Content for TS 29.275 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 General
...
...
1 Scope p. 11
The present document specifies the stage 3 of the PMIPv6 Based Mobility and Tunnelling Protocols used over the PMIP-based S2a, S2b, S5, and S8 reference points defined in TS 23.402, and are thus applicable to the Serving GW, PDN Gateway, ePDG, and Trusted Non-3GPP Access. Protocols specifications are compliant with relevant IETF RFCs. In this specification PMIP refers to PMIPv6 as defined in RFC 5213 taking into account the corrections regarding the protocol number definition in RFC 6275.
2 References p. 11
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.401: "GPRS enhancements for E-UTRAN access ".
[3]
TS 23.402: "Architecture Enhancements for non-3GPP accesses".
[4]
RFC 5213: "Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[5]
RFC 5844: "IPv4 Support for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[6]
RFC 5846: "Binding Revocation for IPv6 Mobility".
[7]
RFC 5845: "Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) Key Option for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[8]
RFC 6275: "Mobility Support in IPv6".
[9]
RFC 4282: "The Network Access Identifier".
[10]
RFC 4283: "Mobile Node Identifier Option for Mobile IPv6 (MIPv6)".
[11]
RFC 5149: "Service Selection for Mobile Ipv6".
[12]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, addressing and identification".
[13]
TS 23.007: "Restoration Procedures".
[14] Void
[15] Void
[16]
TS 24.008: "Mobile radio interface Layer 3 specification; Core network protocols".
[17]
RFC 5847: "Heartbeat Mechanism for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[18]
IANA Mobile Ipv6 Parameters Registry, <http://www.iana.org/assignments/mobility-parameters >.
[19]
TS 33.402: "3GPP System Architecture Evolution (SAE); Security aspects of non-3GPP accesses".
[20]
RFC 2784: "Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)".
[21]
RFC 2890: "Key and Sequence Number Extensions to GRE".
[22]
TS 29.274: "3GPP Evolved Packet System (EPS); Evolved General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunnelling Protocol for Control plane (GTPv2-C); Stage 3".
[23]
TS 23.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service description; Stage 2".
[24]
TS 29.282: "Mobile IPv6 vendor specific option format and usage within 3GPP".
[25]
TS 32.251: "Charging Management; Packet Switched (PS) domain charging".
[26]
TS 32.298: "Charging Management; Charging Data Record (CDR) parameter description".
[27]
RFC 4291: "IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture".
[28]
TS 29.060: "General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) across the Gn and Gp interface".
[29]
ITU-T Recommendation E.164: "The international public telecommunication numbering plan".
[30]
TS 29.212: "Policy and Charging Control (PCC); Reference points".
[31]
RFC 2473: "Generic Packet Tunneling in IPv6 Specification".
[32]
IANA Registry of Assigned Numbers. Mobile IPv6 parameters, Status Codes: http://www.iana.org/assignments/mobility-parameters/mobility-parameters.xhtml#mobility-parameters-6 .
[33]
IANA Registry of Assigned Numbers. Mobile IPv6 parameters, Binding Revocation Acknowledgement Status Codes: http://www.iana.org/assignments/mobility-parameters/mobility-parameters.xhtml#binding-revocation-status-codes .
[34]
RFC 5555: "Mobile IPv6 Support for Dual Stack Hosts and Routers".
[35]
RFC 7077: "Update Notifications for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[36]
TS 23.380: "IMS Restoration Procedures".
[37]
RFC 6757: "Access Network Identifier Option".
[38]
RFC 3775, "Mobility Support in IPv6".
[39]
TS 24.302: "Access to the 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) via non-3GPP access networks; Stage 3".
[40]
RFC 5905, "Network Time Protocol Version 4: Protocol and Algorithms Specification".
[41]
RFC 7563: "Extensions to the Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) Access Network Identifier Option".
[42]
RFC 3046: "DHCP Relay Agent Information Option".
