Content for TS 23.632 Word version: 19.0.0
5.4.6 IMEI Retrieval
5.4.7 SRVCC: IMS AS obtaining SRVCC data
5.4.8 SRVCC: IMS AS obtaining SRVCC data - HSS using Nudr
5.4.9 SRVCC: IMS AS updating STN-SR
...
...
5.4.6 IMEI Retrieval p. 29
A pre-requisite for the retrieval of the IMEI when requested by an IMS-AS is that the IMEI for a given UE stored in HSS and UDM is always synchronized. This is, when the HSS detects that the IMEI for a UE changes (e.g. during an Update Location in EPS), the HSS informs the UDM about the IMEI change which stores the new IMEI accordingly. Similarly, when UDM detects that the IMEI changes, the UDM informs the HSS about the IMEI change which stores the new IMEI accordingly.
This allows that the retrieval of the IMEI for a given UE requested by an IMS-AS from HSS via Sh can be executed locally by HSS without the need of additional interworking between the HSS and the UDM
Figure 5.4.6-1 shows the scenario where the HSS receives an IMEI retrieval request from the IMS-AS for a subscriber who has a 5GC subscription.
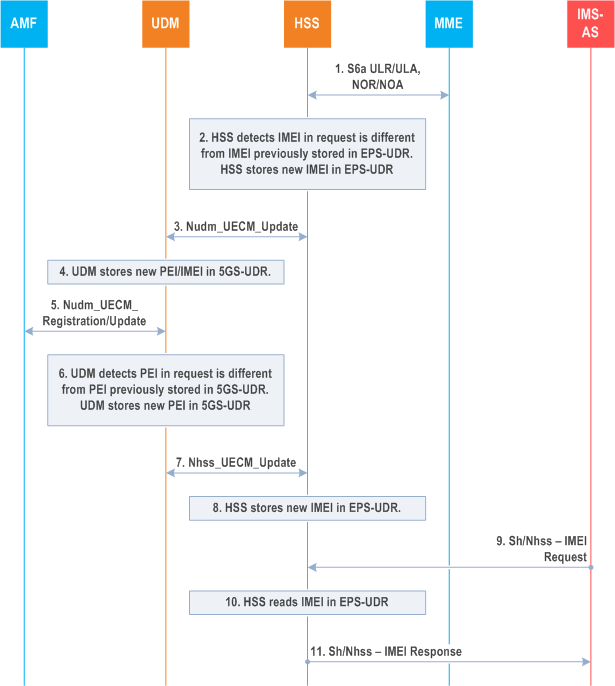
Steps 1 to 4 are executed when the HSS detects a change in the IMEI for a given UE (IMSI).
Step 1.
Steps 5 to 8 are executed when the UDM detects a change in the PEI for a given UE (SUPI).
The HSS receives a request from the MME including an IMEI for the UE (e.g. Update Location Request or Notify Request).
Step 2.
The HSS detects that the IMEI received in the request is different from the previously stored in the EPS-UDR. The HSS stores the new IMEI in the EPS-UDR.
Step 3.
The HSS informs the UDM about the new PEI (IMEI) using the Nudm_UECM_Update service operation.
Step 4.
The UDM stores the new PEI for the UE.
Step 5.
Steps 9 to 11 are executed when the HSS receives an IMEI retrieval request from the IMS-AS for a subscriber who has a 5GC subscription.
The UDM receives a request from the AMF including a PEI for the UE (e.g. Nudm_UECM_Registration /Update).
Step 6.
The UDM detects that the PEI received in the request is different from the previously stored in the 5GS-UDR. The UDM stores the new IMEI in the 5GS-UDR.
Step 7.
The UDM informs the HSS about the new IMEI using the Nhss_UECM_Update service operation.
Step 8.
The HSS stores the new IMEI for the UE.
Step 9.
The HSS receives a request from IMS-AS to retrieve the IMEI for a UE.
Step 10.
The HSS reads the IMEI stored in the EPS-UDR.
Step 11.
The HSS replies to the IMS-AS with the users IMEI. Since the IMEI for the UE has been sinchronized between HSS and UDM at every IMEI/PEI change event as in steps 1 to 4 or 5 to 8, the HSS can reply to the IMS-AS without any additional interworking with the UDM.
5.4.7 SRVCC: IMS AS obtaining SRVCC data p. 30
Figure 5.4.7-1 shows the scenario where the HSS communicates with the IMS-AS in support of (5G) SRVCC for a subscriber who has a 5GC subscription. An operator shall be able to control whether the interaction between HSS and UDM is performed based on local policy.

