Content for TR 23.700-06 Word version: 19.0.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions of terms and abbreviations
3.1 Terms
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Architecture assumptions and requirements
4.1 Architecture assumptions
4.2 Architecture requirements
...
...
1 Scope p. 8
The scope of this Technical Report is to study and identify potential architecture and system level enhancements for the 5G system to support the operation of a mobile gNB mounted on vehicles, using NR for wireless access toward the UE and for wireless backhaul access toward the 5GC. The study addresses the service requirements documented in TS 22.261 for the mobile base station relays, and focuses on the following aspects:
- architecture enhancements for the support of the wireless backhauling of the mobile gNB and its CN/OAM (e.g. N2/N3) interfaces, including e.g. UE access control, mobility aspects;
- the architecture to enable authorization and configuration of the mobile gNB;
- support of UE location services and emergency services via the mobile gNB.
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 23.501: "System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2".
[3]
TS 22.261: "Service requirements for the 5G system; Stage 1".
[4]
TS 38.300: "NR; NR and NG-RAN Overall Description".
[5]
TS 38.401: "NG-RAN Architecture description".
[6]
TS 23.273: "5G System (5GS) Location Services (LCS); Stage 2".
[7]
TS 23.502: "Procedures for the 5G System (5GS); Stage 2".
[8]
TS 38.413: "NG-RAN; NG Application Protocol (NGAP)".
[9]
TS 23.122: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) functions related to Mobile Station (MS) in idle mode".
[10]
TS 23.503: "Policy and charging control framework for the 5G System (5GS); Stage 2".
[11]
TS 38.305: "Stage 2 functional specification of User Equipment (UE) positioning in NG-RAN".
[12]
TS 37.355: "LTE Positioning Protocol (LPP)".
[13]
TS 38.455: "NR Positioning Protocol A (NRPPa)".
[14]
TS 24.501: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS)".
3 Definitions of terms and abbreviations p. 9
3.1 Terms p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the terms given in TR 21.905, TS 23.501 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
mobile gNB with wireless access backhaul:
A mobile base station acts as a gNB for other UEs and provide access to the 5G networks, i.e. providing a NR access link to UEs and connected wirelessly to the 5GC (using NR) through an IP connectivity provided by a PDU sessions established via a NG-RAN cell that the mobile gNB can camp on. The PDU session is provided either by a Terrestrial Network or by a Non-Terrestrial Network. Such mobile gNB may be mounted on a moving vehicle and serve UEs that can be located inside or outside the vehicle (or entering/leaving the vehicle).
3.2 Abbreviations p. 9
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905 and TS 23.501.
MWAB
Mobile gNB with wireless access backhauling
MWAB-gNB
gNB component of the MWAB
MWAB-UE
UE component of the MWAB
NTN
Non-Terrestrial Network
TN
Terrestrial Network
4 Architecture assumptions and requirements p. 9
4.1 Architecture assumptions p. 9
The study should be based on the following architecture assumptions:
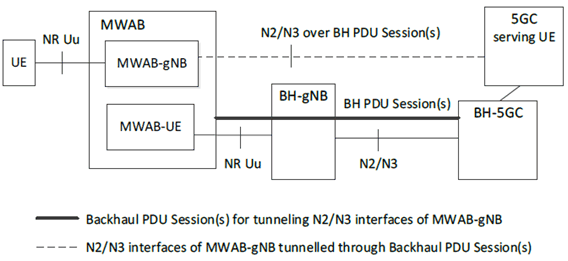
- the MWAB consists of a gNB component (MWAB-gNB) and a UE component (MWAB-UE);
- the MWAB-gNB is based on the gNB functionality specified in TS 38.300 and TS 38.401;
- the MWAB-gNB's N2/N3 and OAM access are over the IP connectivity provided by the PDU sessions(s) of the MWAB-UE;
- the interface between MWAB-UE and MWAB-gNB is not in scope of SA WG2 if it needs to be standardized;
- the MWAB-UE has a single NR Uu hop to the NG-RAN (i.e. MWAB-UE access a gNB via NR Uu interface which may use either TN or NTN technology);
- the MWAB may serve UEs located inside or outside the vehicle mounted with the relay;
- NR Uu is used for the radio link between a MWAB-gNB and served UEs. The NR Uu radio link between the MWAB-gNB and served UE does not use NTN technology;
- LCS framework as defined in TS 23.273 is used for providing the location service to the served UEs;
- the MWAB may connect to an NG-RAN of a PLMN or an SNPN;
- the MWAB-gNB may broadcast a PLMN ID that is different to the PLMN ID of the PLMN that the MWAB-UE is connected to;
- the UE's serving PLMN is the one broadcast by the MWAB-gNB it is camped on/connected to. This may be a different PLMN ID to that of the PLMN serving the MWAB-UE;
- the MWAB-UE supports emergency services.
4.2 Architecture requirements p. 10
Solutions of the study should provide architecture and system level enhancements to the 5G system to support the operation of MWAB to satisfy the normative requirements of a mobile base station relay specified in TS 22.261. Specifically:
- a MWAB shall be capable to serve legacy UE(s) to connect via MWAB;
- support end-to-end service continuity for the UEs served by a MWAB upon MWAB mobility should be specified;
- support the mobile network operator to configure, provision and control the operation of a MWAB;
- support of regulatory requirements (e.g. for support of emergency services, priority services) when UEs access 5GS via a MWAB;
- support roaming of the MWAB-UE from its HPLMN into a VPLMN.