Content for TS 23.632 Word version: 19.0.0
5.3 5GC-EPC Mobility Scenarios
5.3.1 General
5.3.2 Mobility from 5GC to EPC
5.3.3 Mobility from EPC to 5GC
...
...
5.3 5GC-EPC Mobility Scenarios p. 14
5.3.1 General p. 14
As defined in TS 23.501, when interworking procedures with N26 are used, the UE operates in single-registration mode. For the 3GPP access, either the AMF or the MME is registered in the HSS+UDM. This implies that:
- The registration of an MME in HSS for a UE that is capable to access the 5GC, triggers the cancellation of the AMF address for 3GPP access registered in the UDM, if any.
- The registration of an AMF in UDM for a UE that is capable to access the EPC, triggers the cancellation of the MME address registered in the HSS, if any.
5.3.2 Mobility from 5GC to EPC p. 14
Figure 5.3.2-1 shows the interaction between the HSS and UDM in an interworking scenario when the UE attaches to the EPC.
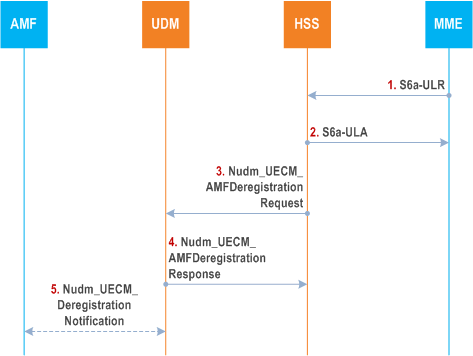
Step 1.
The HSS receives an S6a ULR request containing the IMSI of the subscriber.
The HSS stores the new MME address. If the EPC UDR is used, the HSS updates the EPS-UDR with the new MME address and reads the subscription information related to the IMSI from the EPS-UDR.
The UE's subscription may include restriction for Core Network Type (5GC). If restriction for Core Network Type indicates that the UE can access to 5GC, it implies that the UE has 5G subscription data.
Step 2.
The HSS responds to the MME with an S6a-ULA.
Step 3.
If the dual registration 5GS indicator is not set in the S6a ULR request and the subscription information related to the IMSI does not indicate that 5GC is restricted, then the HSS uses the Nudm_UECM_AMFDeregistration service operation to request the UDM to cancel the registration of the user in 5GC for 3GPP access, if any. The HSS includes the user's IMSI received in step 1 as the user's SUPI in this request.
If the S6a ULR request includes the initial attach indicator set, the HSS indicates to the UDM that the deregistration reason is due to "Initial Registration". When the initial attach indicator is not set, the HSS indicates to the UDM that the deregistration reason is due to 5GS to EPS mobility.
Step 4.
The UDM responds to the HSS.
The UDM checks if the user is registered in 5GC over 3GPP access. The UDM may use the 5GS-UDR to retrieve the address of the AMF for 3GPP access registered in UDM for that user, if any. If the user is registered at an AMF for 3GPP access, step 5 is executed.
Step 5.
If there is an AMF address for 3GPP access found for the user, the UDM cancels the user registration in 5GC by sending a Nudm_UECM_DeregistrationNotification to the AMF.
5.3.3 Mobility from EPC to 5GC p. 15
Figure 5.3.3-1 shows the interaction between the UDM and the HSS in an interworking scenario when the UE attaches to the 5GC.

Step 1.
The UDM receives a Nudm_UECM_Registration request for 3GPP access containing the SUPI of the subscriber. In this case the SUPI shall be based on an IMSI.
The UDM stores the new AMF address for 3GPP access. If the 5GS UDR is used, the UDM updates the 5GS-UDR with the new AMF address for 3GPP access and reads the subscription information related to the SUPI from the 5GS-UDR.
The UE's subscription may include restriction for Core Network Type (EPC). If restriction for Core Network Type indicates that the UE can access to EPC, it implies that the UE has EPC subscription data and that the UE may also be able to access via GERAN/UTRAN.
Step 2.
The UDM responds to the AMF with a Nudm_UECM_Registration Response.
Step 3.
If the dual registration and the initial registration flags are not set in the Nudm_UECM_Registration request and the subscription information related to the SUPI does not indicate that EPC is restricted, then the UDM uses the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicating that the deregistration reason is due to EPS to 5GS mobility to request the HSS to cancel the MME/SGSN registration of the user in EPC, if any. The UDM includes the IMSI based on SUPI received in step 1 as the user's IMSI in this request.
If the dual registration flags is set in the Nudm_UECM_Registration request and the subscription information related to the SUPI does not indicate that EPC is restricted, then the UDM uses the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicating that the deregistration reason is due to Initial and Dual Registration to request the HSS to cancel the SGSN registration of the user in EPC, if any. The UDM includes the IMSI based on SUPI received in step 1 as the user's IMSI in this request.
If the dual registration flag is not set and the initial registration flag is set in the Nudm_UECM_Registration request and the subscription information related to the SUPI does not indicate that EPC is restricted, then the UDM uses the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicating that the deregistration reason is due to Initial and Single Registration to request the HSS to cancel the MME/SGSN registrations of the user in EPC, if any. The UDM includes the IMSI based on SUPI received in step 1 as the user's IMSI in this request.
If the EPS to 5GS mobility without N26 interworking indication (i.e. eps5GsMobilityWoN26 IE) is set in the Nudm_UECM_Registration request and the subscription information related to the SUPI does not indicate that EPC is restricted, then the UDM uses the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicating that the deregistration reason is due to EPS to 5GS mobility without N26 Interworking (i.e. that the UE is in EMM-REGISTERED state, EPS to 5GS mobility is triggered, the UE works in single registration mode and N26 interworking is not supported) to request the HSS to only cancel the SGSN registration of the user in EPC, if any, but not to cancel the MME registration. The UDM includes the IMSI based on SUPI received in step 1 as the user's IMSI in this request.
Step 4.
The HSS responds to the UDM.
The HSS checks if the user is registered in EPC. The HSS may use the EPS-UDR to retrieve the address of the MME or SGSN registered in the HSS for that user, if any. If the user is registered at an MME or SGSN, step 5 is executed.
Step 5.
If there is an MME address found for the user and the deregistration reason in the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicated "Initial and Single Registration" or "EPS to 5GS mobility", the HSS cancels the attachment of the IMSI in the MME by sending a CLR via the S6a interface setting the cancellation type to MME Update Procedure, and if a VLR number was found in the HSS for the user, the HSS also cancels attachment of the IMSI in this MSC/VLR by sending the MAP Cancel Location (IMSI) to the MSC/VLR via the D interface.
If there is an SGSN address found for the user and the deregistration reason in the Nhss_UECM_SNDeregistration service operation indicated "Initial and Single Registration", the HSS cancels the attachment of the IMSI in the SGSN by sending a CLR via the S6d interface or by sending the MAP Cancel Loc via the Gr interface setting the cancellation type to SGSN Update Procedure. When deregistration reason indicated "Initial and Dual Registration" or "EPS to 5GS Mobility", the HSS cancels the attachment of the IMSI in the SGSN by sending a CLR via the S6d interface setting the cancellation type to SGSN Update Procedure.