Step 1.
As described in TS 23.237, the IMS-AS sends Sh-Pull message to the UDM/HSS in order to know the SRVCC capability indicated by the UE in the EPS, and to retrieve the STN-SR stored in the UDM/HSS.
Step 2.
The HSS reads STN-SR and UE SRVCC Capability data from the EPS-UDR. The HSS reads the C-MSISDN bound to the IMS Private User Identity.
Step 3.
The HSS, based on operator policy, may query UDM to retrieve SRVCC parameters. The HSS uses the Nudm_MT_Provide5GSRVCCInfo service operation to retrieve the STN-SR and the UE SRVCC Capability indicated by the UE in the 5GS (see TS 23.008).
Step 4.
The UDM reads the STN-SR and this UE SRVCC Capability data from the 5GS-UDR.
Step 5.
The UDM provides the C-MSISDN, STN-SR and UE SRVCC Capability data to the HSS.
Step 6.
The HSS provides a single C-MSISDN, a single STN-SR and UE SRVCC Capability data to the IMS-AS, as follows:
- if the C-MSISDN from the HSS and the C-MSISDN from the UDM are empty, the HSS indicates an empty C-MSISDN to the SCC AS. The HSS indicates a non-empty C-MSISDN, otherwise;
- if the STN-SR from the HSS or the STN-SR from the UDM is empty, it indicates the user is not subscribed to (5G) SRVCC. If the HSS and the UDM indicate the user is not subscribed to (5G) SRVCC, the HSS indicates an empty STN-SR to the SCC AS. The HSS indicates a non-empty STN-SR, otherwise.
5.4.8 SRVCC: IMS AS obtaining SRVCC data - HSS using Nudr p. 31
When the HSS receives an S6a-AIR from the MME, it may check (by means of an EPC-UDR query) whether the subscriber has a 5G subscription. If so, the HSS can use of the Nudr_DM_Query Get service operation to retrieve the 5G SRVCC subscription data from the 5GS UDR.
Figure 5.4.8-1 shows the scenario where the HSS communicates with the IMS-AS in support of (5G) SRVCC for a subscriber who has a 5GC subscription. An operator shall be able to control whether the interaction between HSS and 5GS-UDR is performed based on local policy.

Step 1.
As described in TS 23.237, the IMS-AS sends Sh-Pull message to the UDM/HSS in order to know the SRVCC capability indicated by the UE in the EPS, and to retrieve the STN-SR stored in the UDM/HSS.
Step 2.
The HSS reads STN-SR and this UE SRVCC Capability data from the EPS-UDR. The HSS reads the C-MSISDN bound to the IMS Private User Identity.
Step 3.
The HSS, based on operator policy, may query 5G-UDR to retrieve SRVCC parameters. The HSS uses the Nudr_DM_Query service operation to retrieve the STN-SR and the UE SRVCC Capability indicated by the UE in the 5GS (see TS 23.008) from the 5GS-UDR.
Step 4.
The HSS provides a single C-MSISDN, a single STN-SR and UE SRVCC Capability data to the IMS-AS, as follows:
- if the C-MSISDN from the HSS and the C-MSISDN from the UDM are empty, the HSS indicates an empty C-MSISDN to the SCC AS. The HSS indicates a non-empty C-MSISDN, otherwise;
- if the STN-SR from the HSS or the STN-SR from the UDM is empty, it indicates the user is not subscribed to (5G) SRVCC. If the HSS and the UDM indicate the user is not subscribed to (5G) SRVCC, the HSS indicates an empty STN-SR to the SCC AS. The HSS indicates a non-empty STN-SR, otherwise.
5.4.9 SRVCC: IMS AS updating STN-SR p. 31
Figure 5.4.9-1 shows the scenario where the IMS-AS updates the STN-SR at the HSS. An operator shall be able to control whether the interaction between HSS and UDM is performed based on local policy.

Step 1.
As described in TS 23.237, the IMS-AS can use Sh-Update to provide the STN-SR received from the ATCF to the UDM/HSS in order to replace the STN-SR at the UDM/HSS.
Step 2.
While this updated STN-SR is a transient value and subject to the user being subscribed to SRVCC, the HSS can update the STN-SR at the EPS-UDR. If the user is subscribed to SRVCC, the HSS updates the STN-SR at the EPS-UDR and at the MME/SGSN (not shown).
Step 3.
The HSS, based on operator policy, may update UDM: the HSS updates the STN-SR at the UDM.
Step 4.
While this updated STN-SR is a transient value, the UDM can update the STN-SR at the 5GS-UDR using Nudr_DM_Update . The UDM updates the STN-SR at the AMF using Nudm_SDM_Notification service operation (not shown).
Step 5.
The UDM responds to the request to update the STN-SR.
Step 6.
The HSS responds by sending Sh-Update Response message to the IMS AS.