44]
RFC 7761: "Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM): Protocol Specification (Revised)".
[45]
RFC 3973: "Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM): Protocol Specification (Revised)".
[46]
TS 29.571: "5G System; Common Data Types for Service Based Interfaces Stage 3".
[47]
RFC 2132: "DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions".
[48]
RFC 3925: "Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4)".
[49]
RFC 8415: "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)".
[50]
TS 29.274: "3GPP Evolved Packet System. Evolved GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for EPS (GTPv2)".
[51]
CableLabs WR-TR-5WWC-ARCH: "5G Wireless Wireline Converged Core Architecture".
[52]
BBF WT-470: "5G FMC Architecture".
[53]
TS 23.401: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) enhancements for Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) access".
[54]
BBF TR-456: "AGF Functional Requirements".
[55]
CableLabs DOCSIS MULPI: "Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications DOCSIS 3.1, MAC and Upper Layer Protocols Interface Specification".
[56]
RFC 7542: "The Network Access Identifier".
[57]
RFC 2661: " Layer Two Tunneling Protocol "L2TP".
[58]
TS 29.244: "Interface between the Control Plane and the User Plane of EPC Nodes; Stage 3".
[59]
TS 33.501: "Security architecture and procedures for 5G system".
[60]
TS 23.247: "Architectural enhancements for 5G multicast-broadcast services; Stage 2".
[61]
TS 26.502: "5G Multicast-Broadcast User Service Architecture".
[62]
RFC 6603: "Prefix Exclude Option for DHCPv6-based Prefix Delegation".
[63]
TS 23.434: "Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals (SEAL); Functional architecture and information flows".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 9
3.1 Definitions p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
MA PDU Session:
A PDU Session that provides a PDU connectivity service, which can use one access network at a time, or simultaneously one 3GPP access network and one non-3GPP access network.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
5G-BRG
5G Broadband Residential Gateway
5G-CRG
5G Cable Residential Gateway
AMF
Access and Mobility Management Function
BBF
Broadband Forum
CH
Credentials Holder
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CHF
Charging Function
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection
DCS
Default Credentials Server
DHCPv4
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4
DHCPv6
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6
DN
Data Network
DNAI
DN Access Identifier
DR
Designated Router
DSL
Digital Subscriber Line
FN-BRG
Fixed Network Broadband RG
FN-CRG
Fixed Network Cable RG
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name
GCI
Global Cable Identifier
GLI
Global Line Identifier
GPSI
Generic Public Subscription Identifier
HFC
Hybrid Fiber Coax
I-SMF
Intermediate SMF
L2TP
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol
LAC
L2TP Access Concentrator
LNS
L2TP Network Server
MBS
Multicast/Broadcast Service.
MBSTF
Multicast/Broadcast Service Transport Function.
MB-UPF
Multicast/Broadcast User Plane Function
N3IWF
Non-3GPP InterWorking Function
NGAP
NG Application Protocol
NRM
Network Resource Management
NSS
Network Slice Specific
NSSAAF
Network Slice-Specific Authentication and Authorization Function
ON-SNPN
Onboarding Standalone Non-Public Network
PAP
Password Authentication Protocol
PIM
Protocol-Independent Multicast
PIM-DM
Protocol-Independent Multicast- Dense Mode
PIM-SM
Protocol-Independent Multicast- Sparse Mode
PON
Passive Optical Network
PtP
Point-to-Point
RG
Residential Gateway
RP
Rendezvous Point
RSN
Redundancy Sequence Number
RTP
Real-time Transport Protocol
SD
Slice Differentiator
SEAL
Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals
SFD
Start Frame Delimiter
SMF
Session Management Function
S-NSSAI
Single Network Slice Selection Assistance Information
SNPN
Stand-alone Non-Public Network
SO-SNPN
Subscription Owner Standalone Non-Public Network
SSC
Session and Service Continuity
SST
Slice/Service Type
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TNAP
Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point
TWAP
Trusted WLAN Access Point
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
UPF
User Plane Function
V-SMF
Visited SMF
VAL
Vertical Application Layer
WAN
Wide Area Network
4 Network Characteristics p. 11
4.1 Key characteristics of PLMN p. 11
The PLMN is fully defined in the 3GPP technical specifications. The 5G Network related key characteristics are defined in TS 23.501.
4.2 Key characteristics of IP Networks p. 11
The Internet is a conglomeration of networks utilising a common set of protocols. IP protocols are defined in the relevant IETF RFCs. The networks topologies may be based on LANs (e.g. Ethernet), Point to Point leased lines, PSTN, ISDN, X.25 or WANs using switched technology (e.g. SMDS, ATM).
4.3 Key characteristics of Ethernet p. 11
The Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies commonly used in LAN and is often used to refer to all Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) LANs that generally conform to Ethernet Specifications, including IEEE 802.3 [36]. The key characteristics for Ethernet are defined in IEEE 802.3 [36].
5 Interworking Classifications p. 11
5.1 Service Interworking p. 11
Service interworking is required when the Teleservice at the calling and called terminals are different. No service interworking is specified in this specification.
5.2 Network Interworking p. 11
Network interworking is required whenever a PLMN is involved in communications with another network to provide end-to-end communications. The PLMN shall interconnect in a manner consistent with that of a normal Data Network (type defined by the requirements e.g. IP). Interworking appears exactly like that of Data Networks.
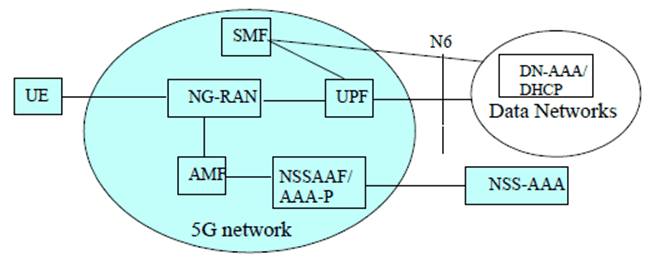
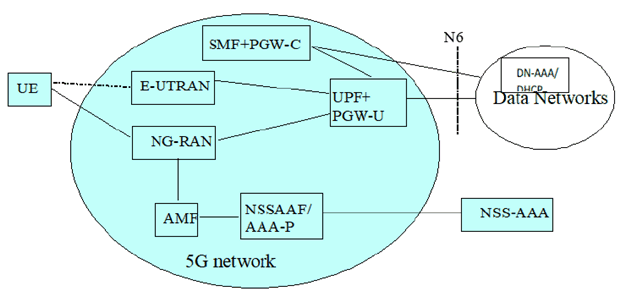
6 Reference Architecture p. 11
Figure 6-1 shows the access interfaces for the 5G Network. Figure 6-2 shows the access interfaces for the 5G and EPC interworking network.
The 5G Network includes both the 3GPP access and the non-3GPP access.
7 Interface to 5G Network services (User Plane) p. 12
The user plane for 5G Network services is defined in clause 8.3 of TS 23.501 and TS 29.281.