[43]
RFC 6463: "Runtime Local Mobility Anchor (LMA) Assignment Support for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[44]
RFC 7389: "Separation of Control and User Plane for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
[45]
RFC 7148: "Prefix Delegation Support for Proxy Mobile IPv6".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 13
3.1 Definitions p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
The following terms used in this Technical Specification are defined in:
- the PMIPv6 specification RFC 5213: IPv6 Home Network Prefix, Proxy Care-of Address, Local Mobility Anchor Address;
- the IPv4 Support for PMIPv6 specification RFC 5844: IPv4 Home Address, IPv4 Local Mobility Anchor Address;
- the MIPv6 specification [8] and extended by the PMIPv6 specification RFC 5213: Binding Cache Entry, Binding Update List Entry;
- the Binding Revocation for IPv6 Mobility [6]: Binding Revocation Indication and Binding Revocation Acknowledgement;
- the Separation of Control and User Plane for PMIPv6 specification RFC 7389: LMA User-Plane Address.
Within EPS the Local Mobility Anchor functionality consists of a PMIPv6 Local Mobility Anchor as described in the PMIPv6 specification RFC 5213 with support of IPv4 Support for PMIPv6 as defined in RFC 5844, Binding Revocation for IPv6 Mobility as defined in RFC 5846, GRE Key Option for PMIPv6 as defined in RFC 5845, and PMIPv6 Heartbeat Mechanism as defined in RFC 5847.
Mobile Access Gateway:
Within EPS the Mobility Access Gateway functionality consists of a PMIPv6 Mobility Access Gateway as described in the PMIPv6 specification RFC 5213 with support of IPv4 Support for PMIPv6 as defined in RFC 5844, Binding Revocation for IPv6 Mobility as defined in RFC 5846, GRE Key Option for PMIPv6 as defined in RFC 5845, and PMIPv6 Heartbeat Mechanism as defined in RFC 5847.
PDN Connection:
The association between a UE represented by one IPv4 Home Address and/or one IPv6 Home Network Prefix, and a PDN represented by an APN. On a PMIPv6 peer (MAG or LMA) there is a one-to-one mapping between a PDN connection and a PMIPv6 binding.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 13
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
3GSPEC
3GPP Specific PMIPv6 Error Code
BCE
Binding Cache Entry
BRA
Binding Revocation Acknowledgement
BRI
Binding Revocation Indication
BULE
Binding Update List Entry
EPC
Evolved Packet Core
ePDG
Evolved Packet Data Gateway
GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation
GW
Gateway
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
IMEI
International Mobile station Equipment Identity
IPv4-LMAA
IPv4 LMAA
LMA
Local Mobility Anchor
LMAA
LMA Address
MAG
Mobility Access Gateway
MIPv6
Mobile IPv6
NAI
Network Access Identifier
PBA
Proxy Binding Acknowledgment
PBU
Proxy Binding Update
PMIPv6
Proxy MIPv6
Proxy-CoA
Proxy Care-of Address
TWAN
Trusted WLAN Access Network
UPN
Update Notification
UPA
Update Notification Acknowledgment
4 General p. 14
4.1 PDN connection p. 14
On a PMIPv6 peer (MAG or LMA) there is a one-to-one mapping between a PDN connection and a PMIPv6 binding.
Traffic sent over a given PDN connection is encapsulated with GRE [20] using different, per-interface per-PDN connection, per direction (uplink and downlink) GRE keys [21] to allow multiplexing and demultiplexing of traffic belonging to different PDN connections at MAG and LMA. For the handover between 3GPP access and non-3GPP access, the uplink GRE Key shall be the same.
4.2 PMIPv6 protocol stacks p. 14
Protocol stacks for PMIPv6 are depicted in Figure 4.2-1. The MAG functions are defined in TS 23.402, e. g., relaying DHCPv4/DHCPv6 packets between the UE and the DHCP server, forwarding the payload packets between the UE and the LMA.
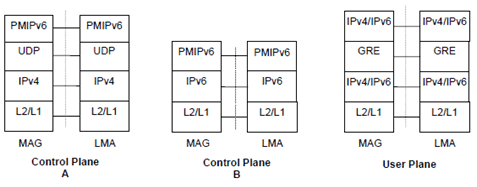
The Control Plane A shall be used if PMIPv6 messages are transported over IPv4 as described in RFC 5844. The Control Plane B shall be used if PMIPv6 messages are transported over IPv6 as described in RFC 5213. User Plane traffic shall be transported with GRE encapsulation as described in RFC 2890 (see also RFC 2784).
(no figure)